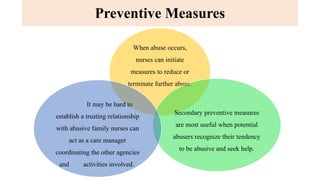
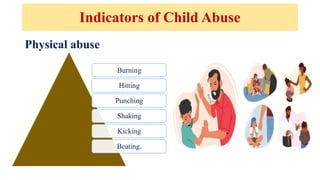
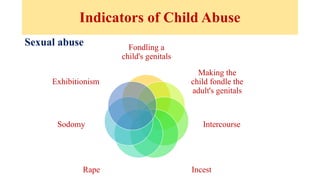
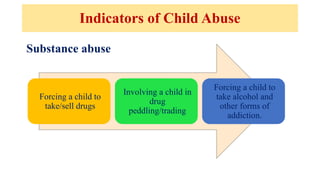
The document discusses the various forms of abuse affecting women and children, including physical, emotional, and sexual abuse, and highlights the signs and health implications of such abuse. It emphasizes the importance of preventive measures, including community awareness, education, and supportive healthcare interventions to help identify and assist victims of abuse. Additionally, it addresses the responsibilities of nurses and healthcare professionals in recognizing abuse and providing necessary care and support to affected individuals.