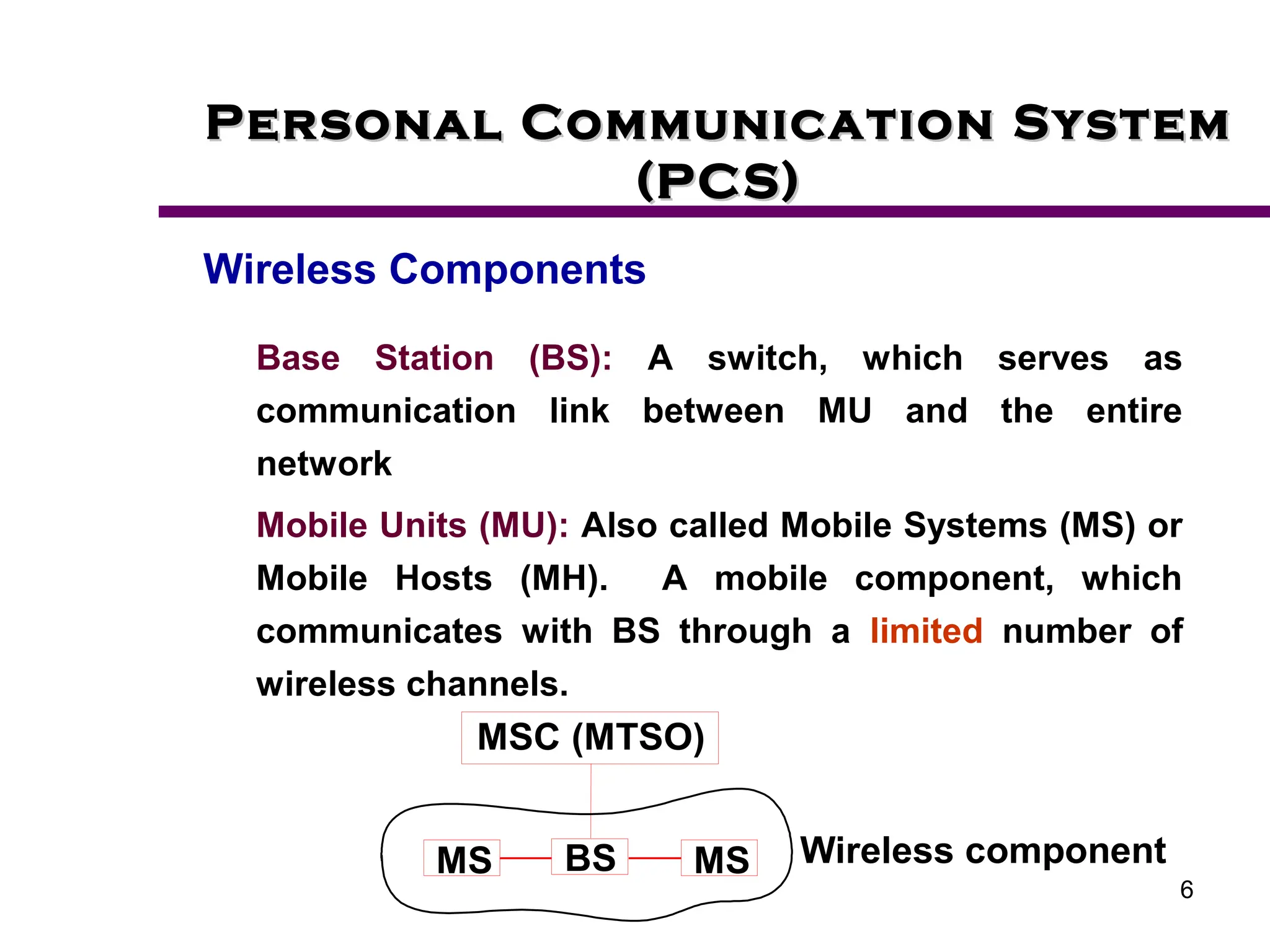
1. The document describes the components and functioning of a Personal Communication System (PCS), including wireless components like base stations and mobile stations.
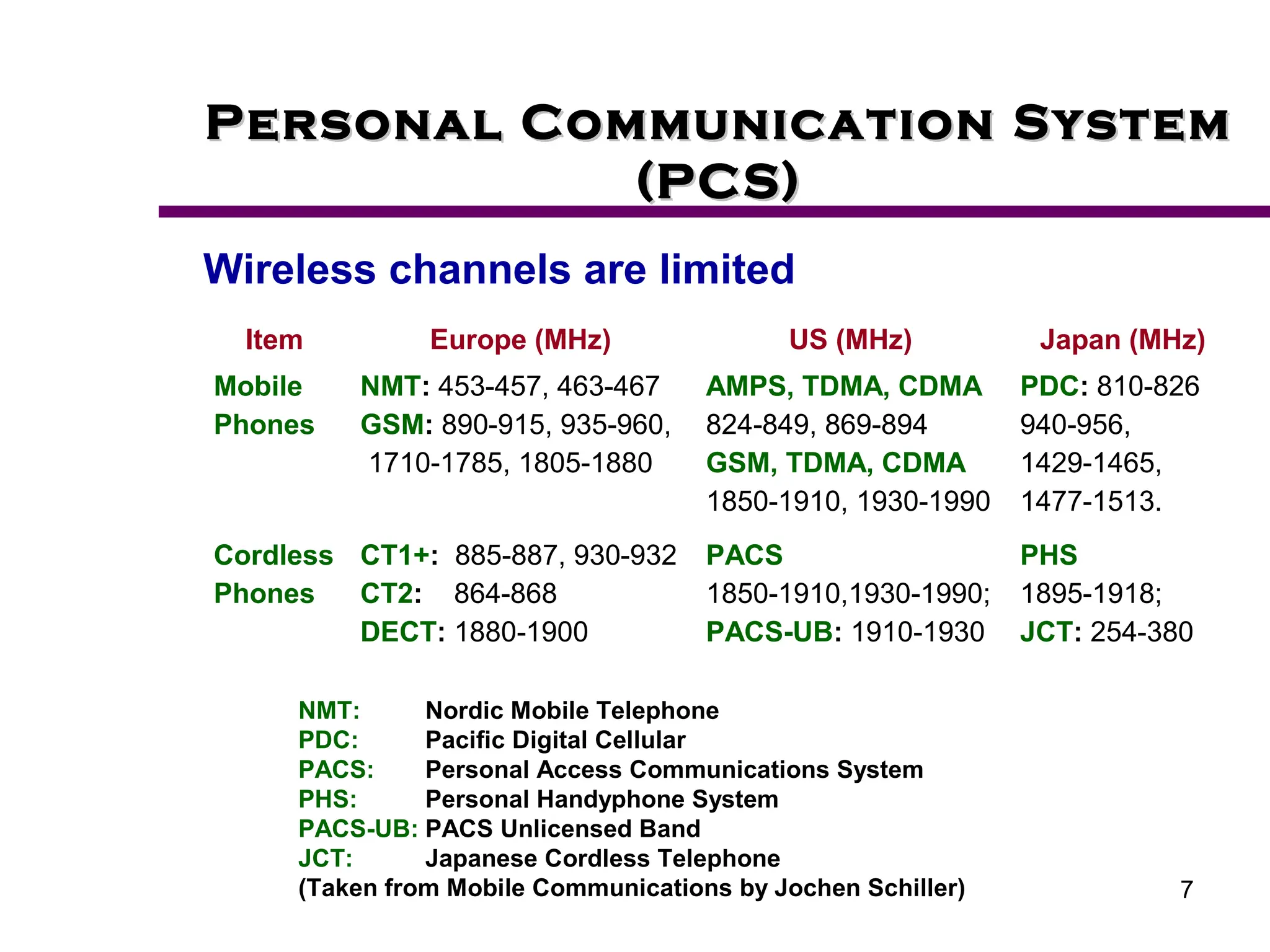
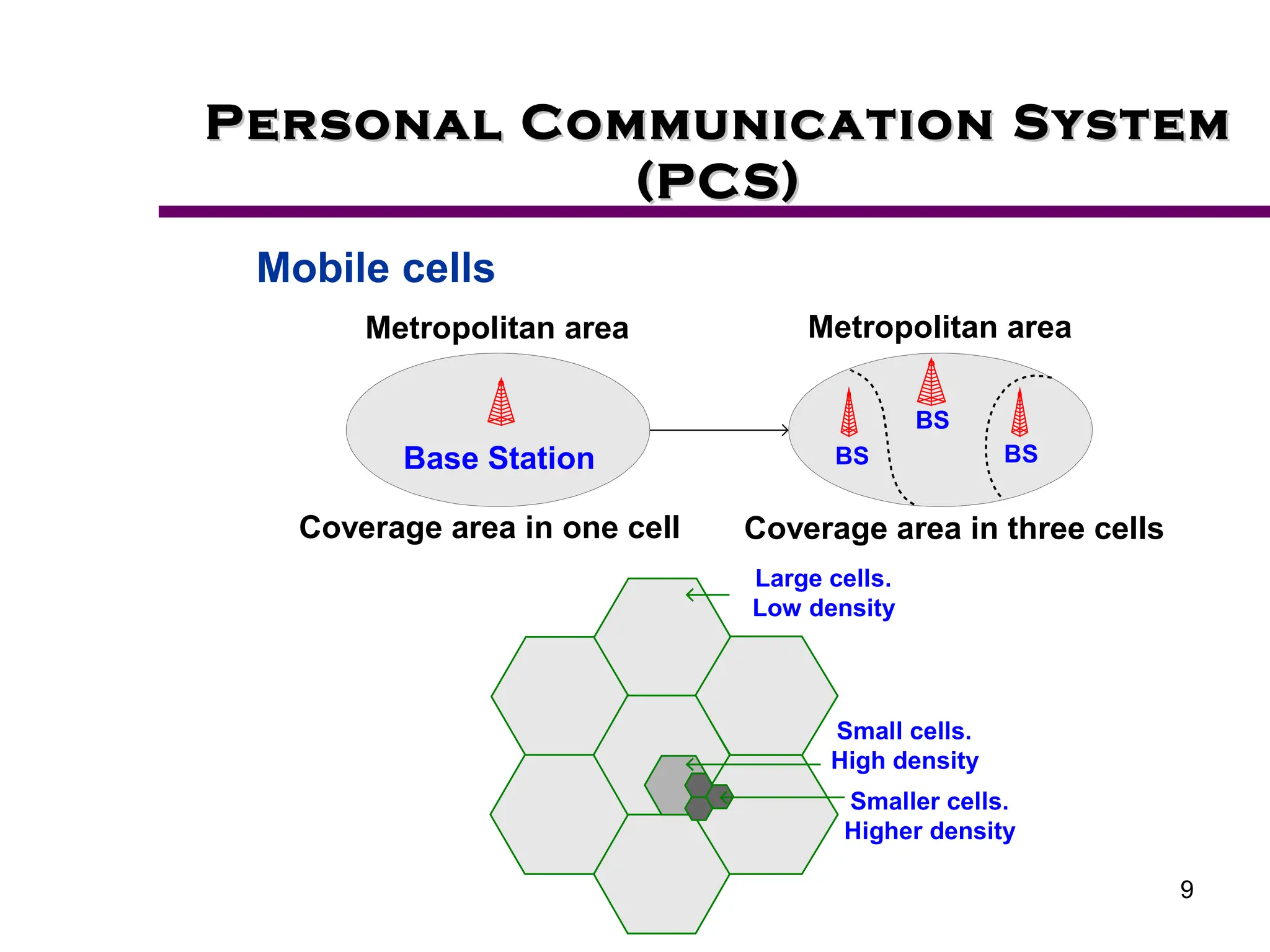
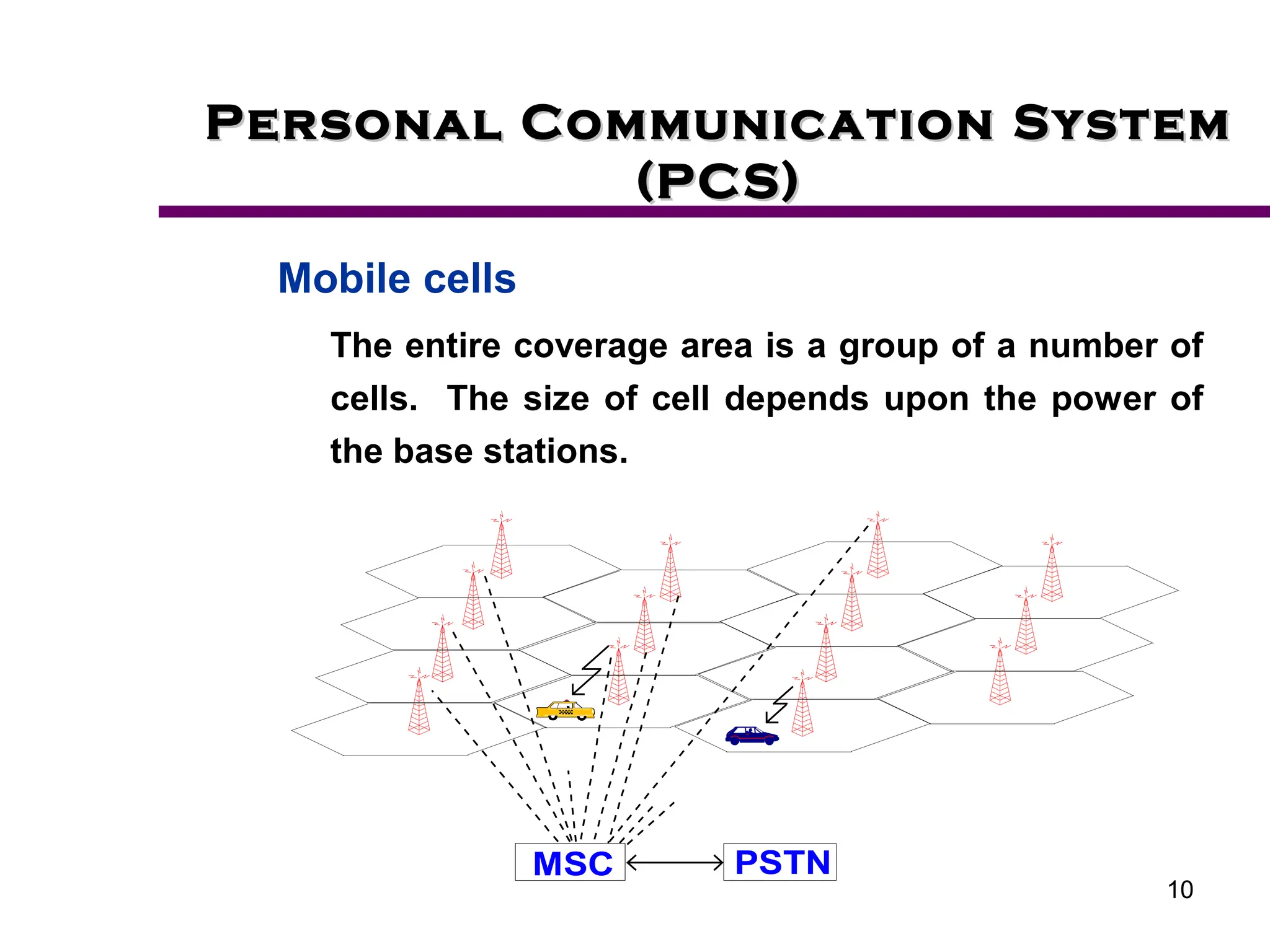
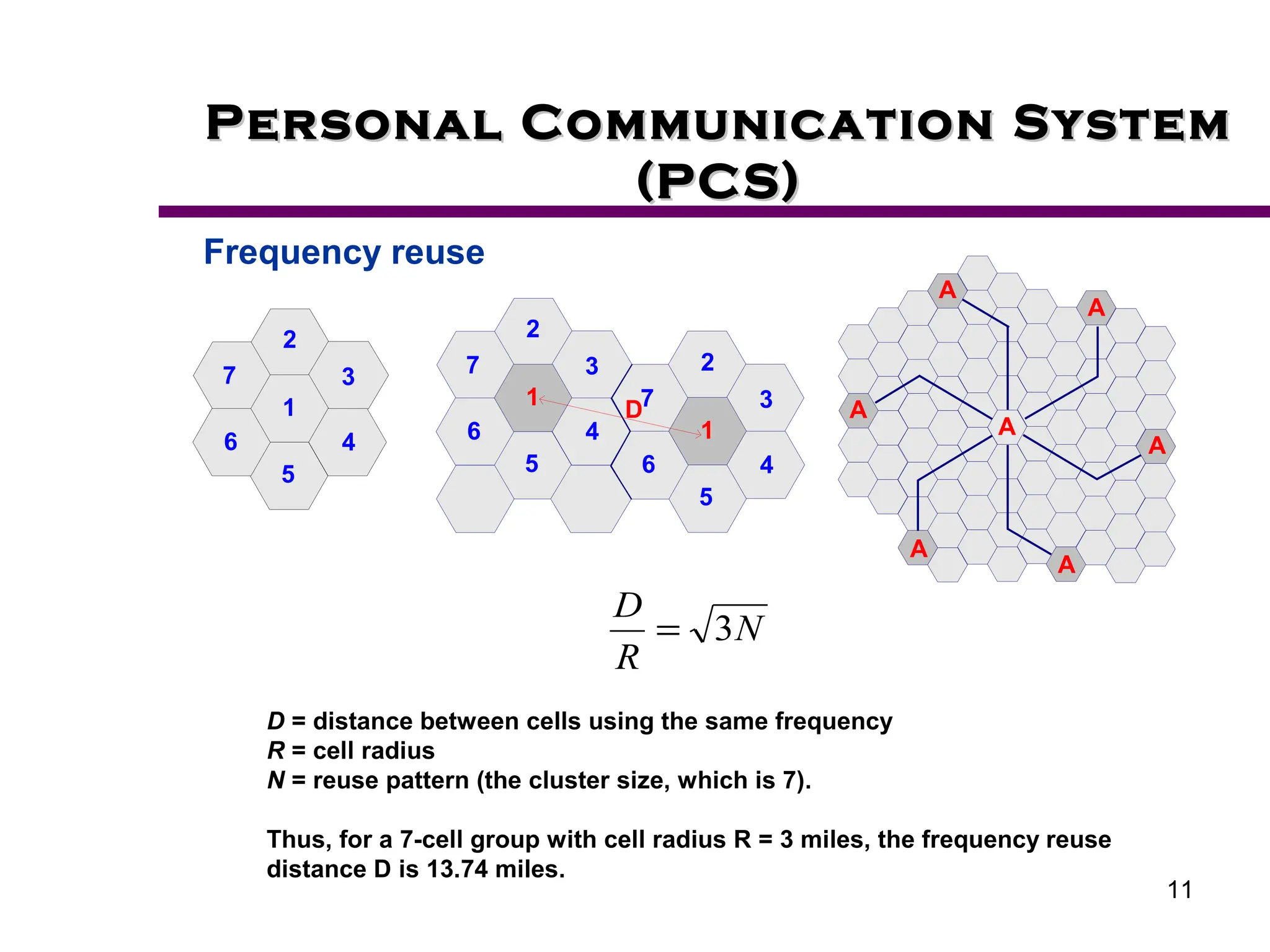
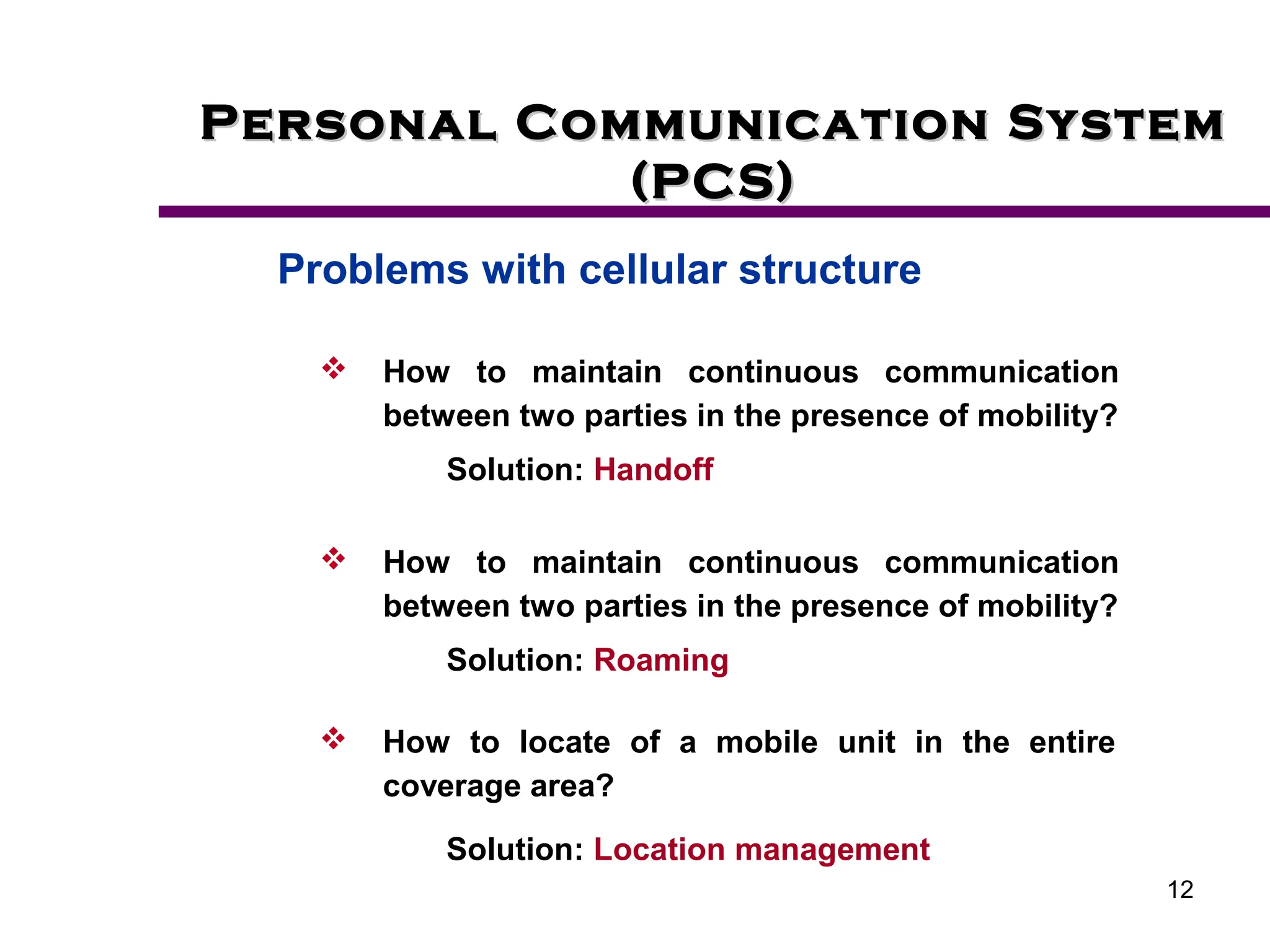
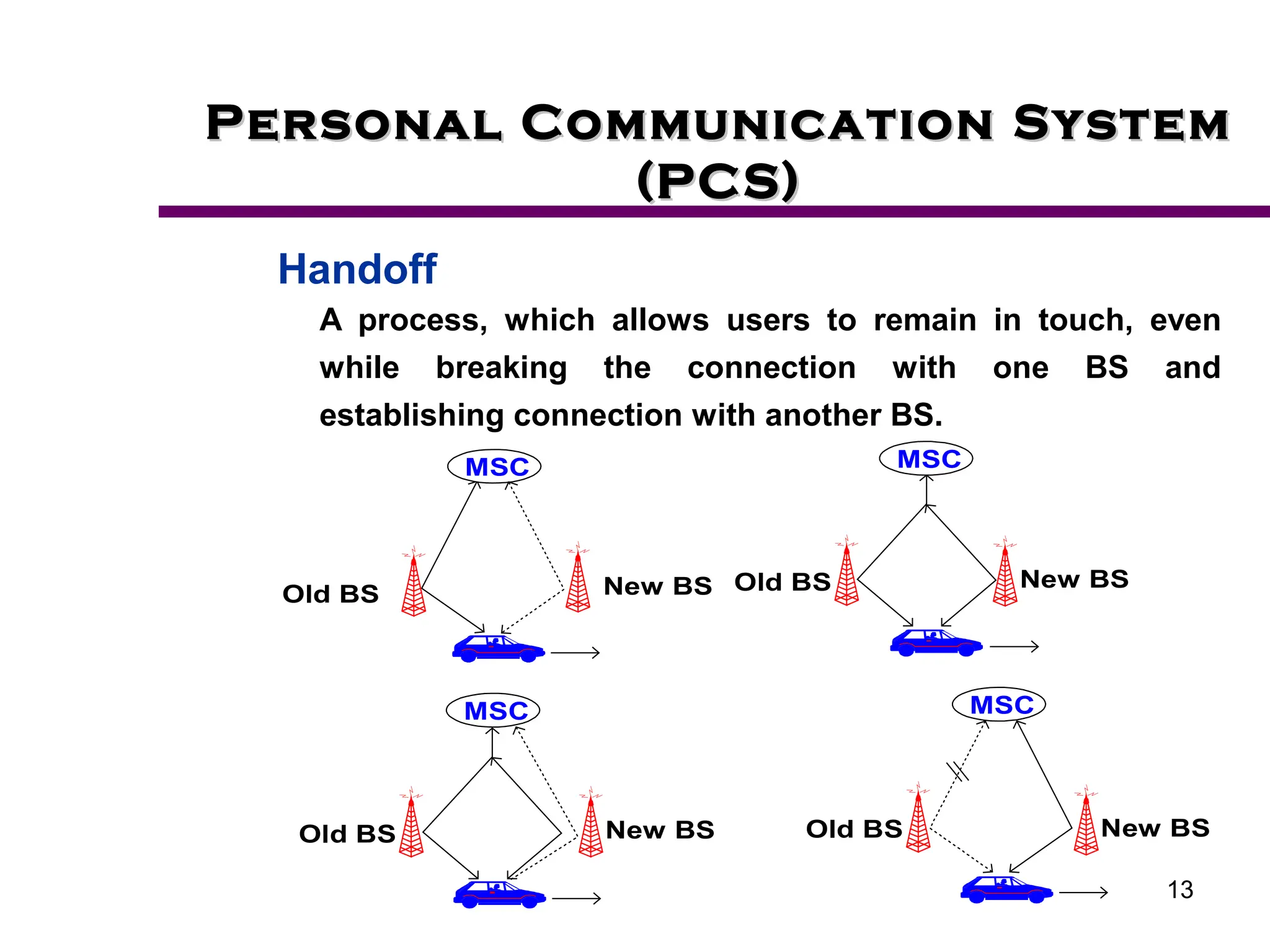
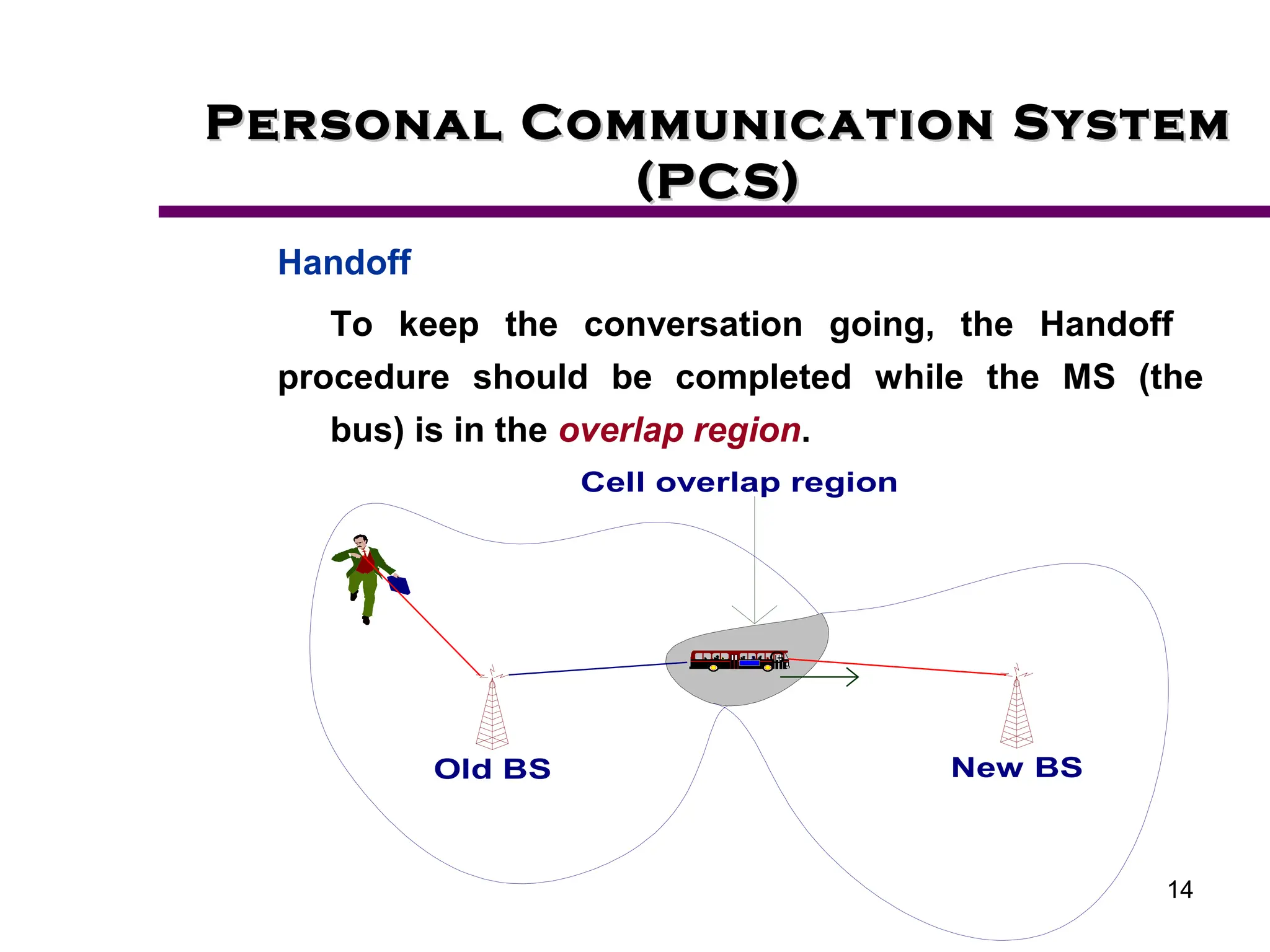
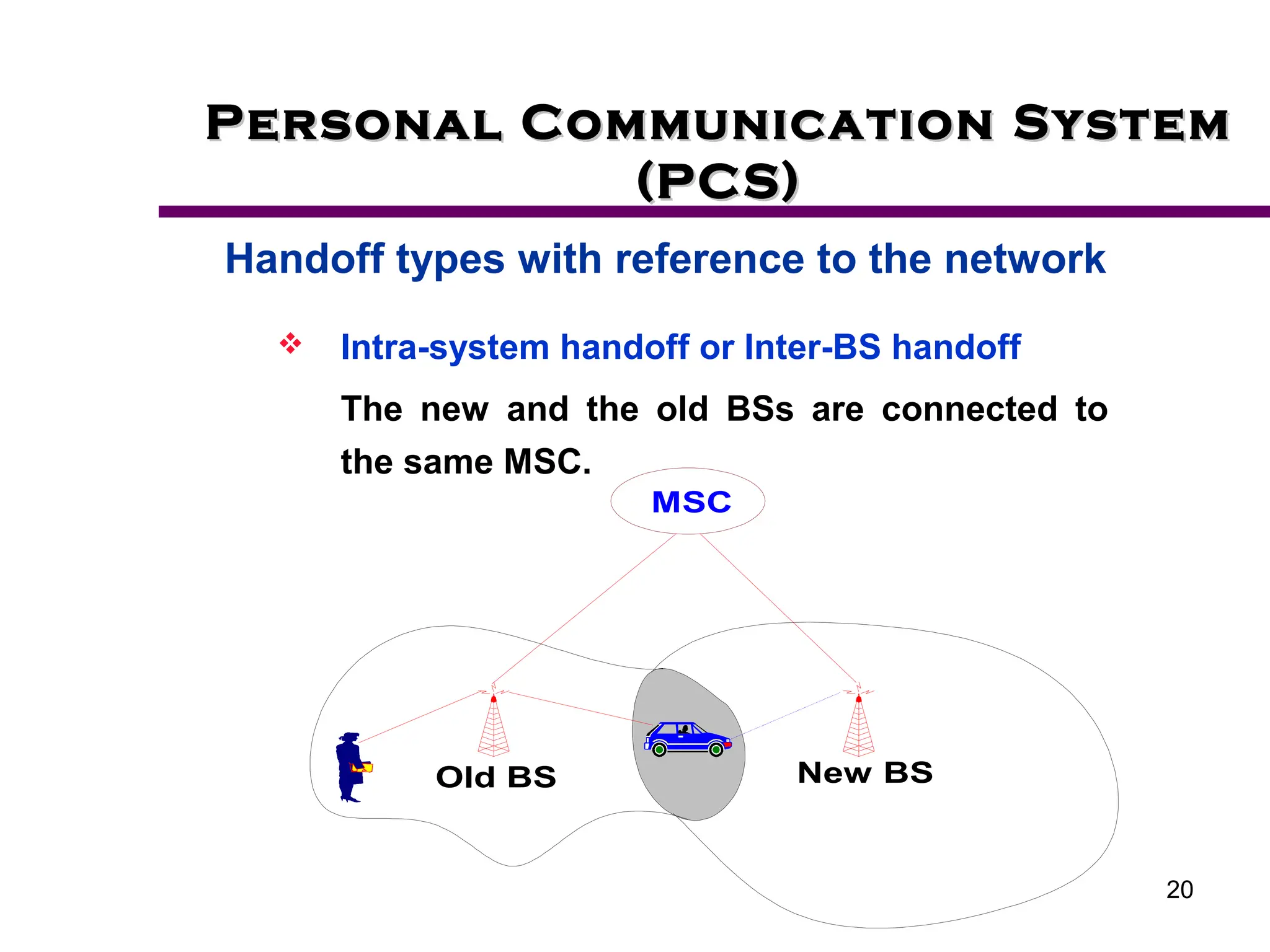
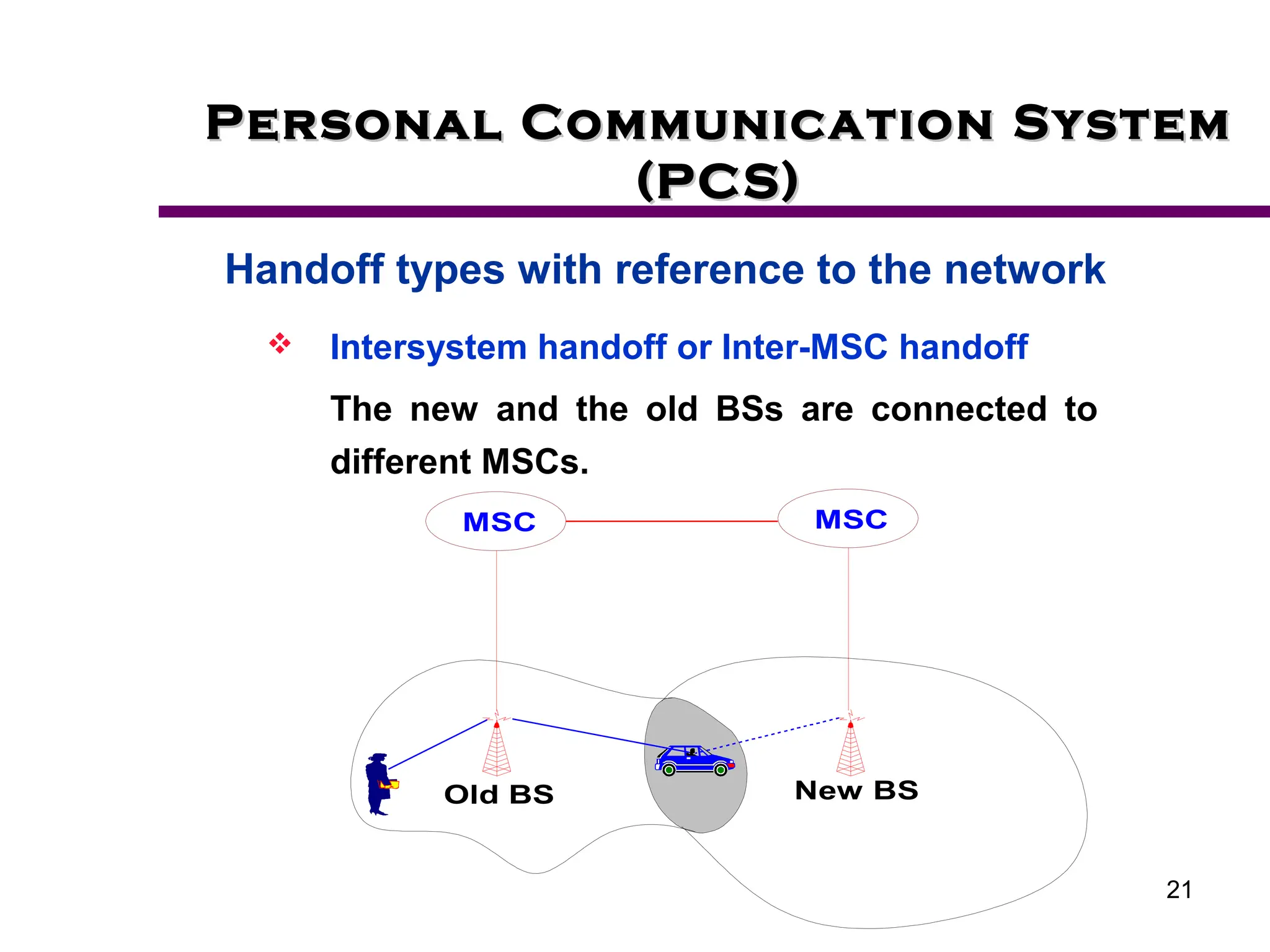
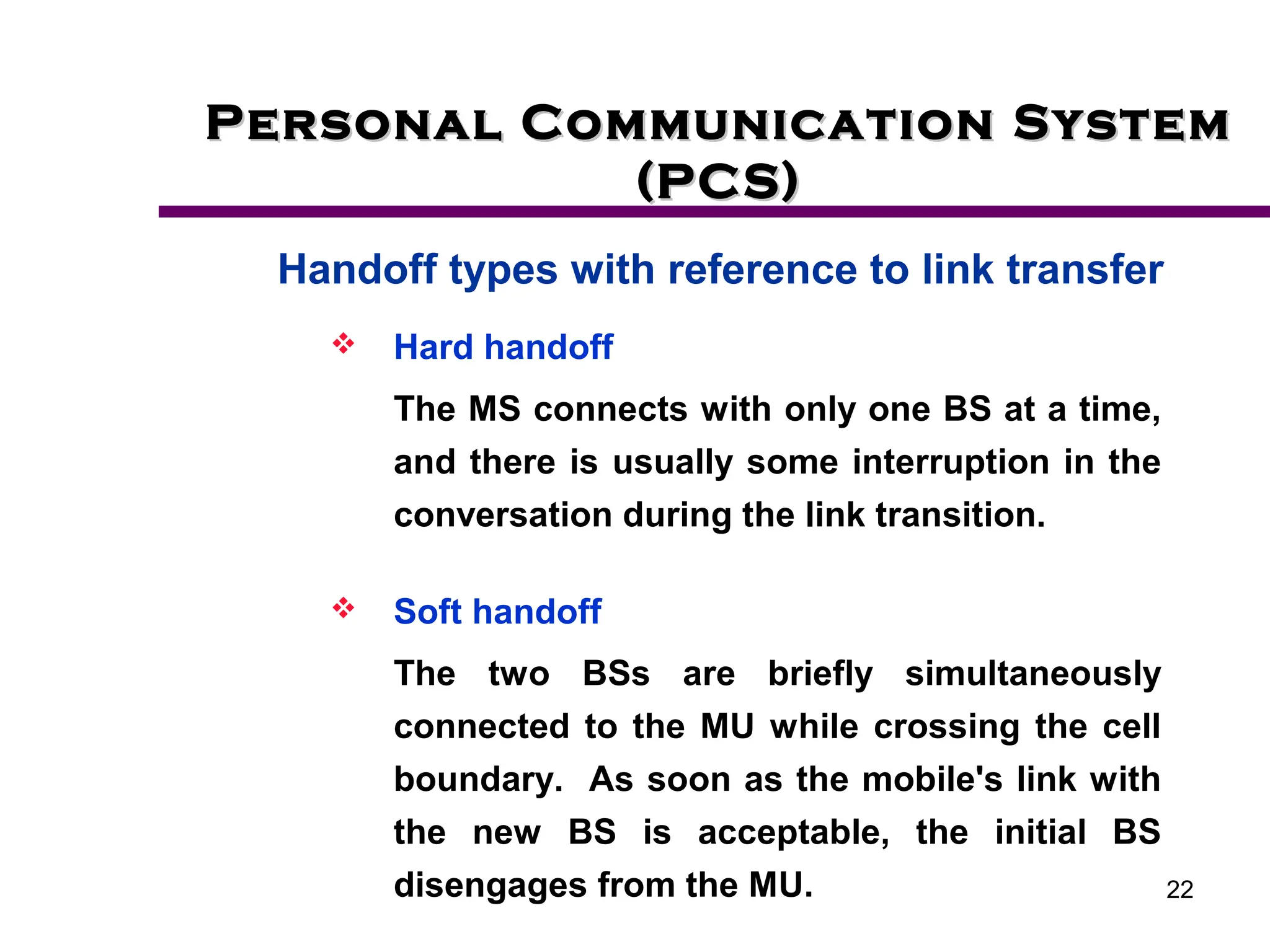
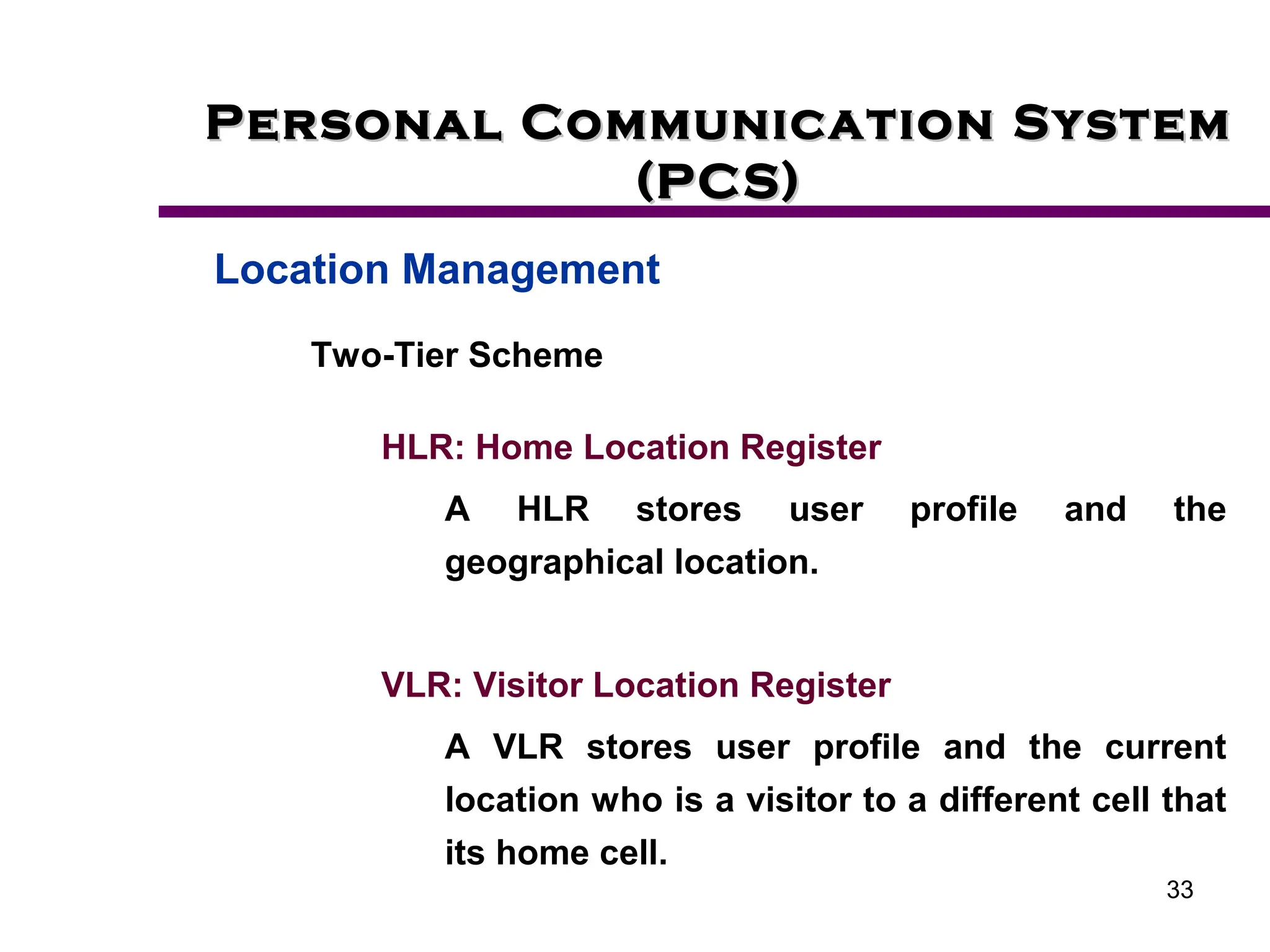
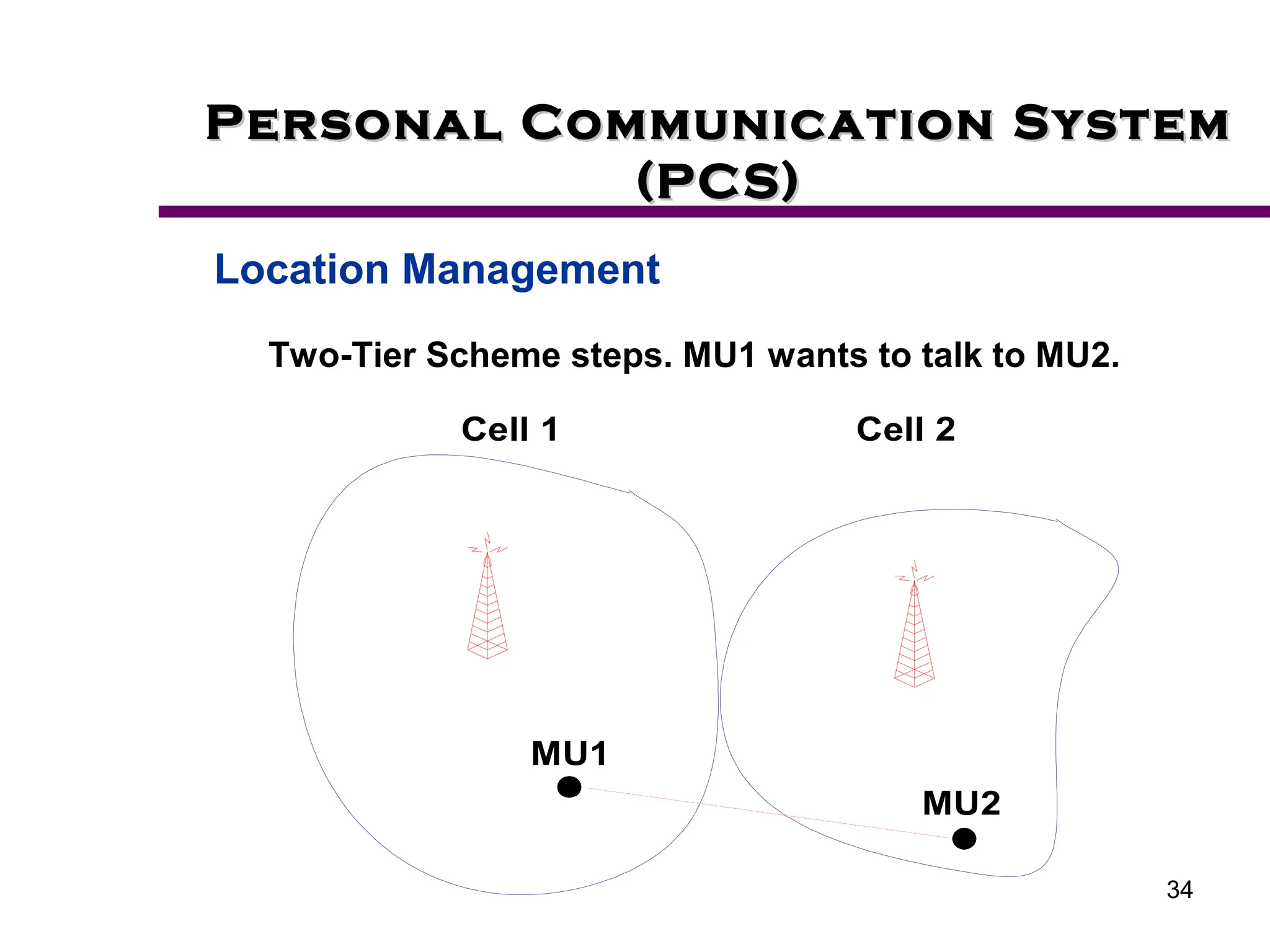
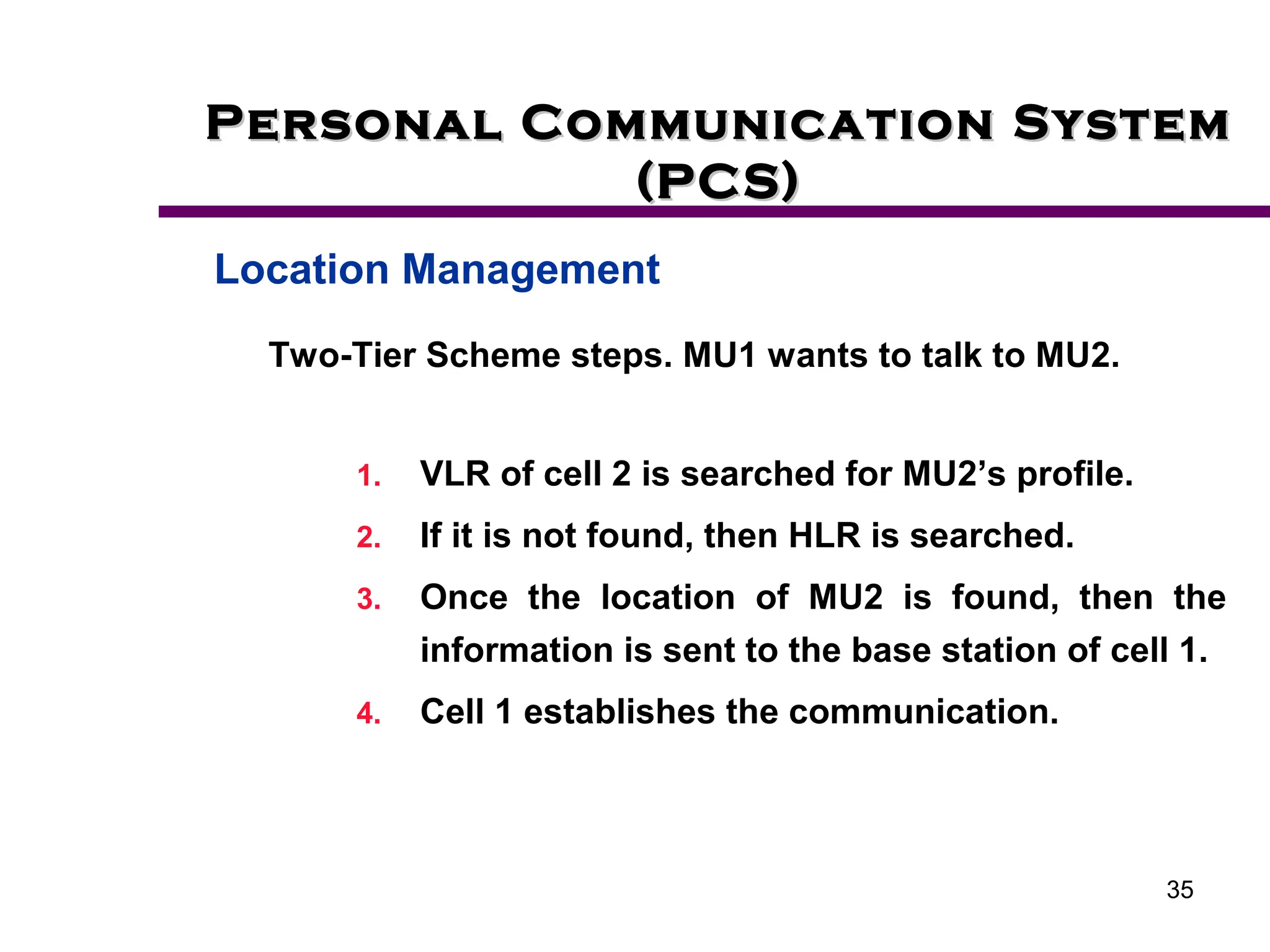
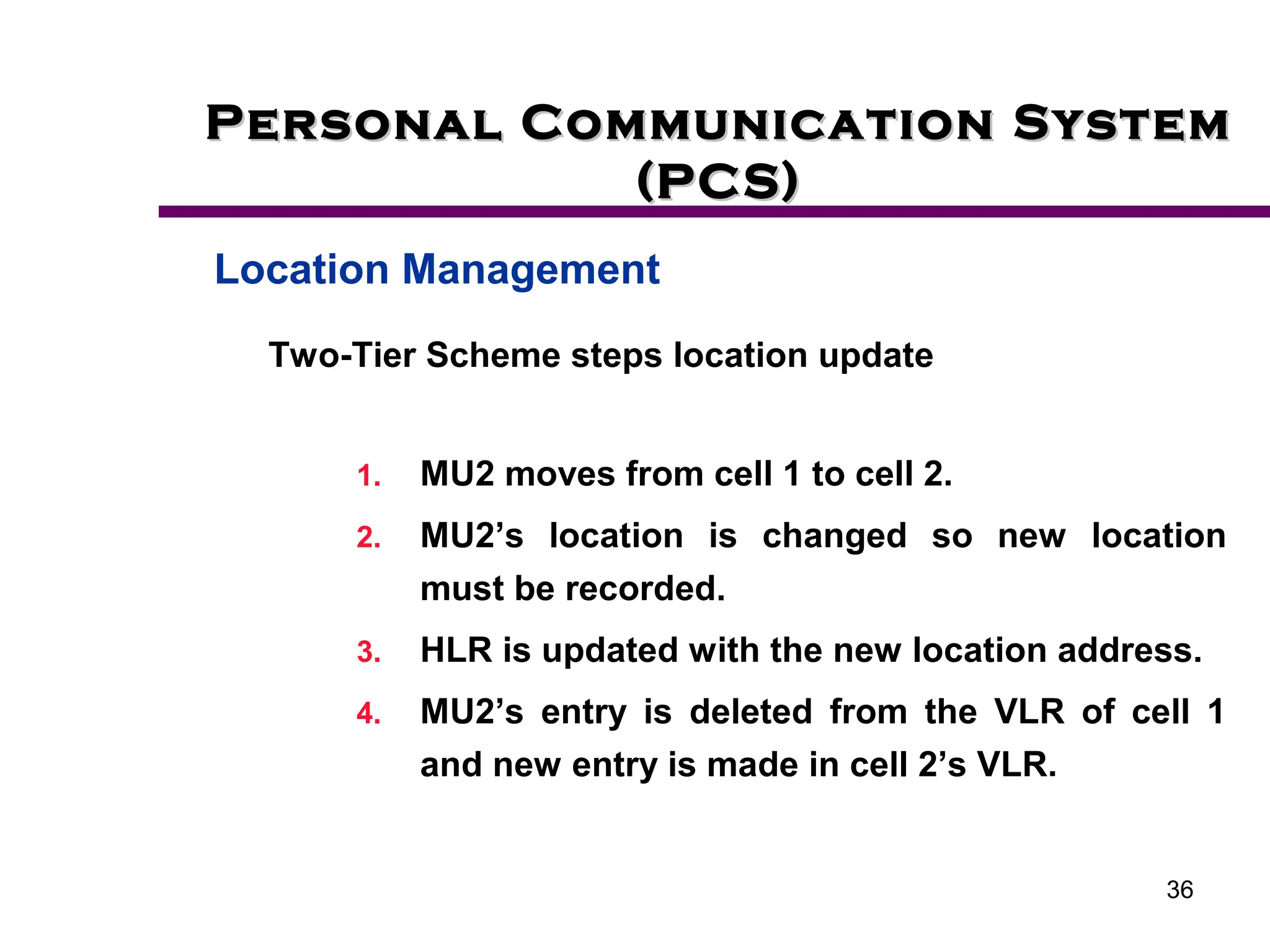
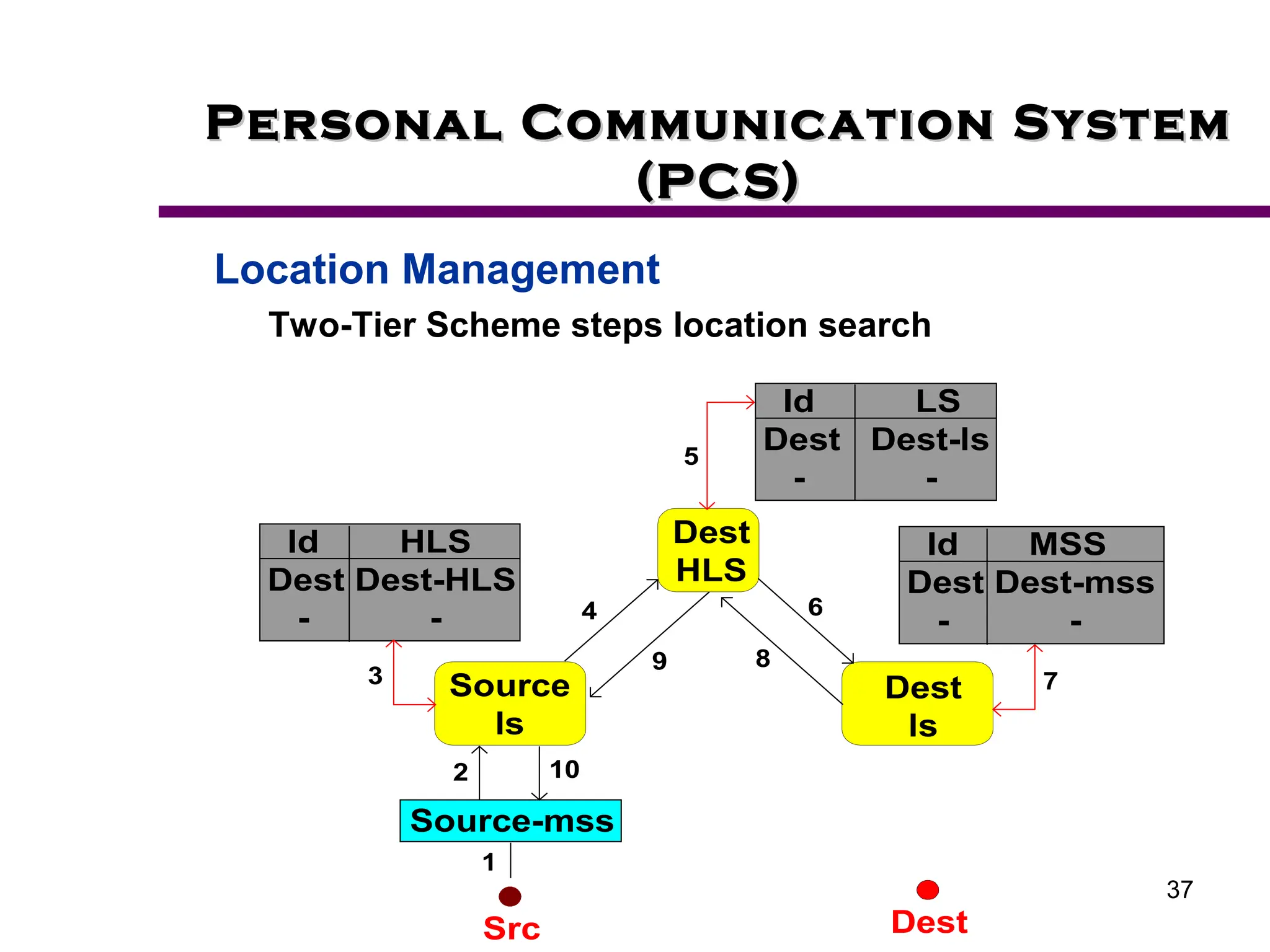
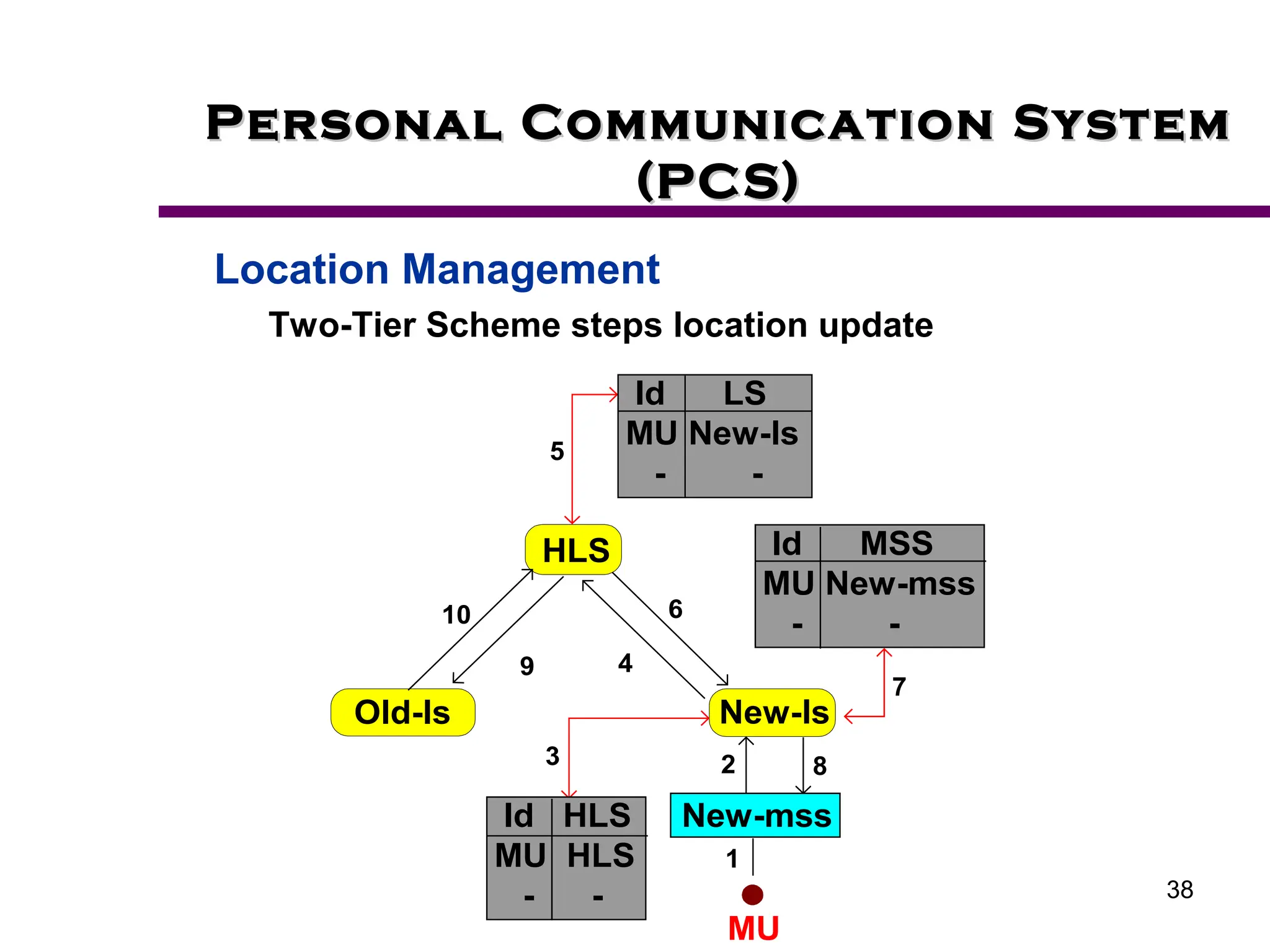
2. Key aspects of PCS discussed include frequency reuse through dividing coverage into cells, handoff procedures for maintaining connections as users move between cells, and location management using home and visitor location registers.
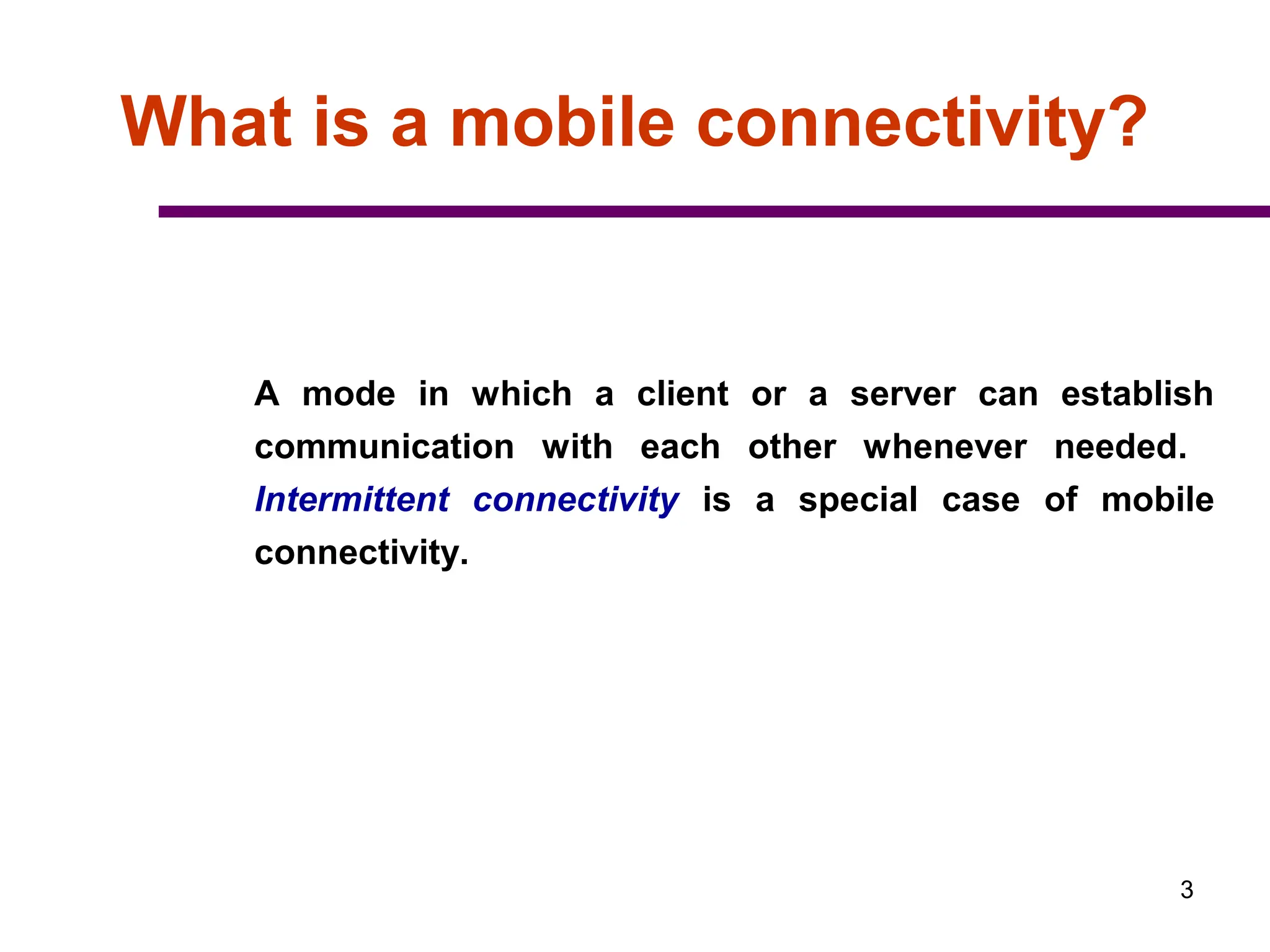
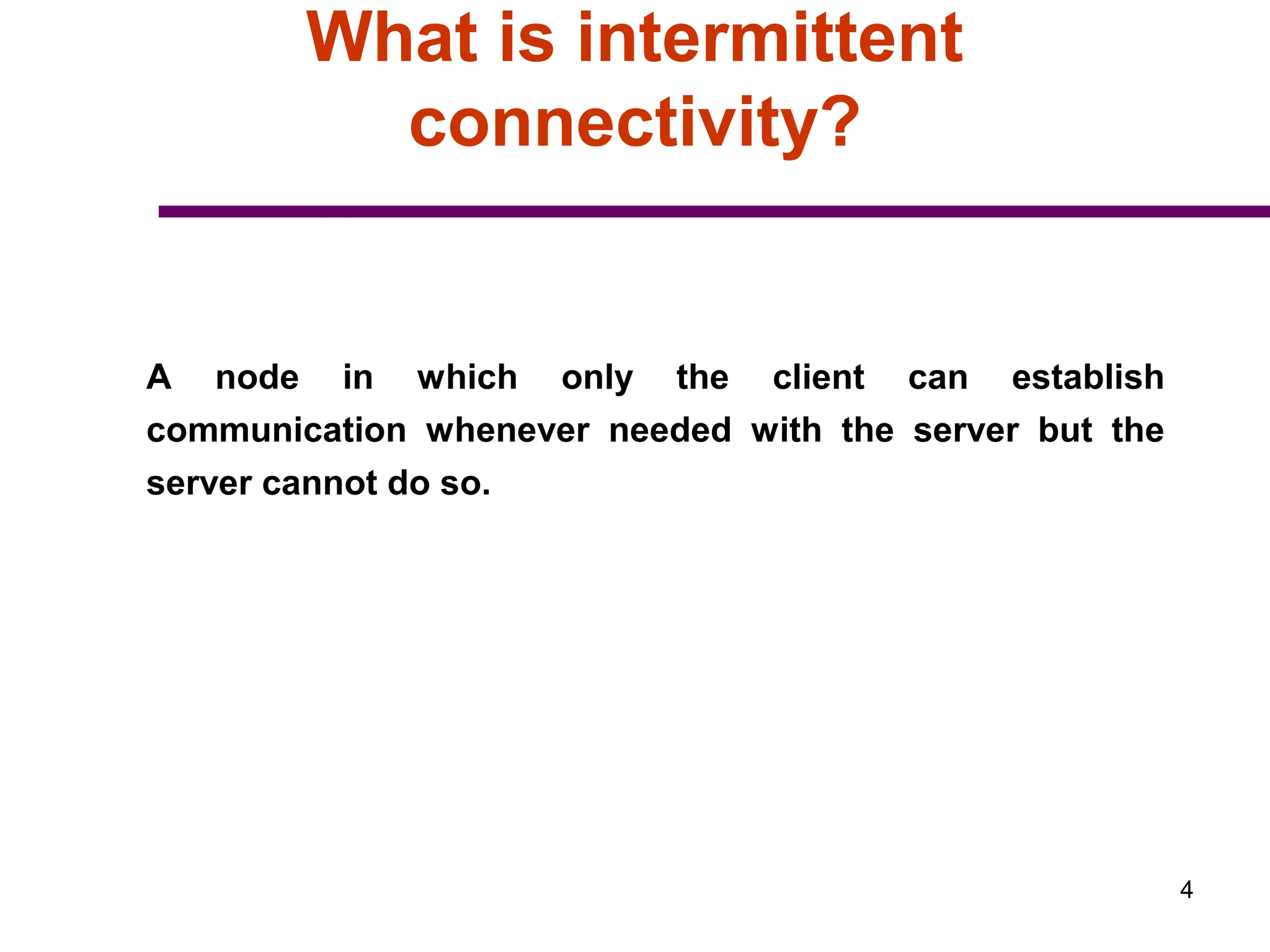
3. The document also covers intermittent connectivity, bandwidth limitations in wireless systems, and roaming capabilities that allow users to access networks beyond their home coverage area.