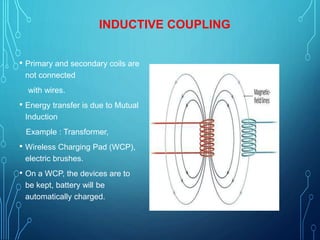
Wireless power transmission involves transmitting electrical energy through electromagnetic fields without physical connections like wires. It works by generating time-varying electromagnetic fields at a transmitter device powered by an energy source, which transmits power across space to a receiver device that extracts power from the field and delivers it to a load. Common techniques for wireless power transfer include inductive coupling using coils, resonant inductive coupling as developed by the WiTricity project at MIT, microwave power transmission using antennas, and laser power transmission for long-range applications. Wireless power holds advantages over wired transmission such as reliability, reduced environmental impact, and efficiency by eliminating energy losses during transmission.