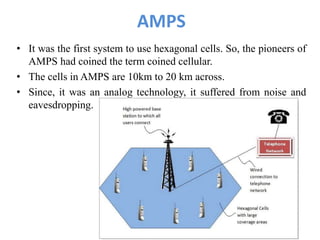
The document discusses the Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS), which is an analog cellular telephone standard introduced by AT&T in 1983 and widely deployed in the U.S. It details how AMPS utilizes frequency division multiple access and has evolved into digital AMPS (D-AMPS) with over 74 million subscribers globally. Additionally, it covers the now-obsolete Total Access Communication System (TACS) and its variants, which were developed for the U.K. and have been largely replaced by the GSM system.