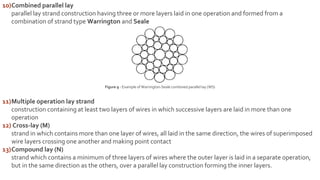
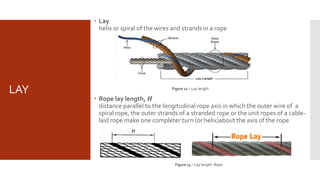
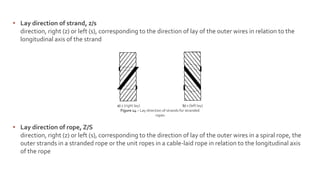
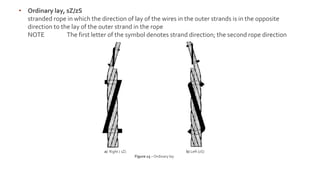
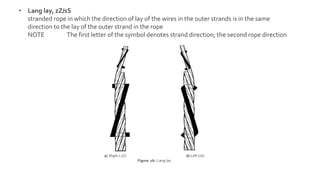
This document provides information on the key components and characteristics of wire rope. It discusses the core, which runs through the center and helps maintain the position of strands under stress. Cores can be made of fibers or steel. The nomenclature provides details on diameter, number of strands and wires, strand pattern, core type, and lay direction. Nominal diameter is specified in millimeters and obtained from certificates. Lay refers to the helical pattern of wires and strands, with direction denoted as right or left. Rope lay can be ordinary or Lang depending on if strand and rope directions are opposite or same.