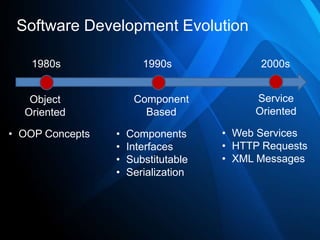
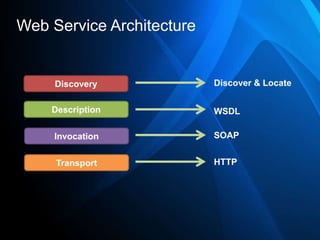
This document provides an overview of Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) and key concepts related to web services. It discusses the evolution of software development from object-oriented programming to component-based to service-oriented approaches. The core components of a web service architecture are described, including discovery, description, invocation, and transport layers. Formats for web services like XML, SOAP, WSDL and UDDI are also summarized. The document concludes with an announcement of a demonstration of these concepts.