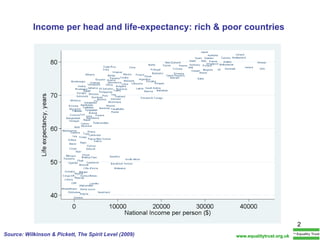
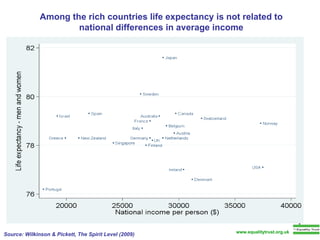
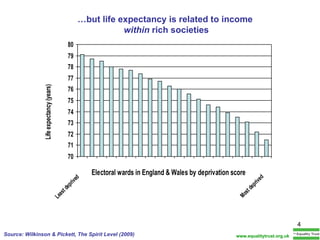
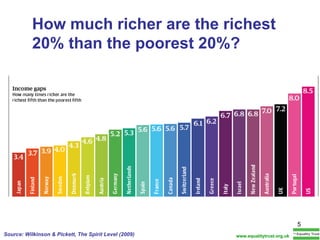
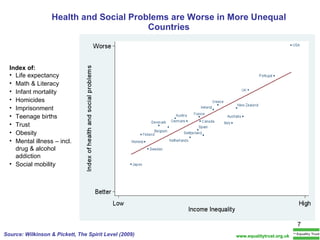
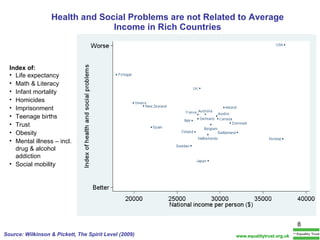
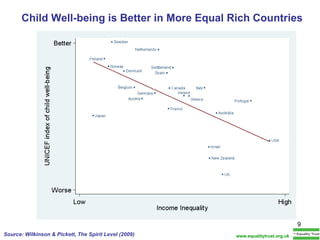
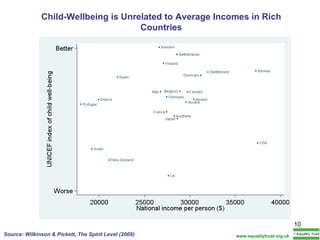
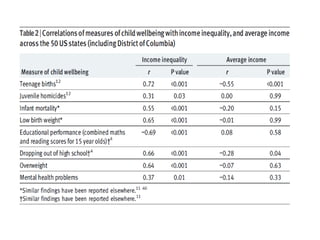
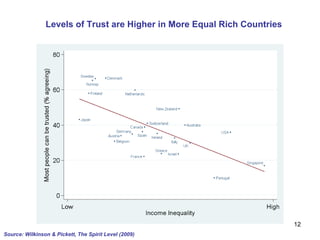
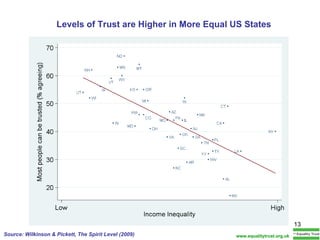
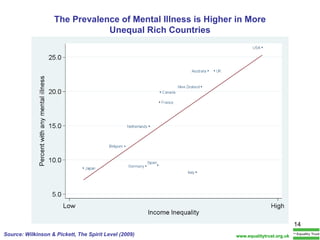
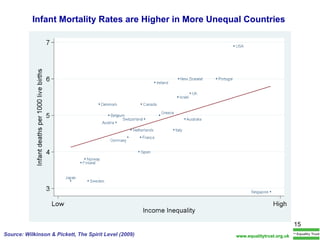
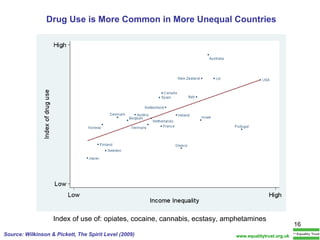
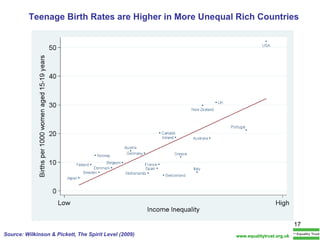
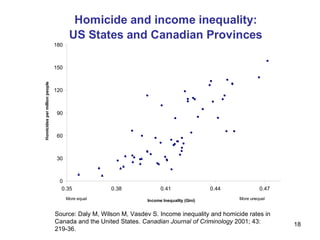
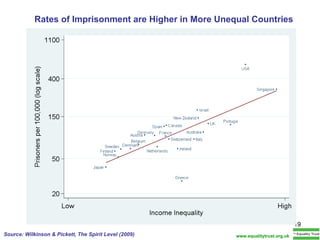
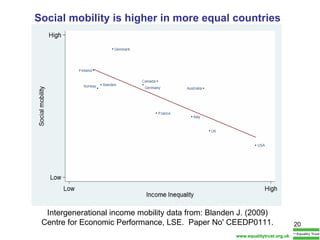
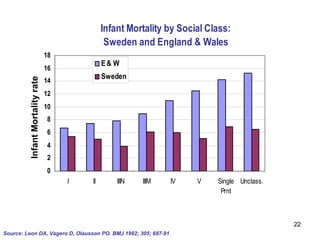
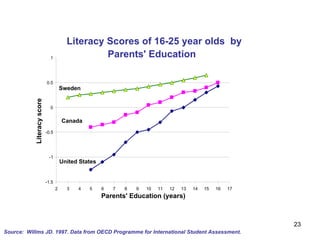
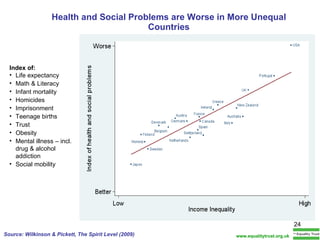
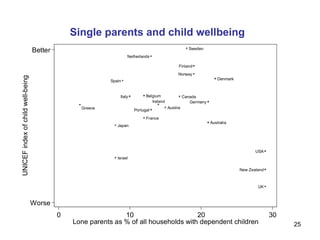
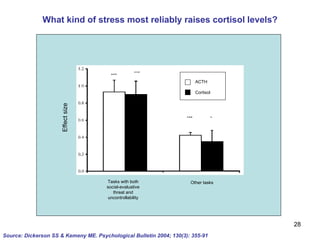
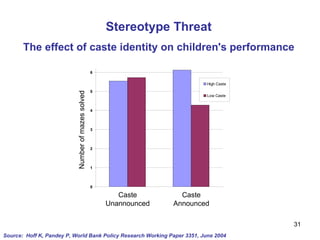
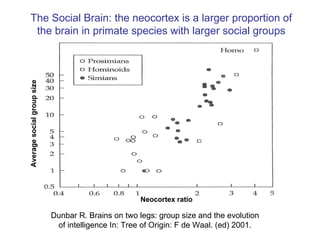
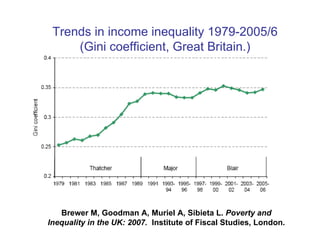
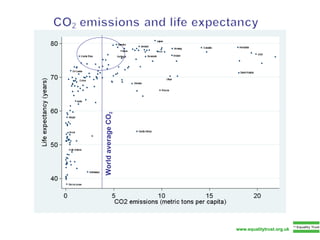
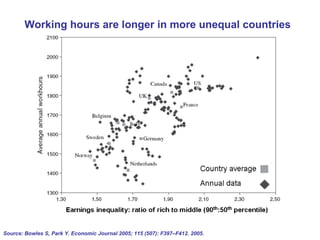
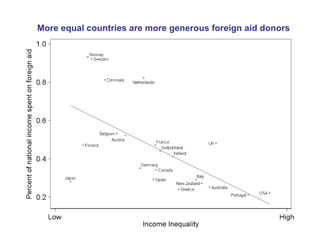
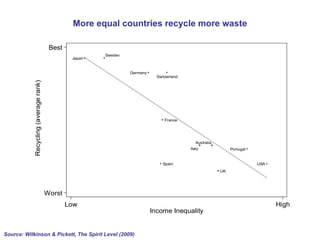
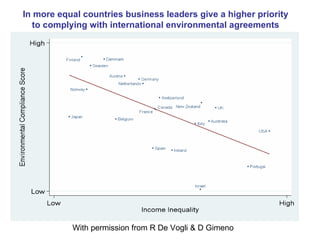
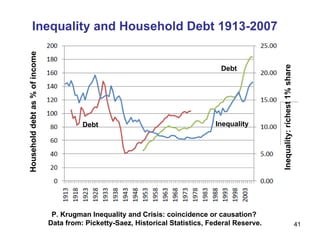
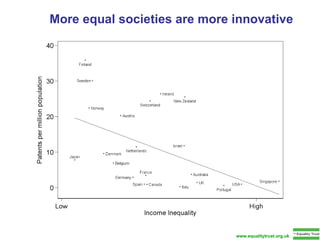
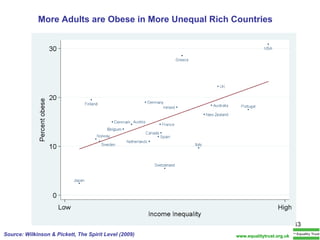
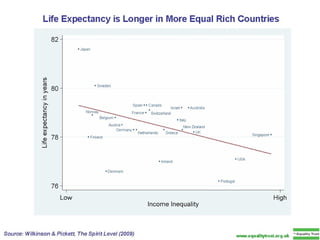
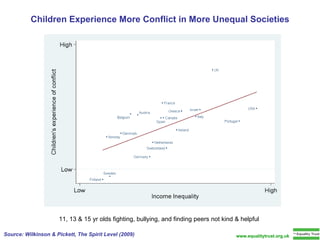
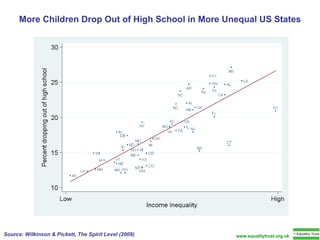
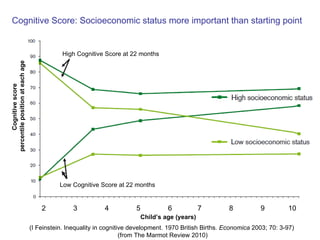
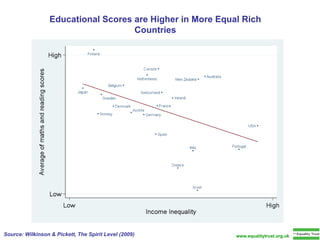
The document summarizes research from Wilkinson & Pickett's book "The Spirit Level" showing correlations between income inequality and various social problems. It presents data demonstrating that countries and US states with higher income inequality have worse health, social, and educational outcomes, even when controlling for average national income. The findings suggest that greater equality benefits societies overall and that inequality itself is psychologically and socially harmful.