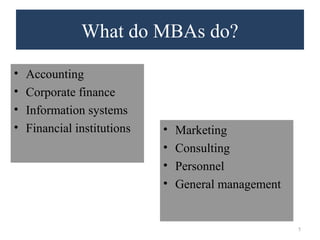
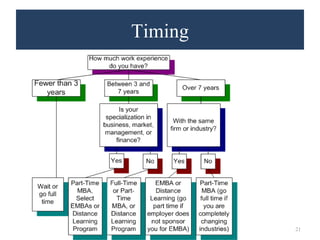
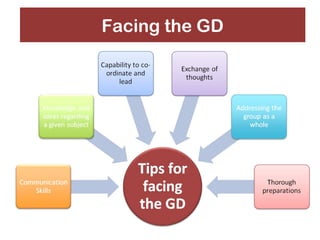
This document provides an overview of getting an MBA degree. It discusses MBA trends over time, typical career paths and salaries of MBA graduates, reasons to pursue and not pursue an MBA, student profiles, skills gained, and factors to consider like program types, curriculum, teaching methods, timing, school selection, admissions, and financial aid. The document aims to help readers decide if an MBA is right for them and provide guidance on navigating an MBA program.