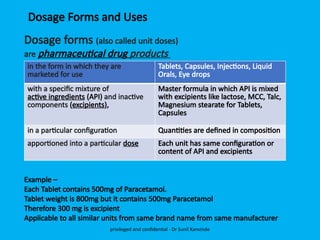
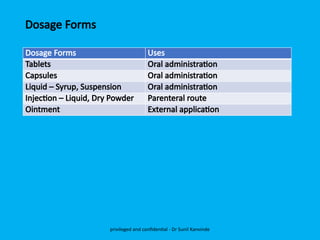
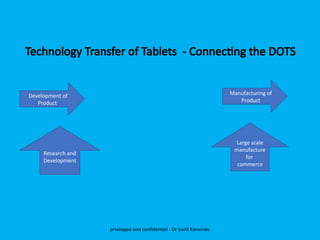
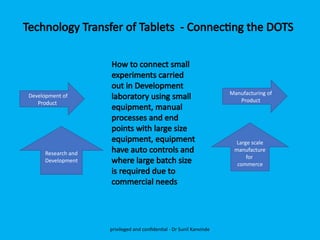
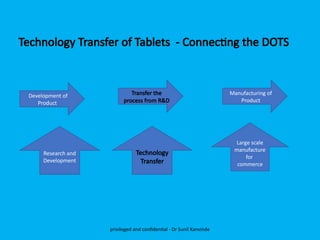
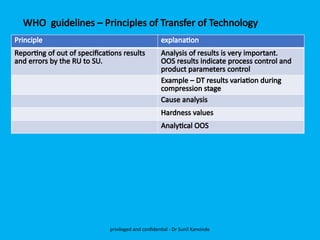
The document discusses the development and transfer of technology in pharmaceutical manufacturing, focusing on dosage forms such as tablets, capsules, and injections. It highlights the process of tablet development, from formulation to production, and emphasizes the importance of adherence to WHO guidelines for effective technology transfer, ensuring quality and compliance. A risk-based approach is recommended for successful knowledge transfer between development and manufacturing sites to maintain consistent medication quality.