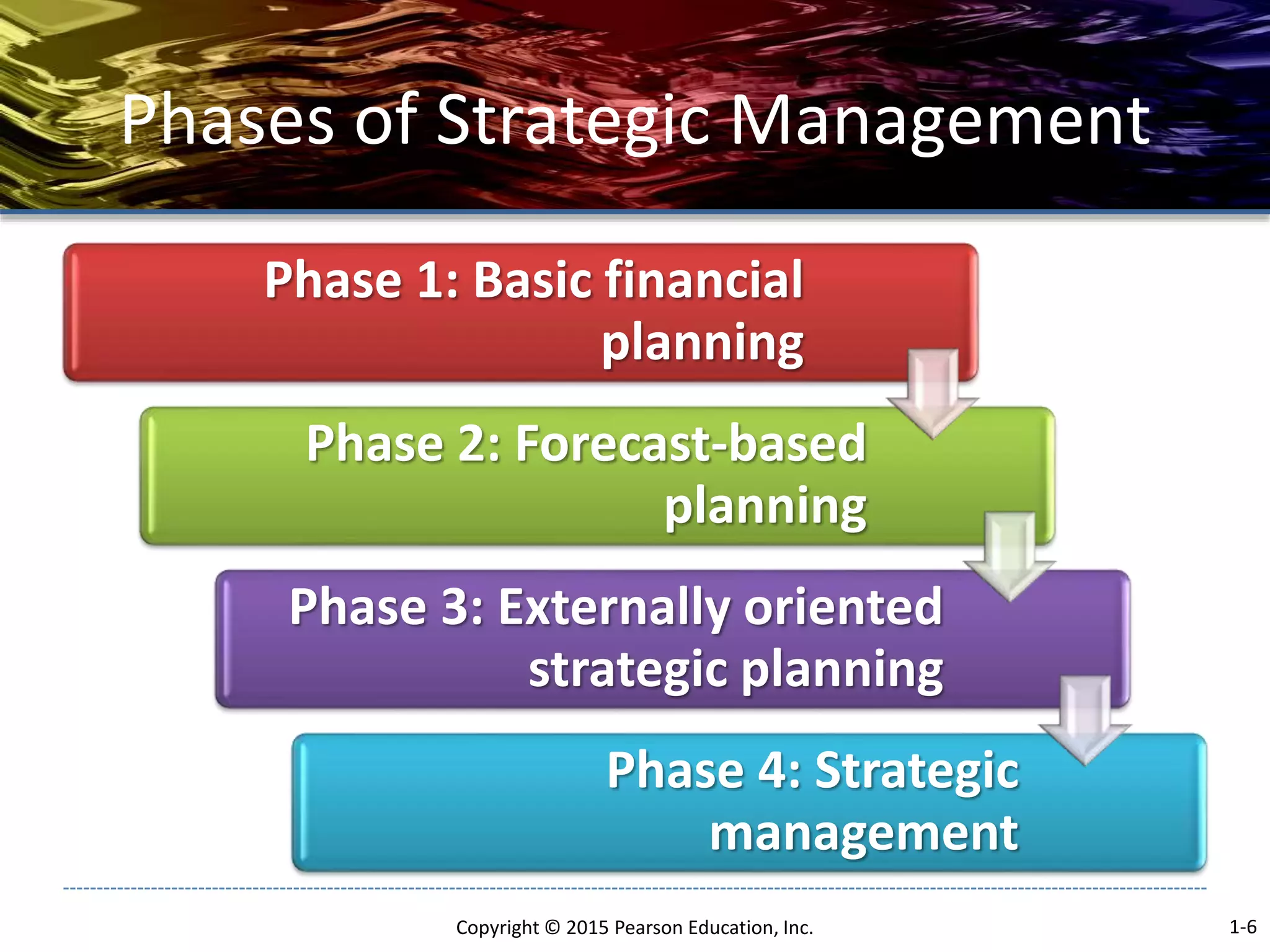
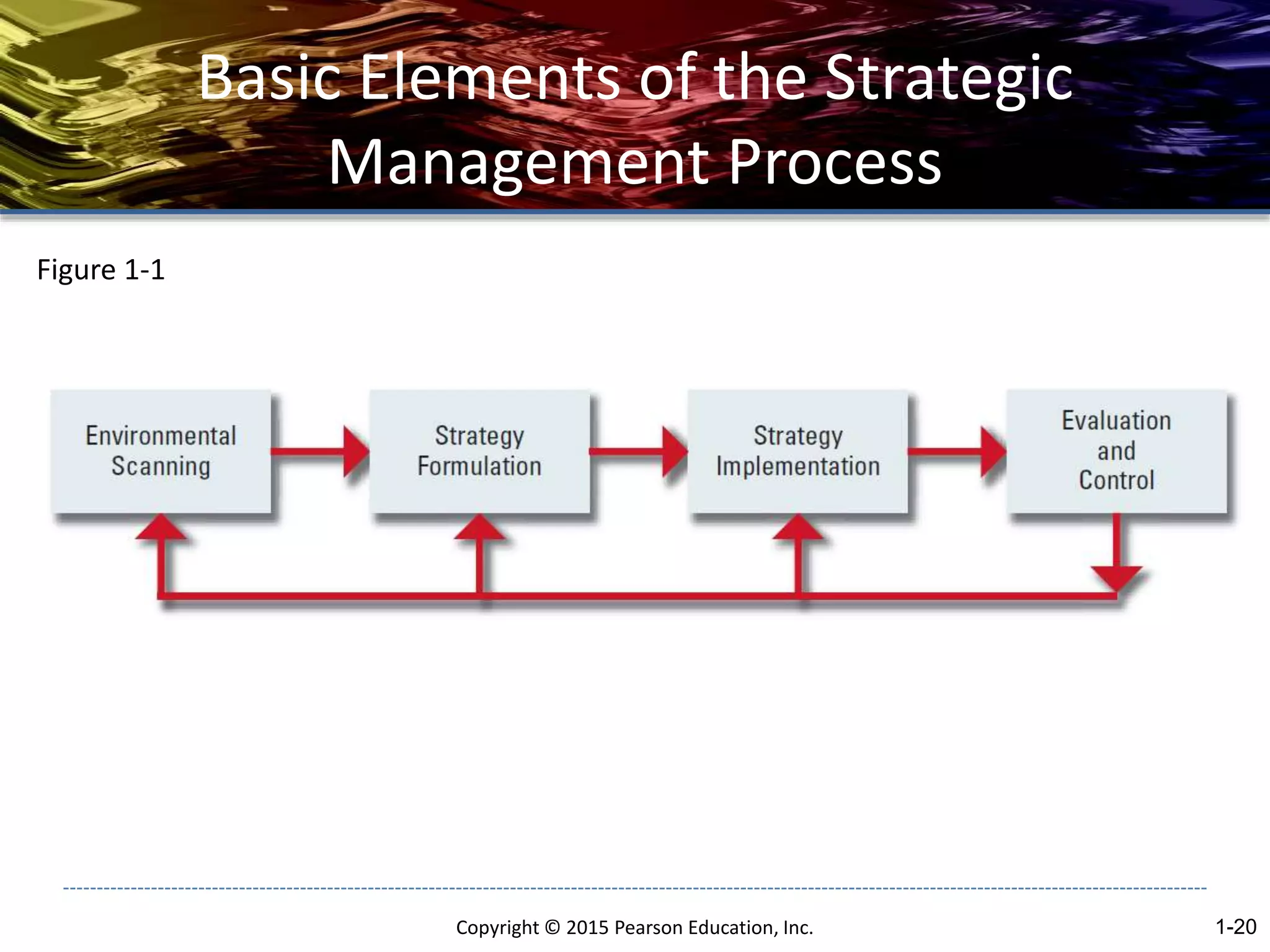
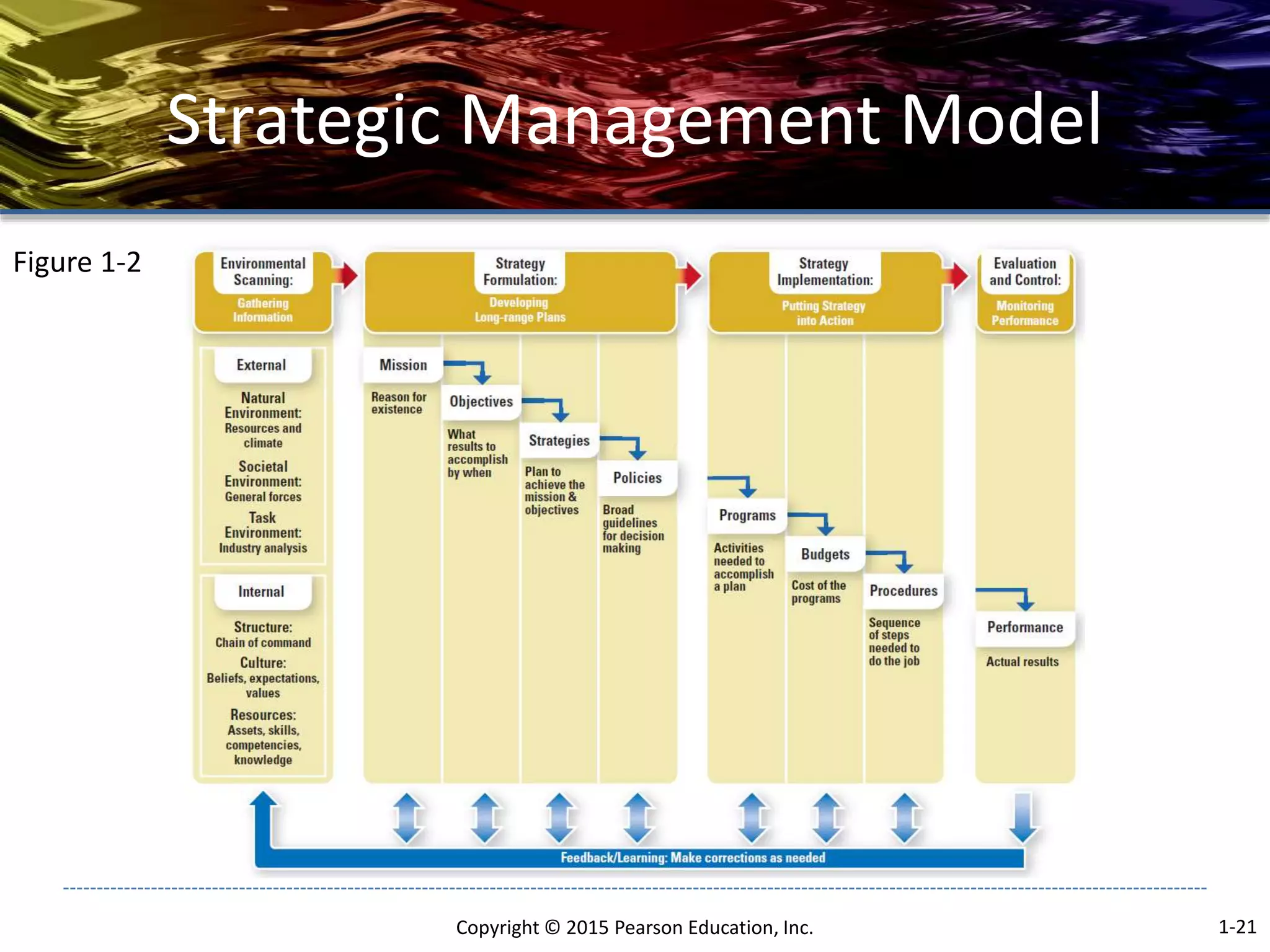
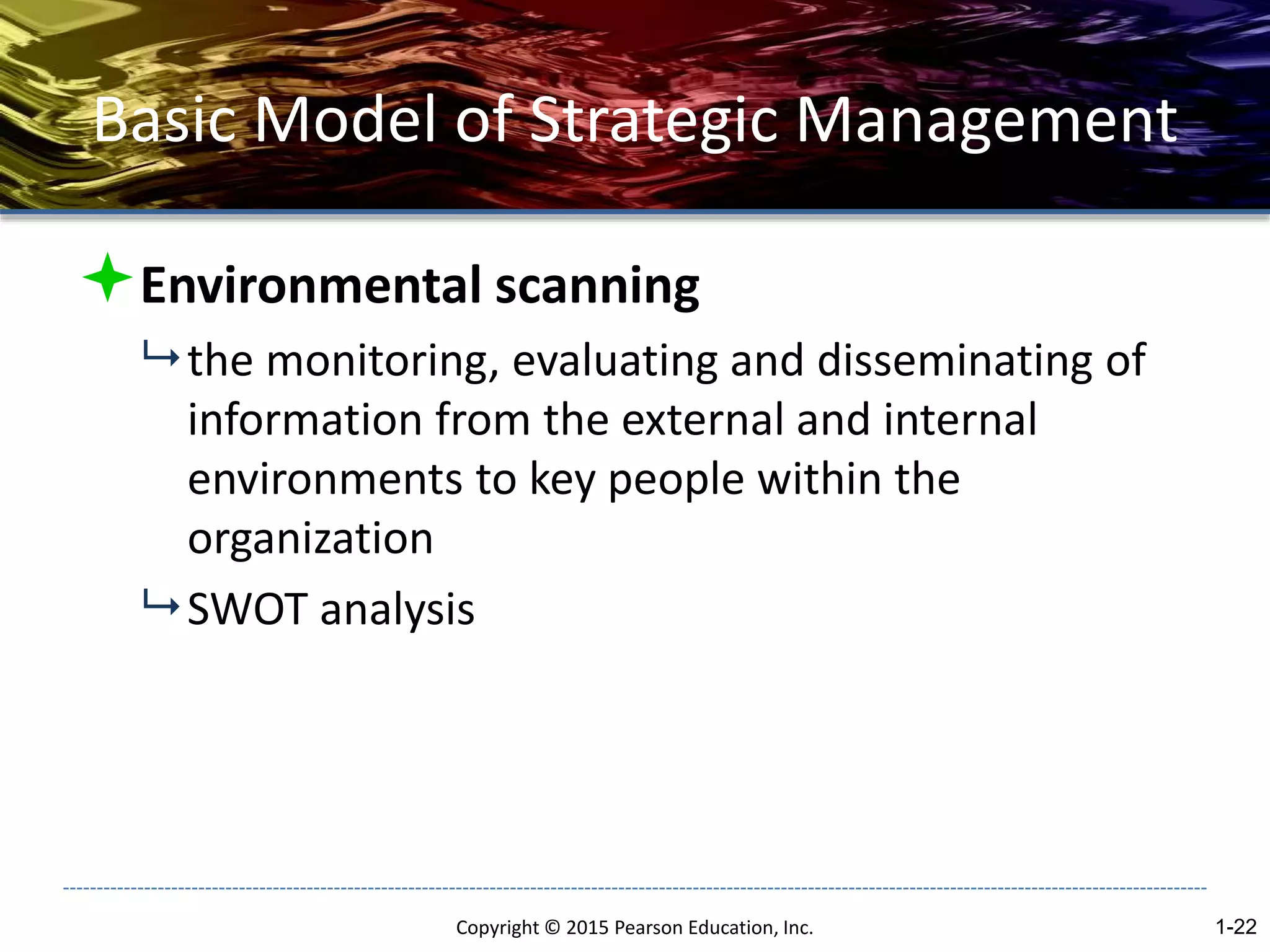
The document outlines the basic concepts of strategic management including:
- The strategic management process consists of environmental scanning, strategy formulation, strategy implementation, and evaluation and control.
- Strategic management helps organizations match their strategy to their external environment which improves performance.
- Globalization, innovation, and sustainability impact how organizations approach strategic management.
- Strategic decisions are rare, consequential, and directive in guiding an organization's long term goals.