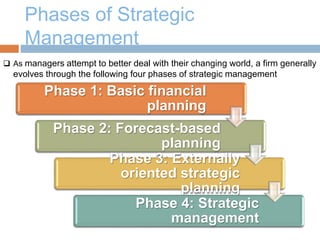
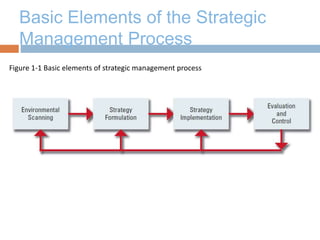
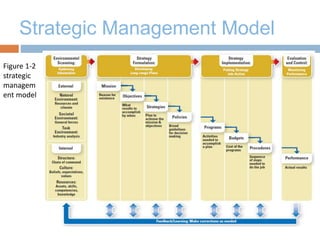
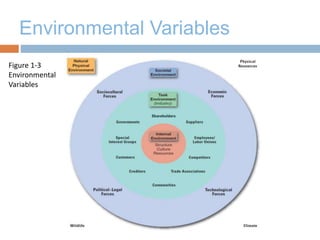
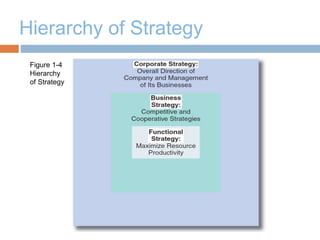
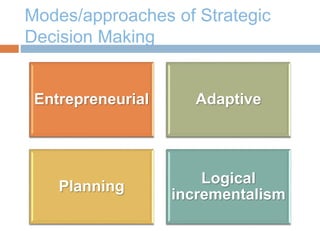
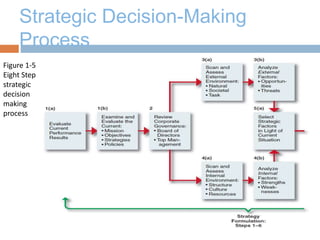
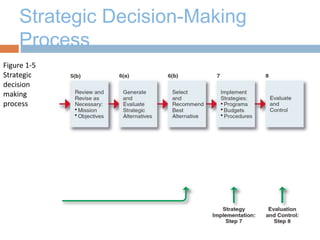
The document discusses strategic management and provides definitions and concepts. It describes strategic management as including environmental scanning, strategy formulation, implementation, and evaluation. It outlines the four phases that organizations typically go through in developing strategic management: basic financial planning, forecast-based planning, externally oriented strategic planning, and strategic management. Key benefits of strategic management include improved vision, focus, and environmental understanding. Globalization, innovation, and sustainability are presented as important challenges for strategic management. Theories of organizational adaptation and creating learning organizations are also covered.