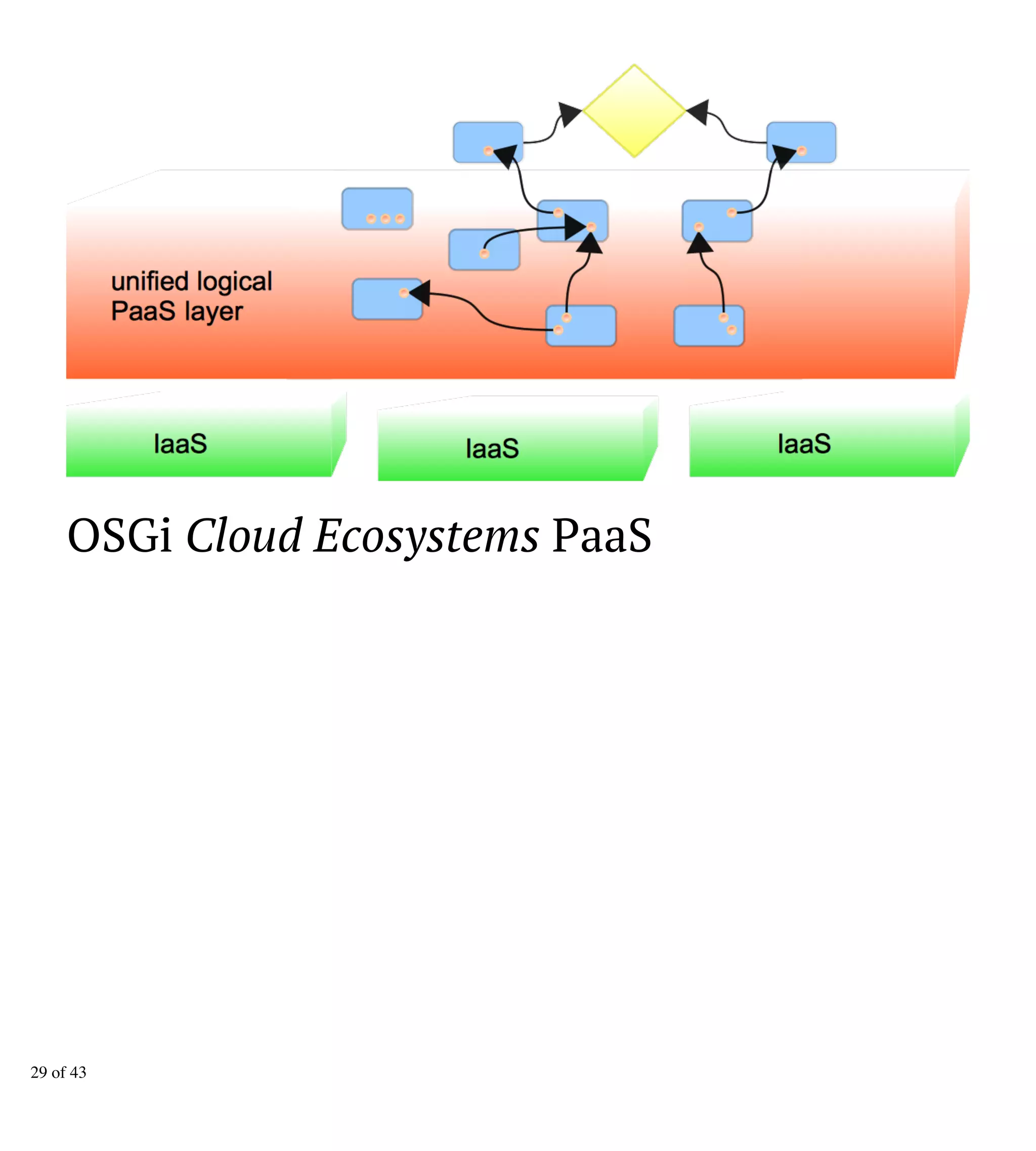
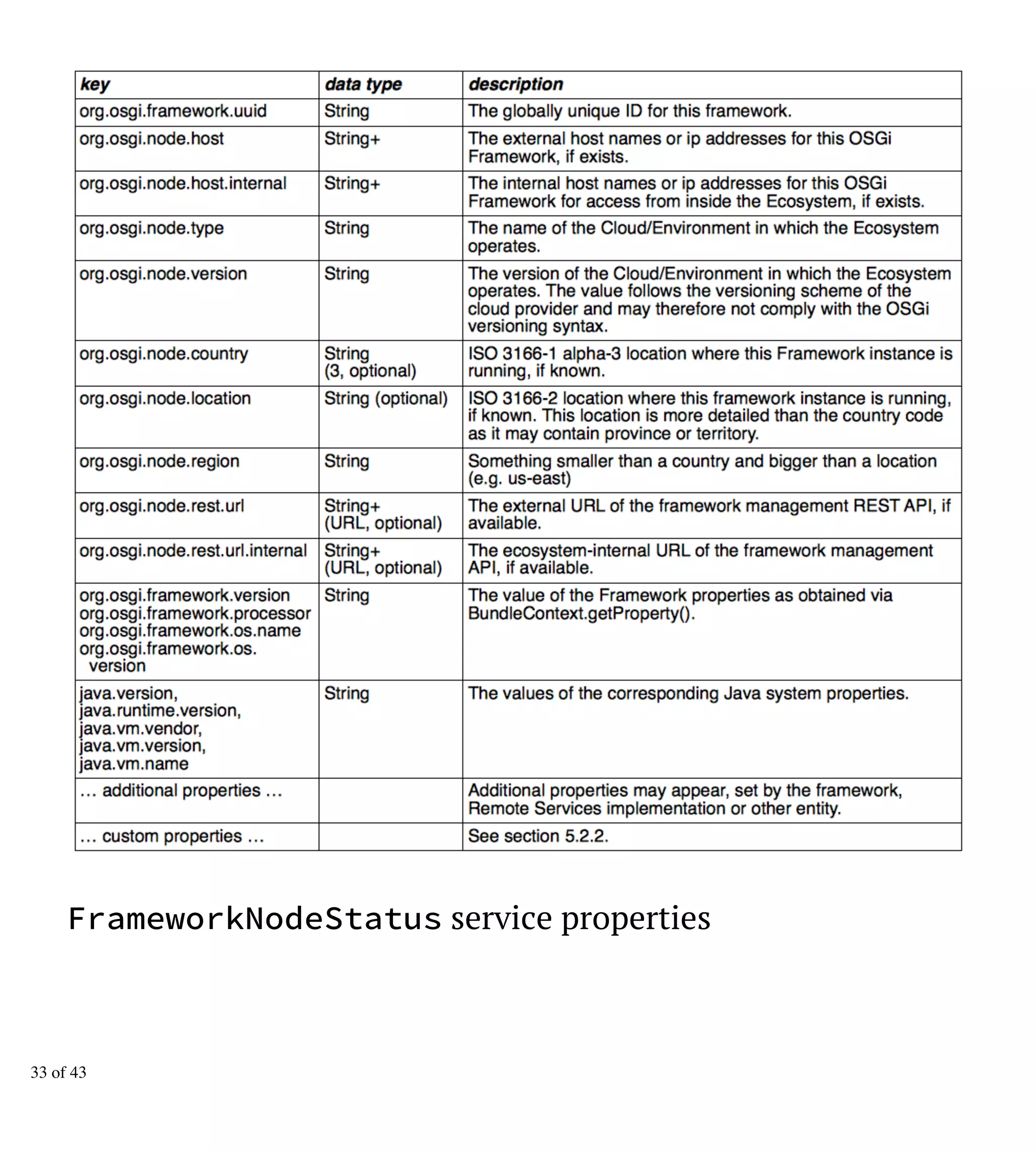
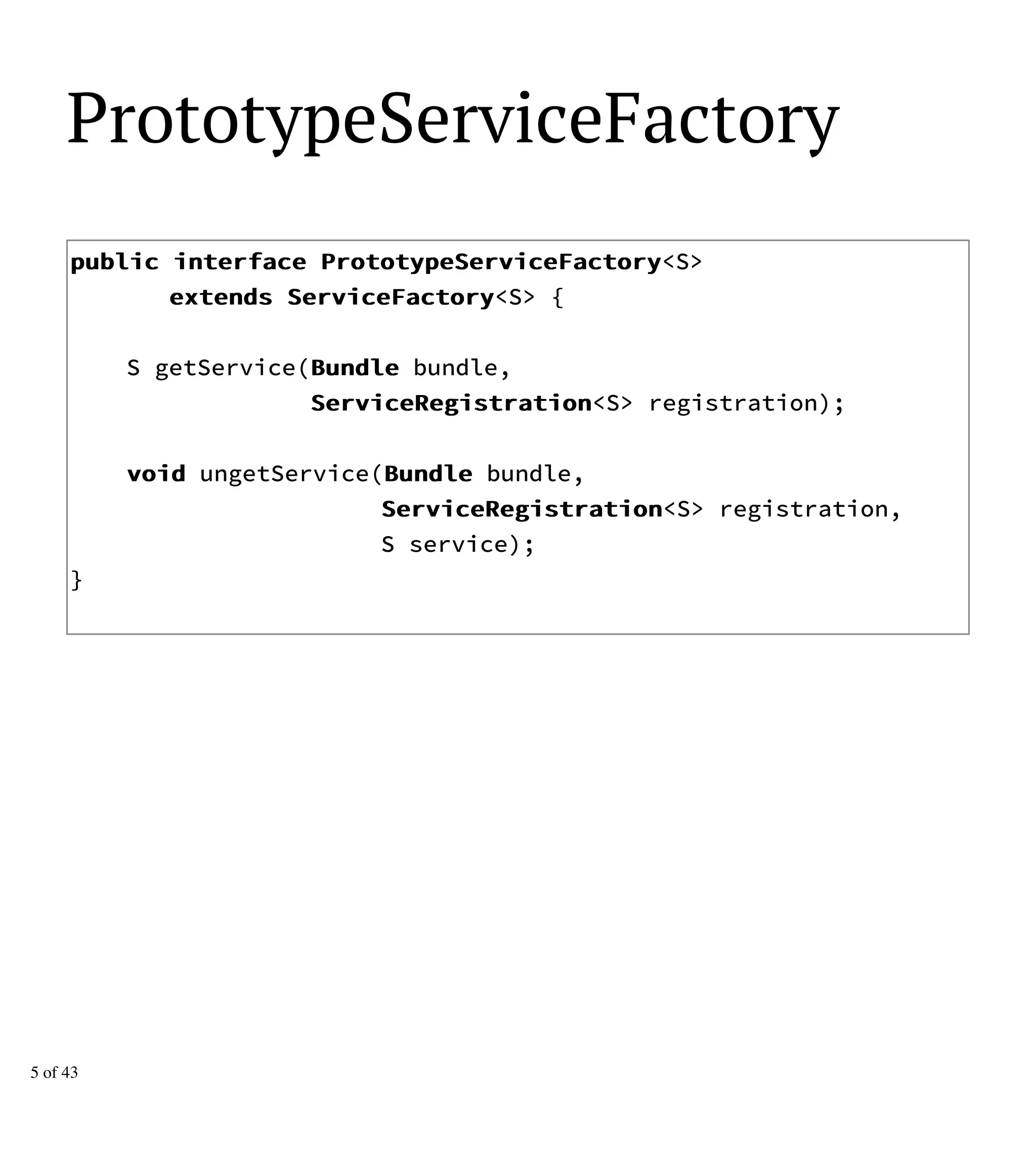
The document discusses updates and enhancements in OSGi specifications, highlighting framework updates, OSGi/CDI integration, repository improvements, and declarative services. Key features include the introduction of new interfaces, annotations for configuration, enhancements to HTTP services, and support for cloud ecosystems. Additional topics cover semantic versioning and various other enterprise specification updates.












![Use annotations for
configuration...
@interface MMyyCCoonnffiigg {
bboooolleeaann enabled() ddeeffaauulltt ttrruuee;
SSttrriinngg[] topic() ddeeffaauulltt {"topicA", "topicB"};
SSttrriinngg userName();
iinntt service_ranking() ddeeffaauulltt 15;
}
16 of 43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ec2014-140320193730-phpapp02/75/What-s-cool-in-the-new-and-updated-OSGi-Specs-EclipseCon-2014-16-2048.jpg)
![...and reference them in
lifecycle methods
@Component
ppuubblliicc ccllaassss MMyyCCoommppoonneenntt {
SSttrriinngg userName;
SSttrriinngg[] topics;
@Activate
pprrootteecctteedd vvooiidd activate(ffiinnaall MMyyCCoonnffiigg config) {
// note: annotation MyConfig used as interface
iiff ( config.enabled() ) {
tthhiiss.userName = config.userName();
tthhiiss.topics = config.topic();
}
}
}
17 of 43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ec2014-140320193730-phpapp02/75/What-s-cool-in-the-new-and-updated-OSGi-Specs-EclipseCon-2014-17-2048.jpg)


![Additional Metatype
Support (RFC 208)
@ObjectClassDefinition(label="My Component",
description="Coolest component in the world.")
@interface MMyyCCoonnffiigg {
@AttributeDefinition(label="Enabled",
description="Topic and user name are used if enabled")
bboooolleeaann enabled() ddeeffaauulltt ttrruuee;
@AttributeDefinition(...)
SSttrriinngg[] topic() ddeeffaauulltt {"topicA", "topicB"};
@AttributeDefinition(...)
SSttrriinngg userName();
iinntt service_ranking() ddeeffaauulltt 15; // maps to service.ranking
}
20 of 43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ec2014-140320193730-phpapp02/75/What-s-cool-in-the-new-and-updated-OSGi-Specs-EclipseCon-2014-20-2048.jpg)