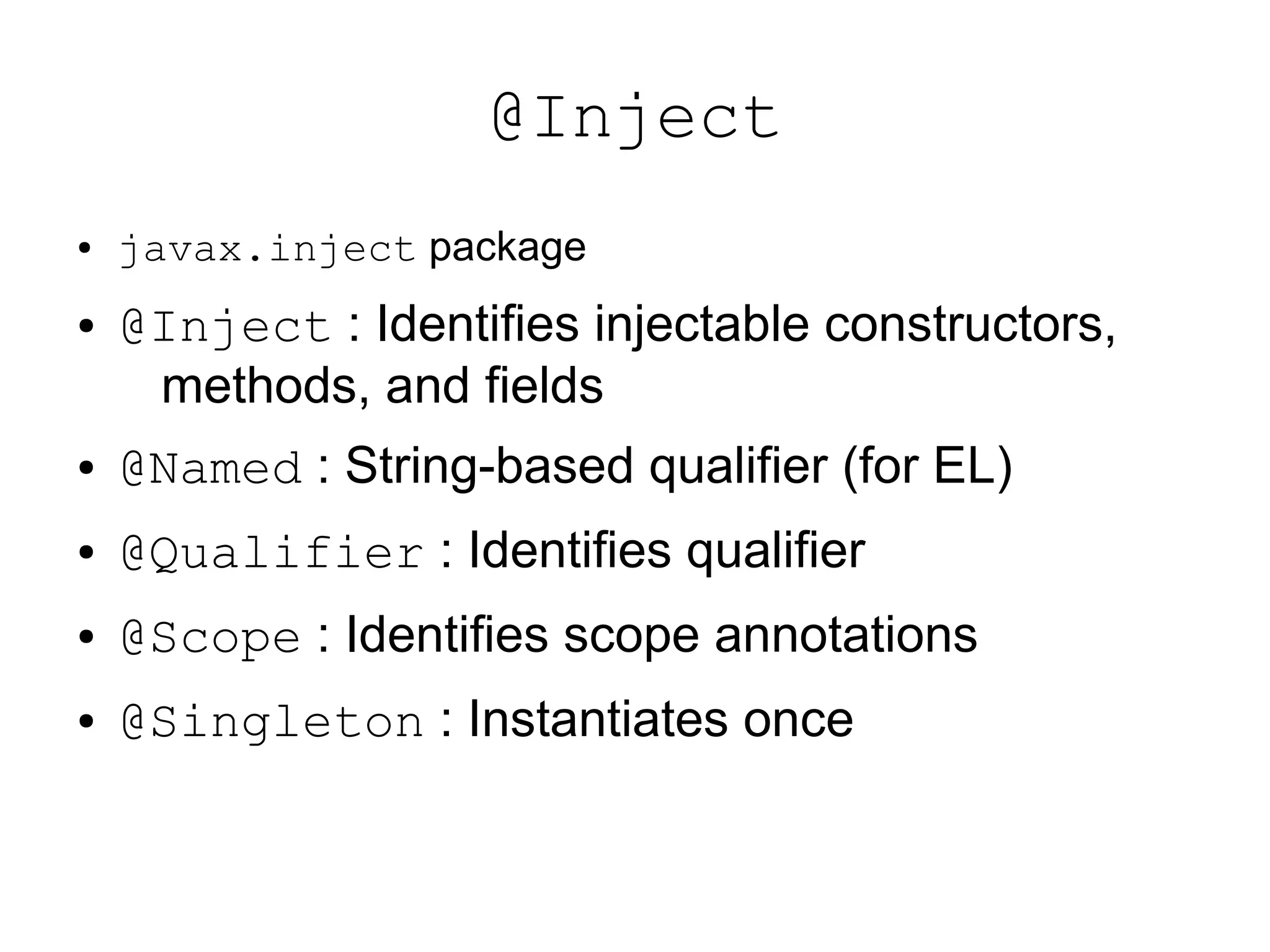
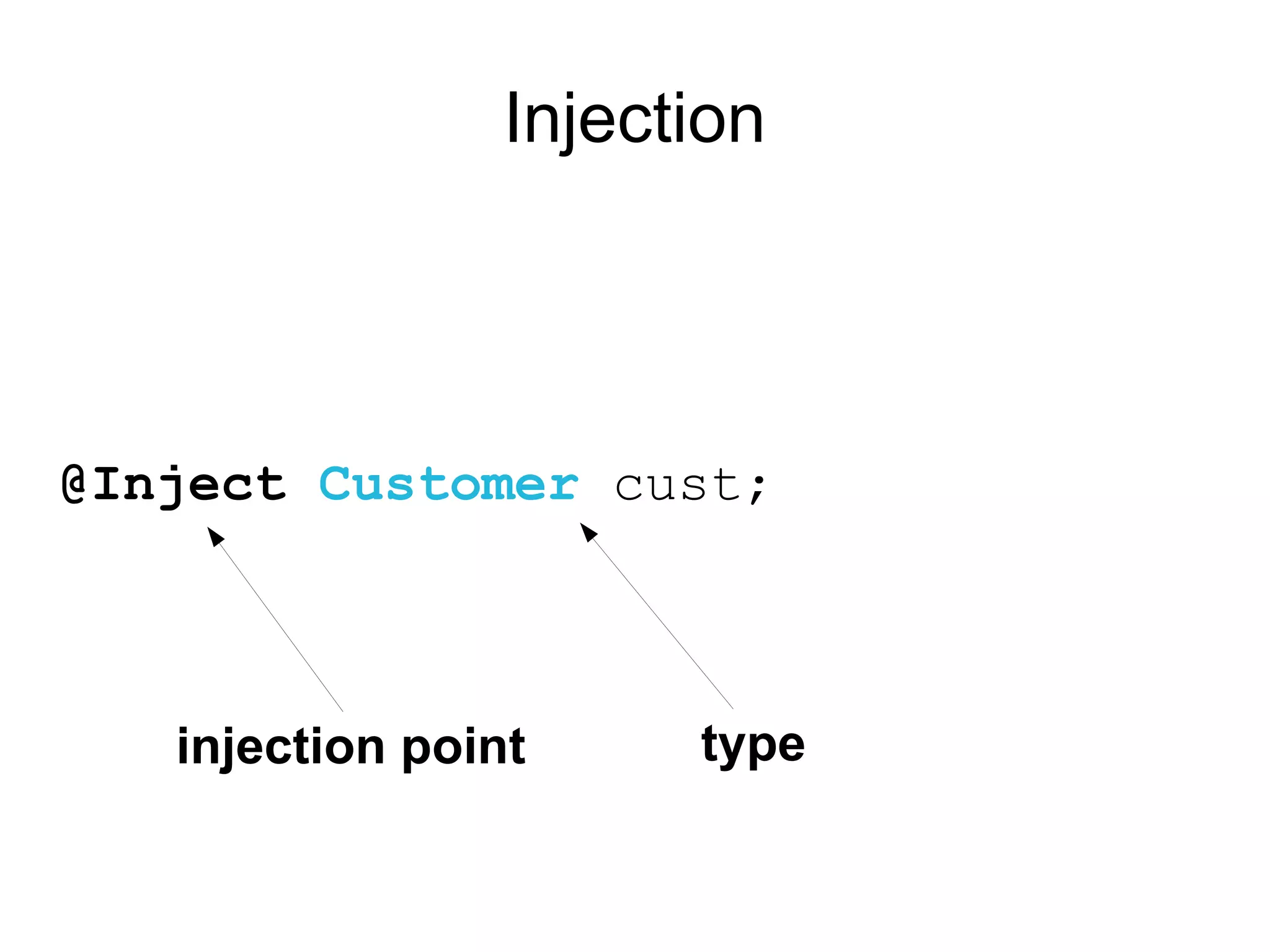
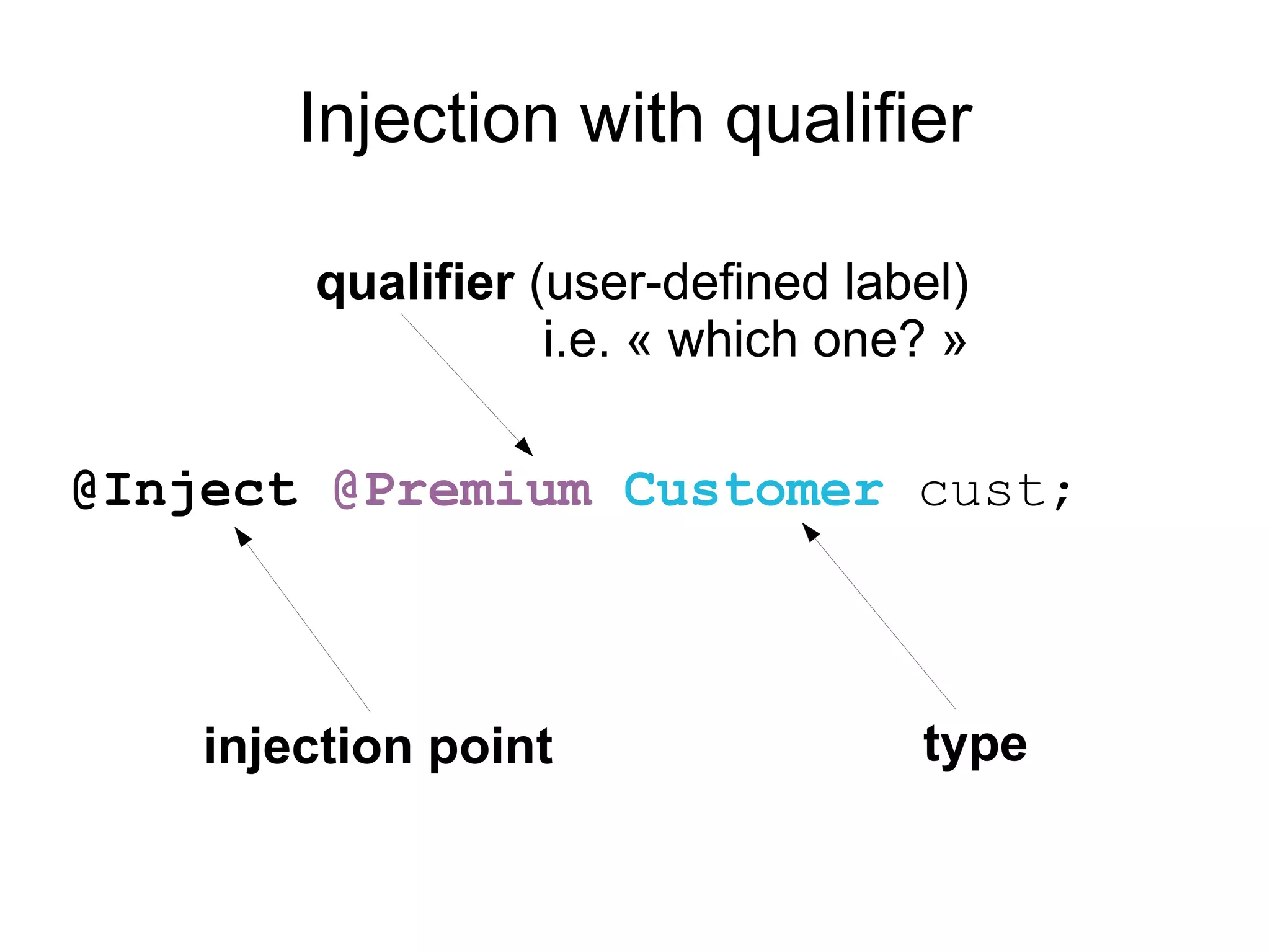
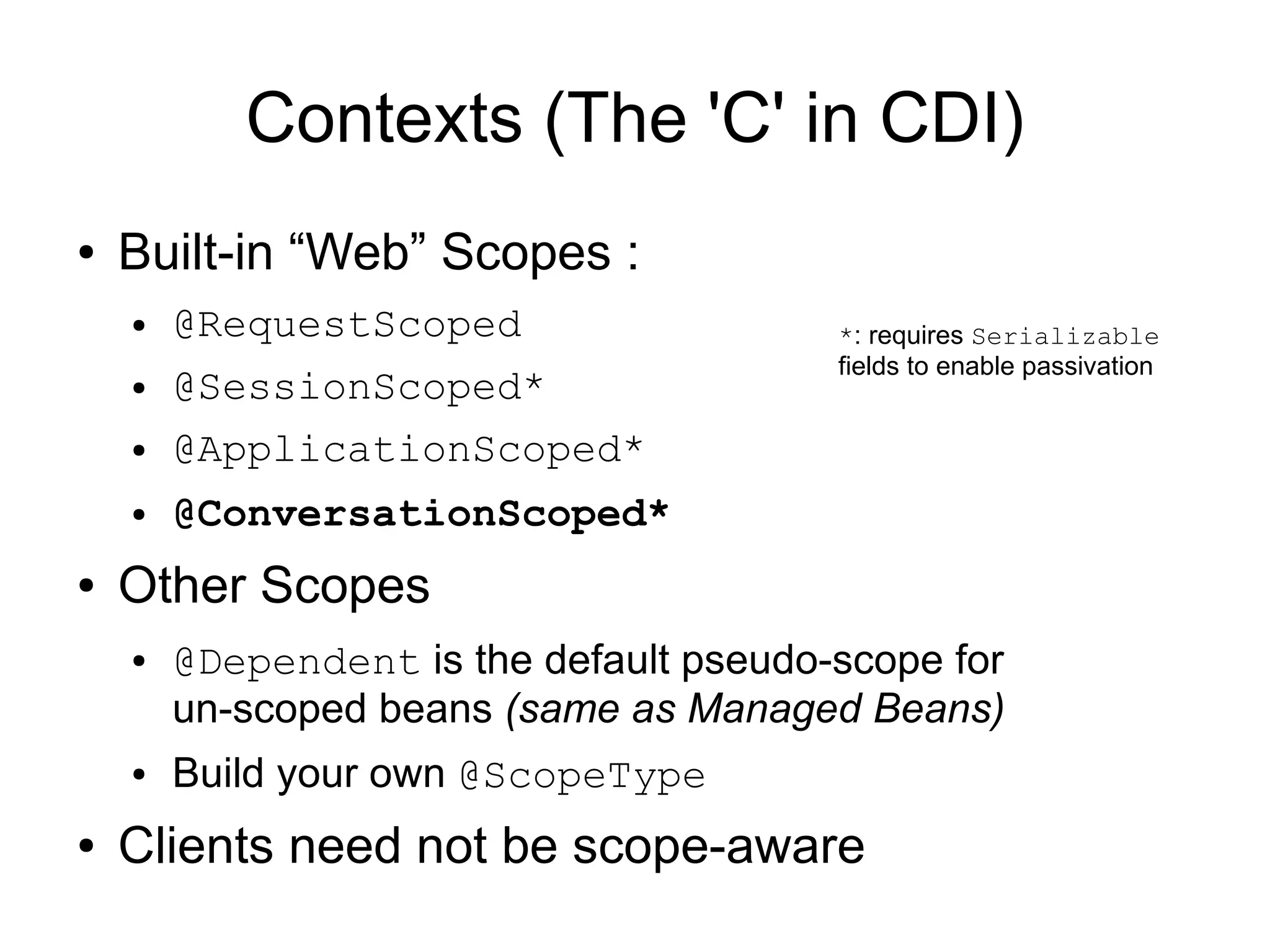
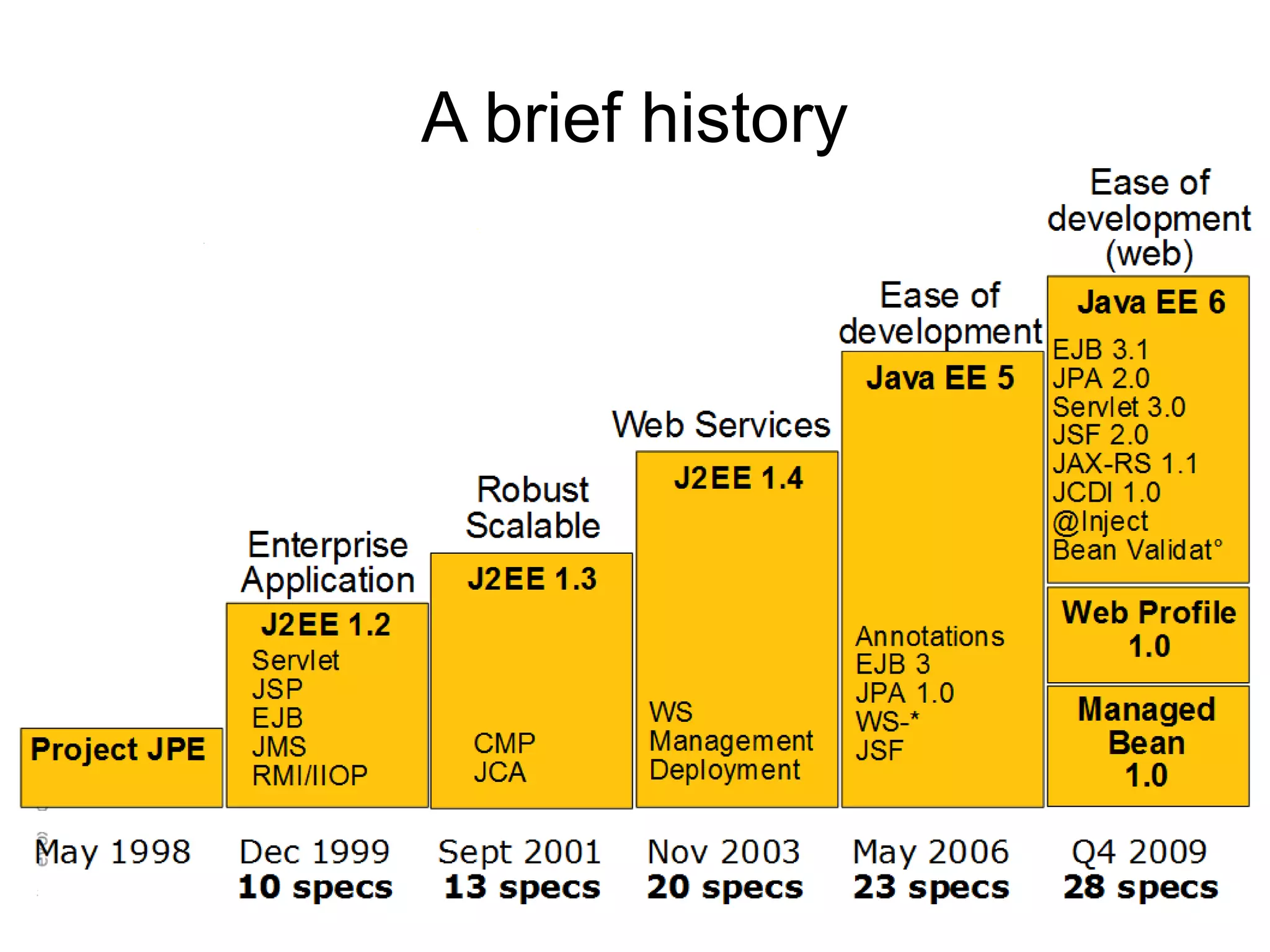
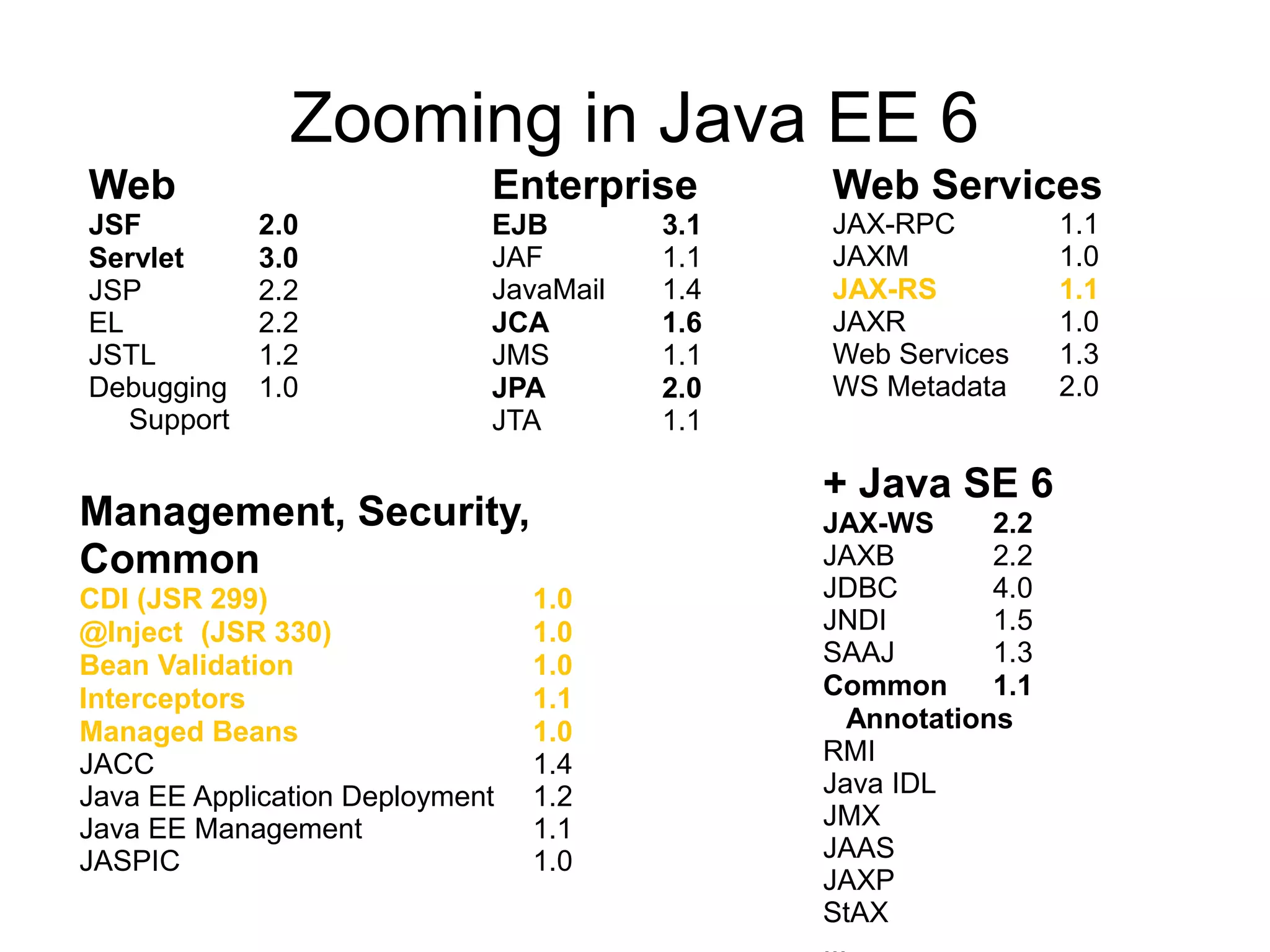
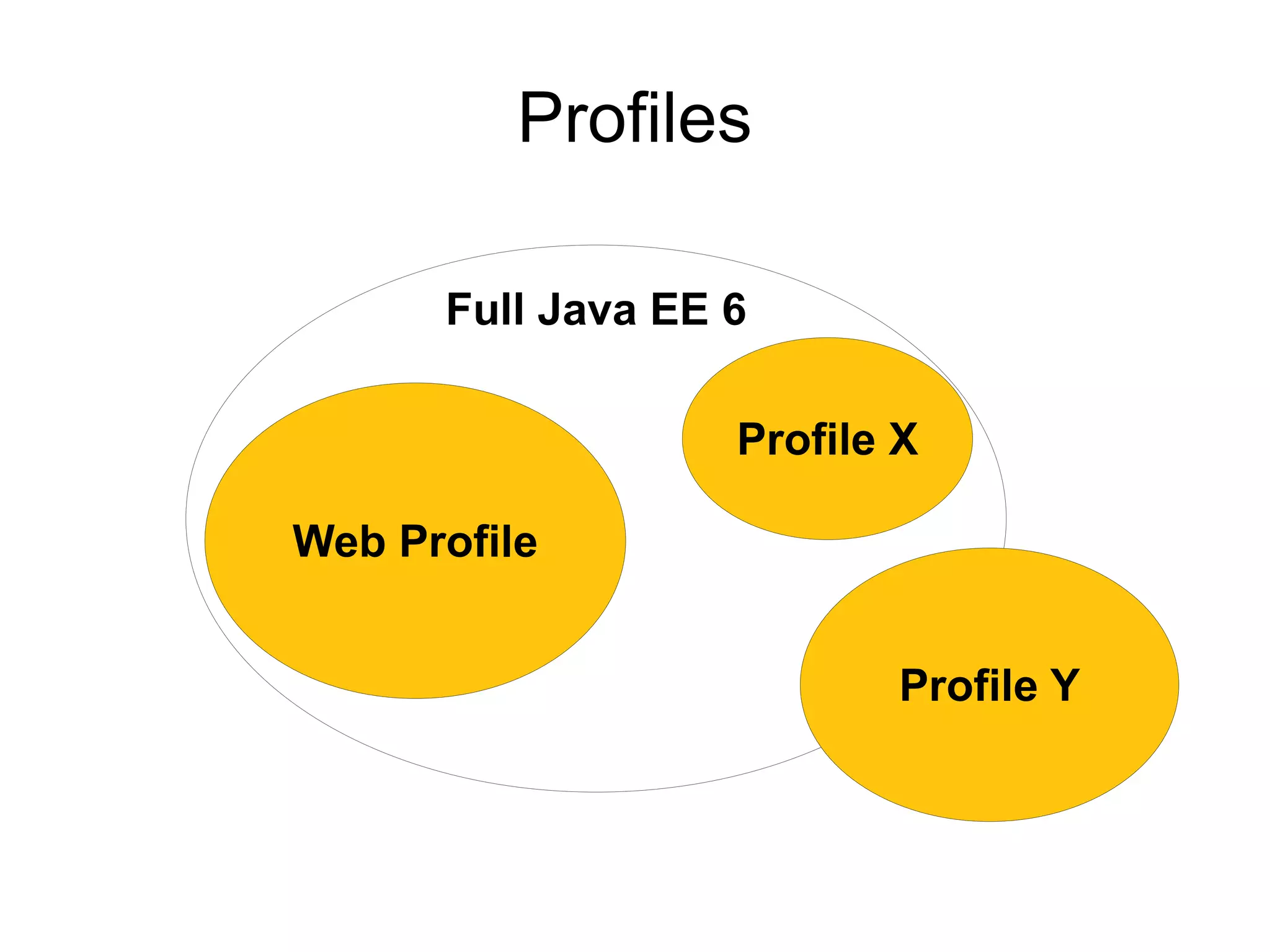
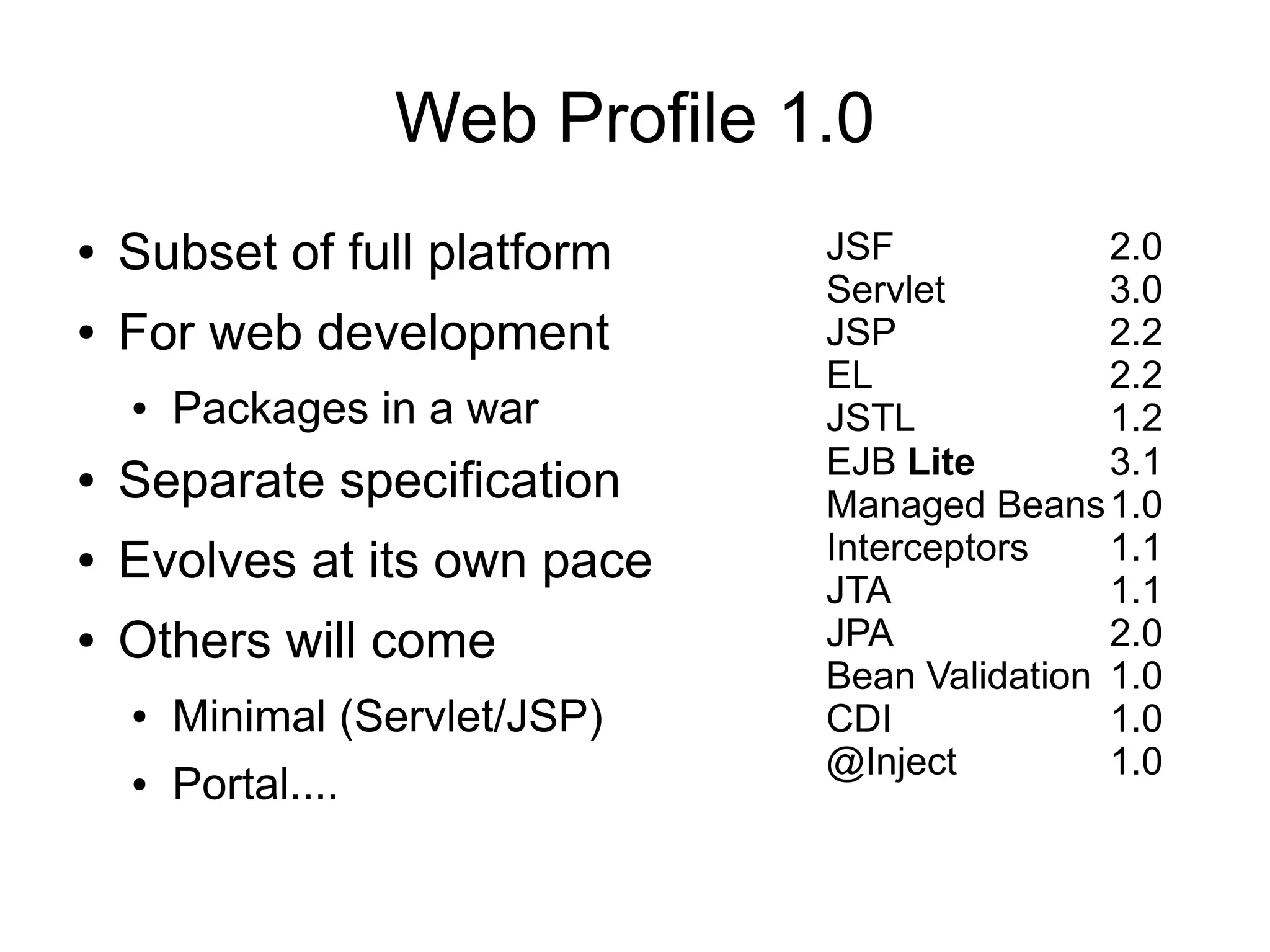
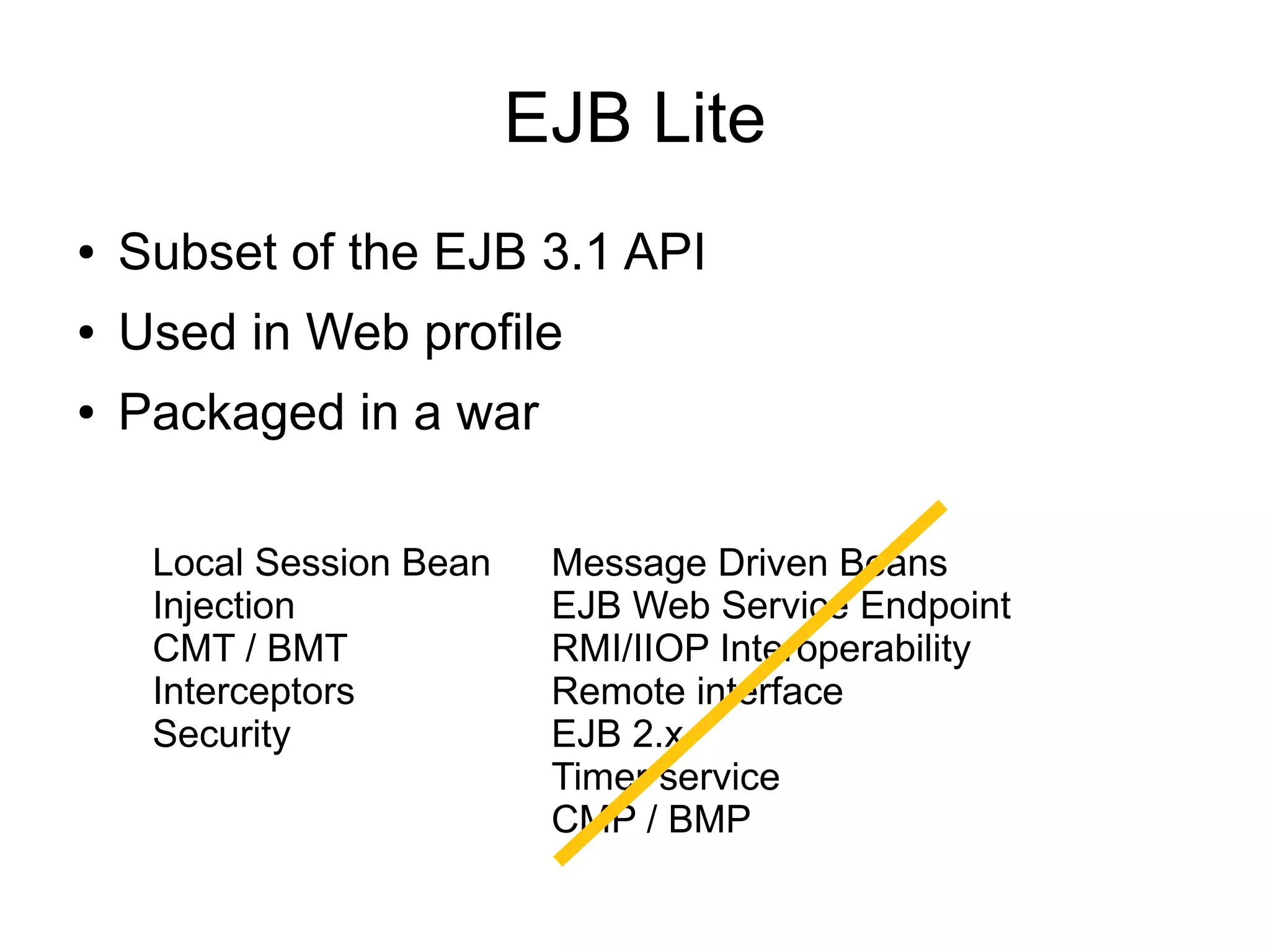
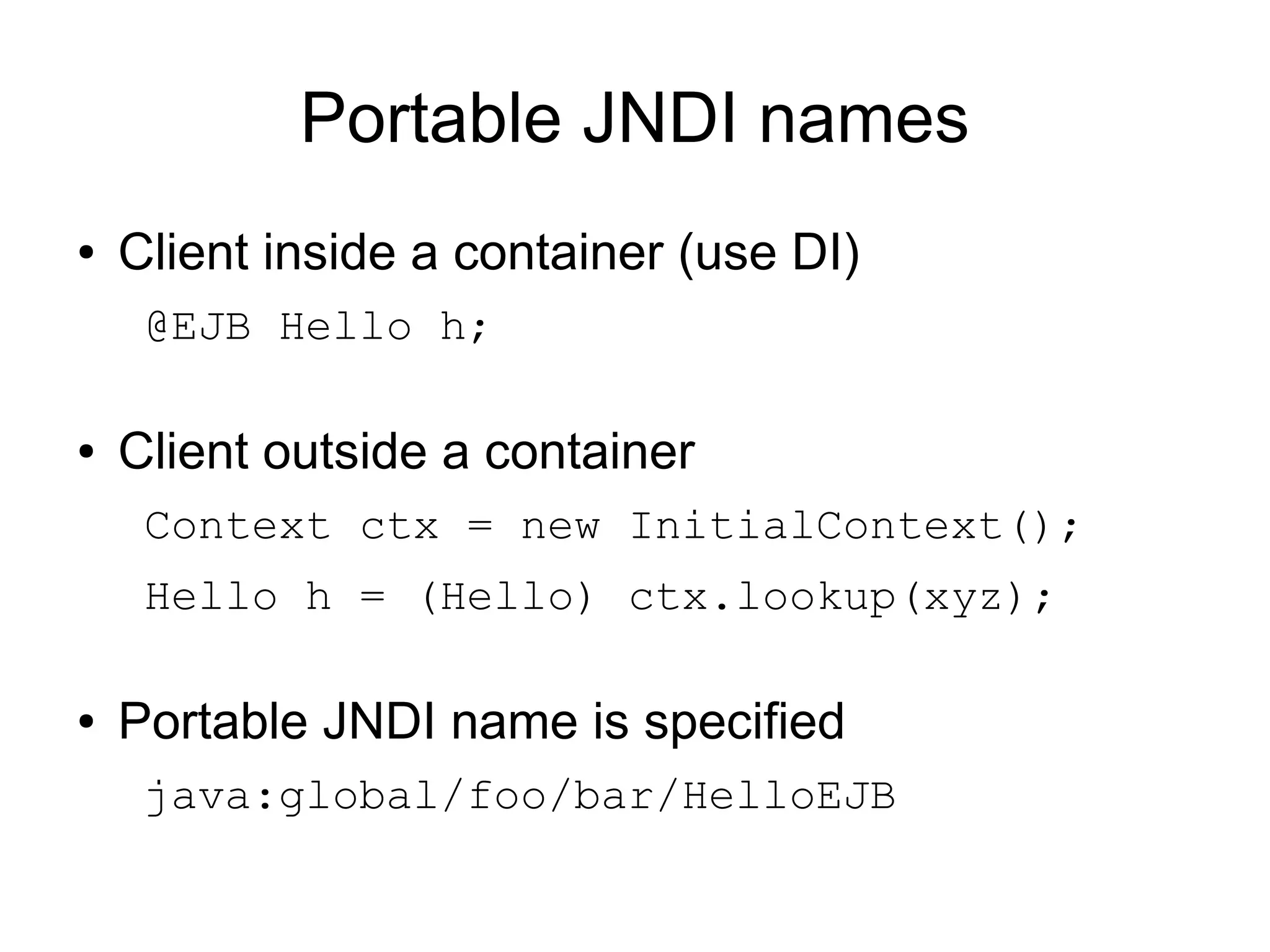
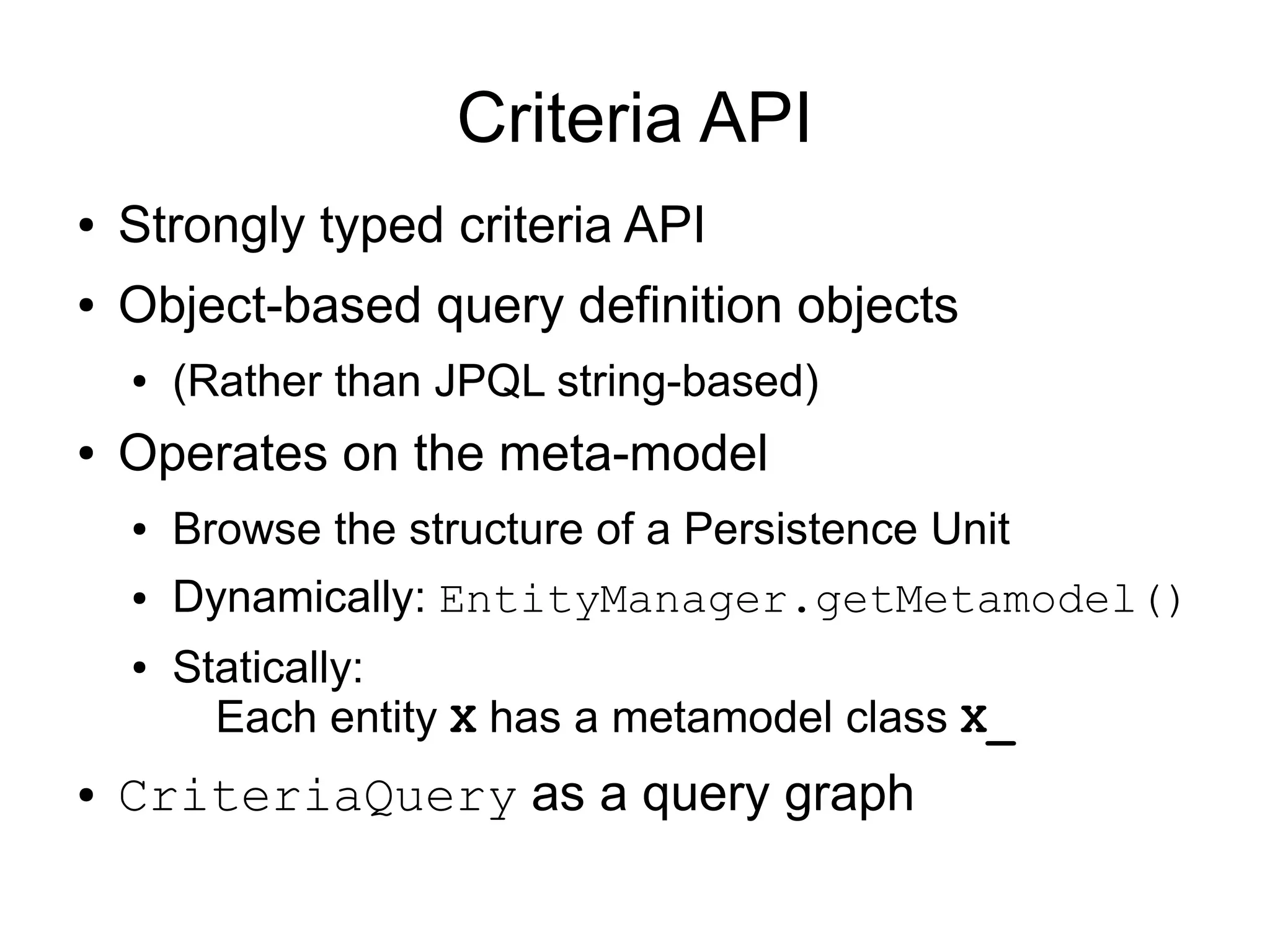
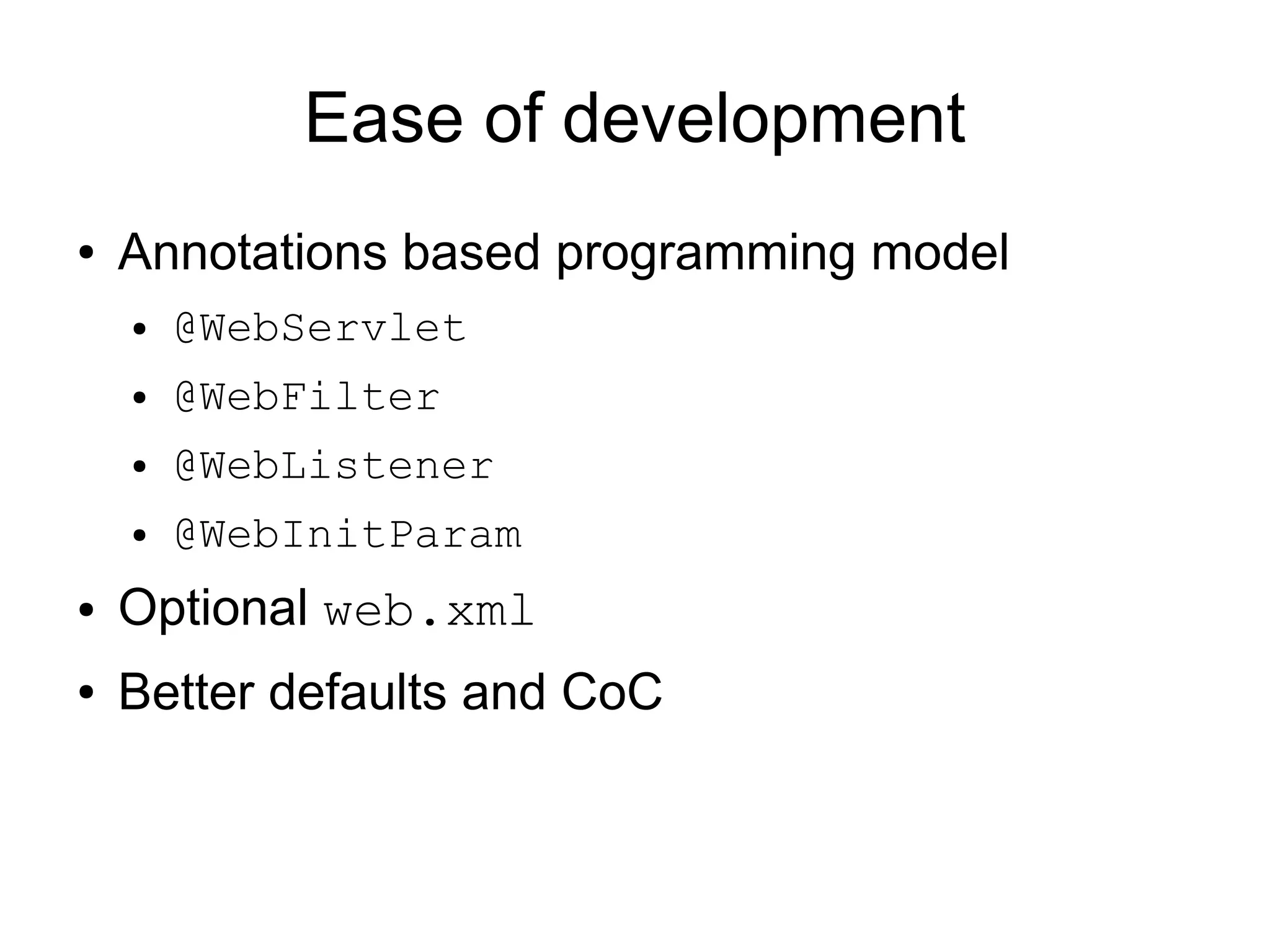
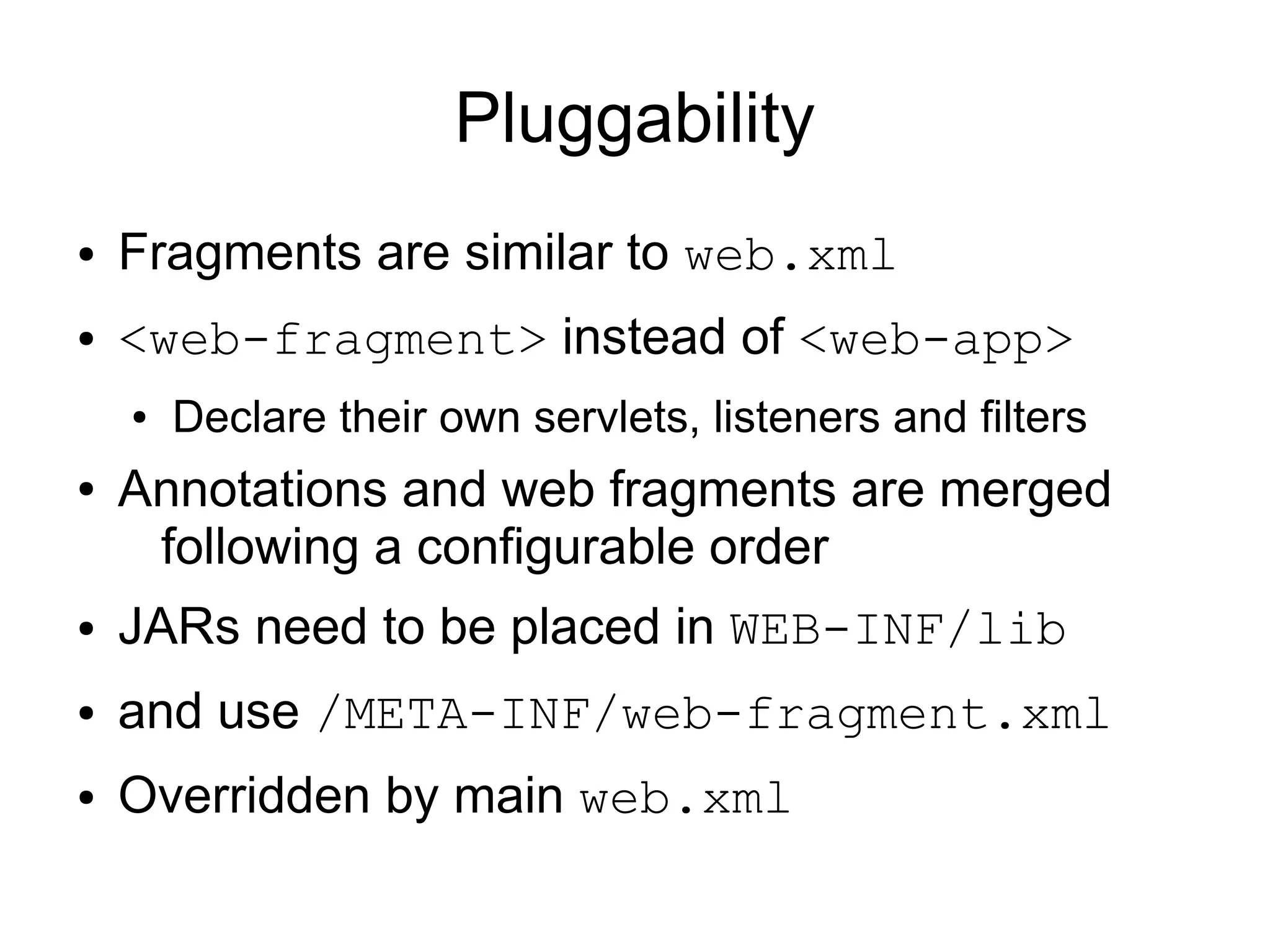
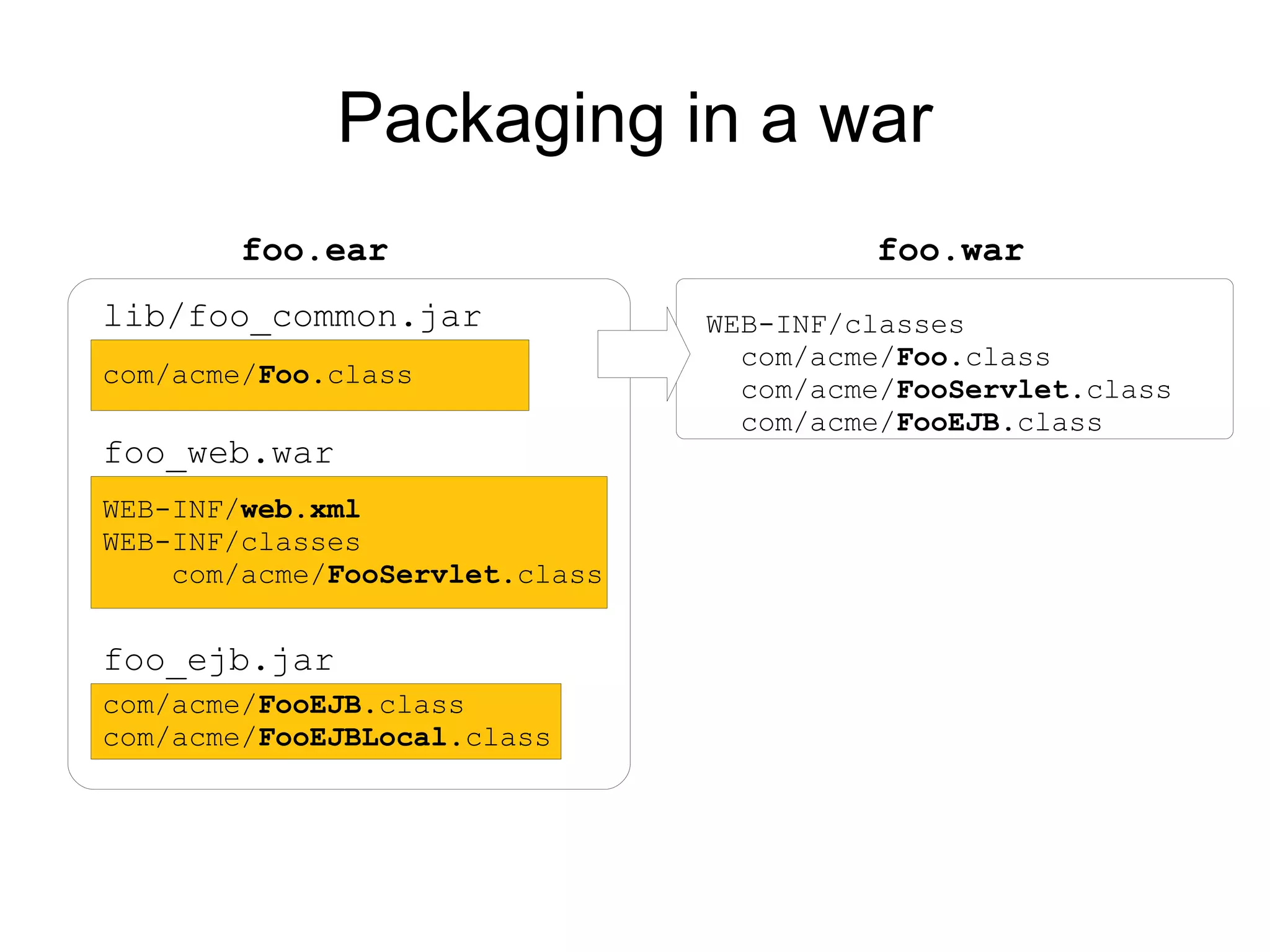
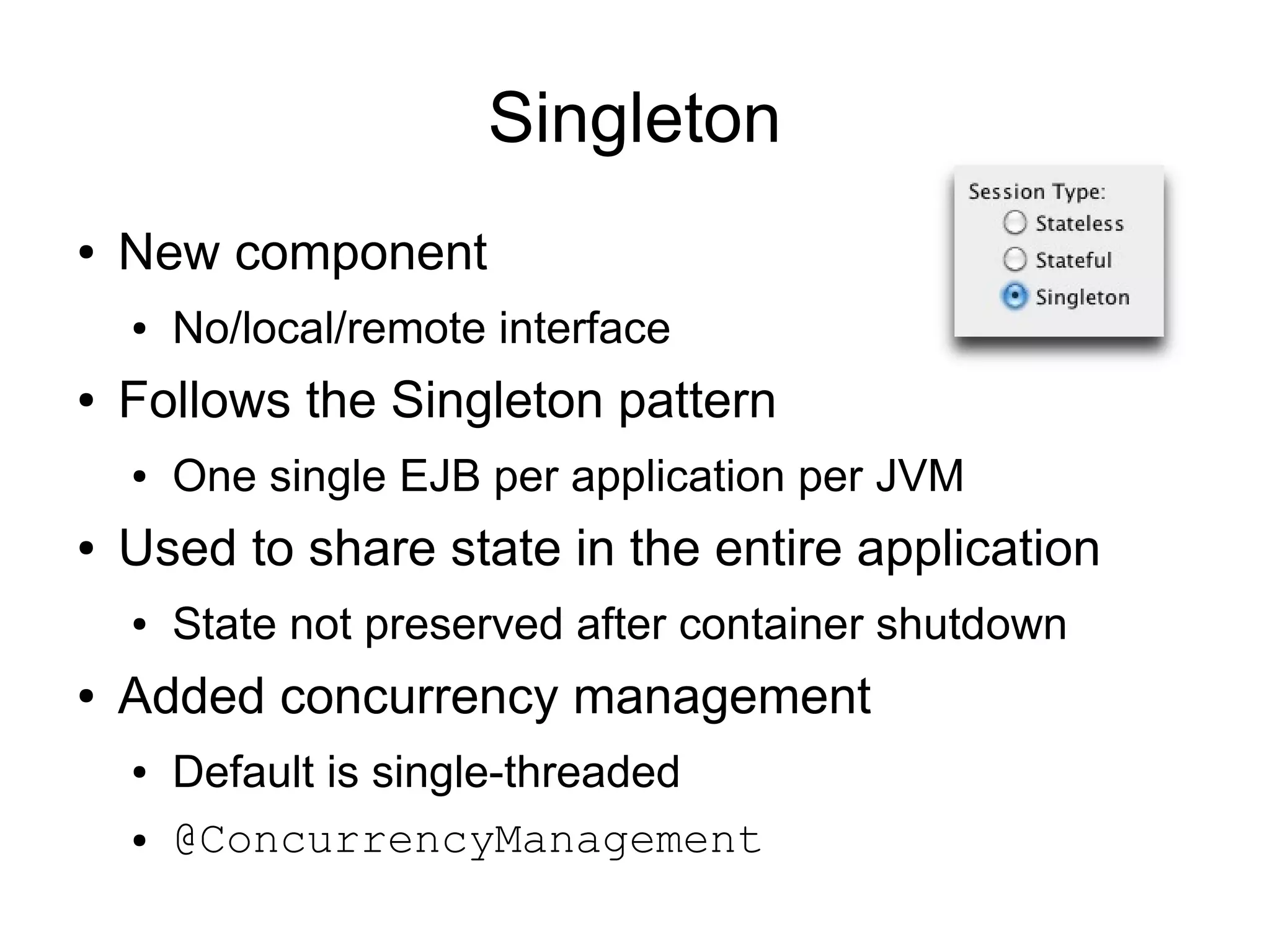
This document provides an overview of new features in Java EE 6, as presented by Antonio Goncalves. It discusses several major new concepts, including profiles, pruning of specifications, portable JNDI names, managed beans, and interceptors. It also summarizes new features for various specifications, such as JPA 2.0 adding richer mappings and criteria queries, EJB 3.1 introducing asynchronous calls and timers, Servlet 3.0 focusing on ease of development and pluggability, and JSF 2.0 making Facelets the preferred view definition language. The document aims to give attendees an understanding of the key changes and improvements in Java EE 6.



























![Timer Service
● Programmatic and Calendar based scheduling
● « Last day of the month »
● « Every five minutes on Monday and Friday »
● Cron-like syntax
● second [0..59], minute[0..59], hour[0..23]...
● dayOfMonth[1..31]
● dayOfWeek[0..7] or [sun, mon, tue..]
● Month[0..12] or [jan,feb..]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatsnewinjavaee6-100321083902-phpapp02/75/Whats-New-In-Java-Ee-6-39-2048.jpg)

![Embeddable Container
public static void main(String[] args){
EJBContainer container =
EJBContainer.createEJBContainer();
Context context = container.getContext();
Hello h = (Hello)context.lookup("Global_JNDI_Name");
h.sayHello();
container.close();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatsnewinjavaee6-100321083902-phpapp02/75/Whats-New-In-Java-Ee-6-44-2048.jpg)








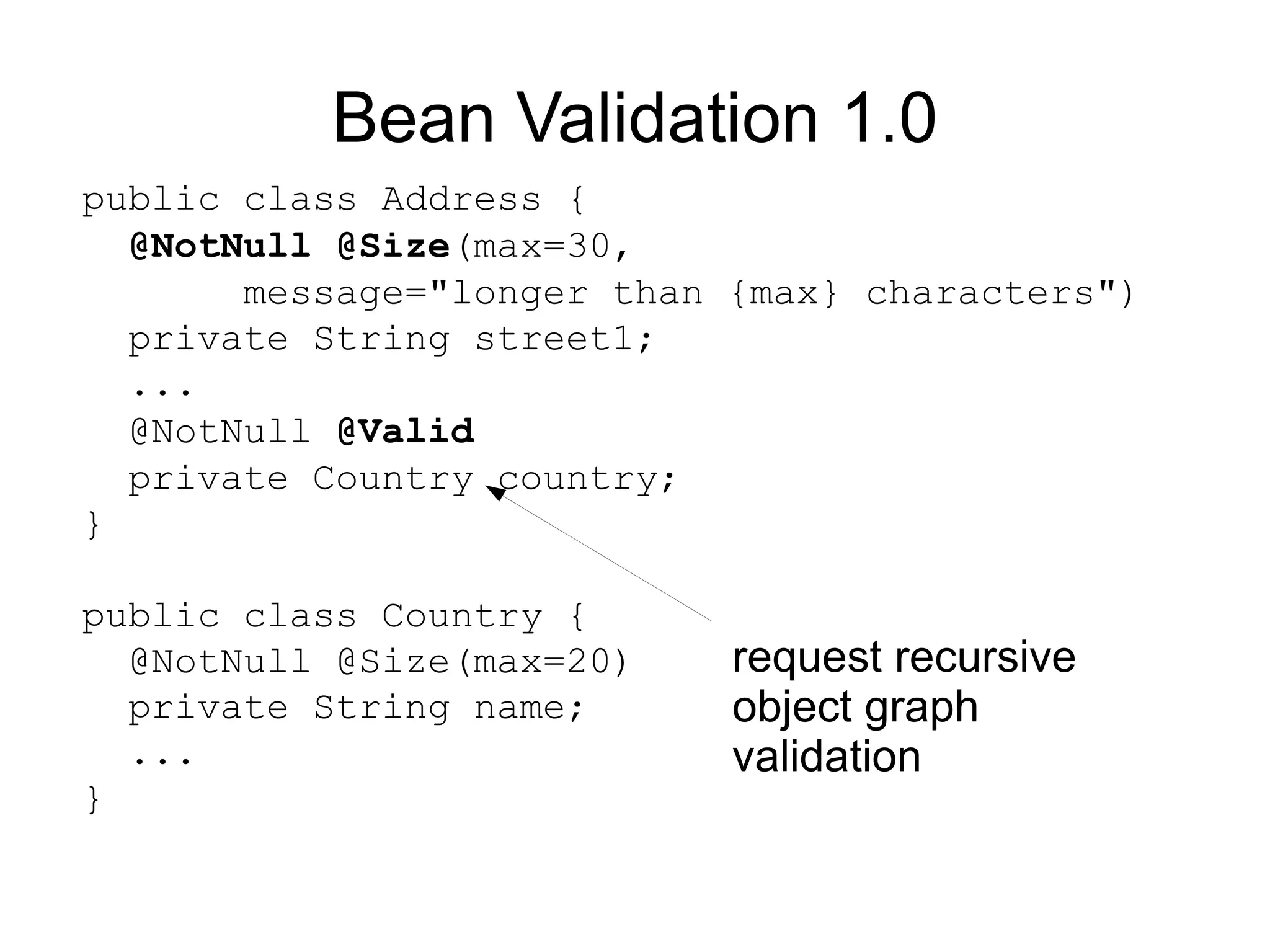
![Build your own!
@Size(min=5, max=5)
@ConstraintValidator(ZipcodeValidator.class)
@Documented
@Target({ANNOTATION_TYPE, METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface ZipCode {
String message() default "Wrong zipcode";
String[] groups() default {};
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatsnewinjavaee6-100321083902-phpapp02/75/Whats-New-In-Java-Ee-6-56-2048.jpg)



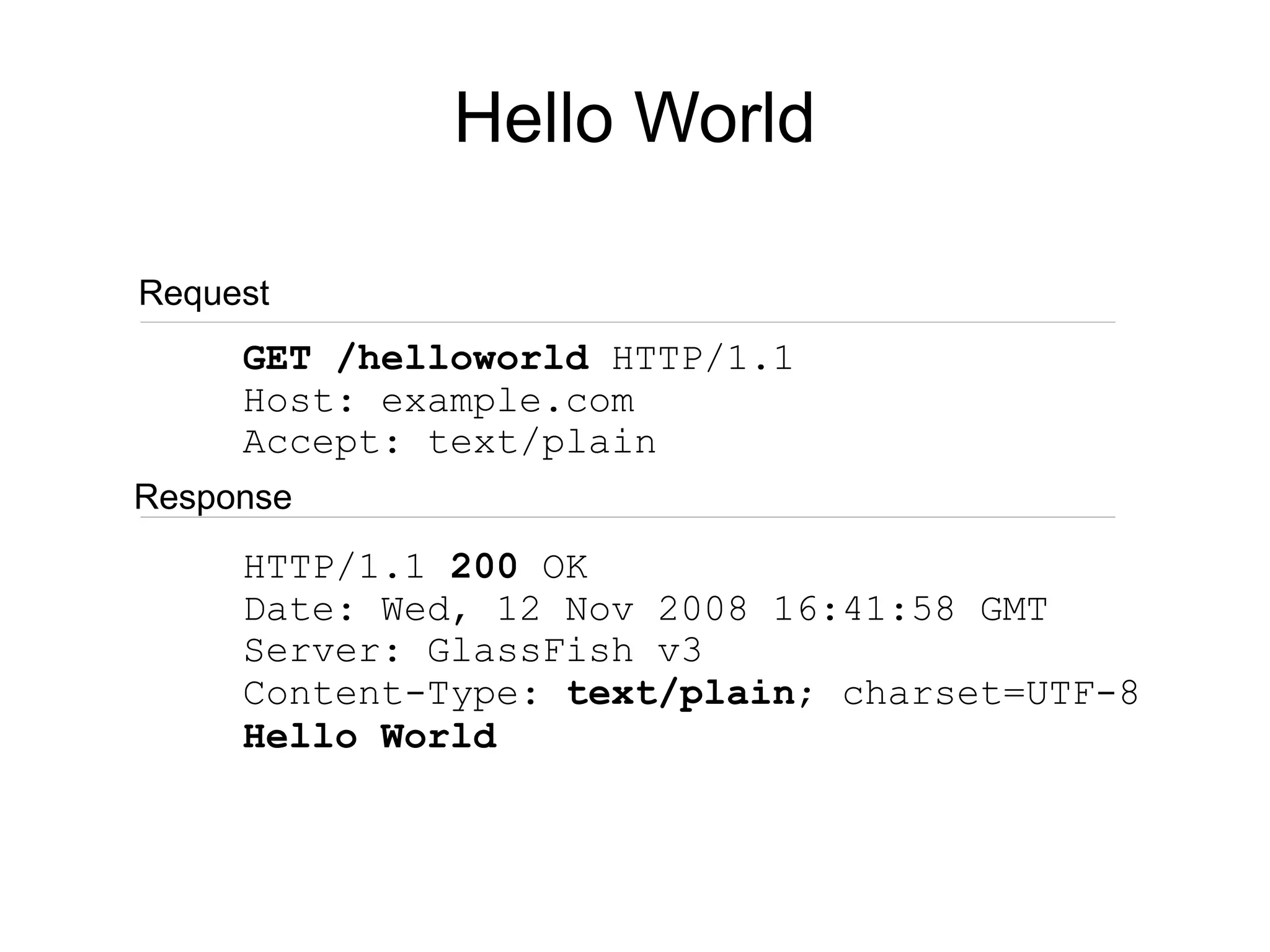
![Different Mime Types
@Path("/helloworld")
public class HelloWorldResource {
@GET @Produces("image/jpeg")
public byte[] paintHello() {
...
@GET @Produces("text/plain")
public String displayHello() {
...
@POST @Consumes("text/xml")
public void updateHello(String xml) {
...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatsnewinjavaee6-100321083902-phpapp02/75/Whats-New-In-Java-Ee-6-62-2048.jpg)