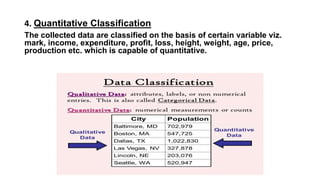
This document discusses statistics, including its definition as a branch of mathematics dealing with data collection, organization, analysis, interpretation and presentation. It then provides examples of how statistics are important in financial markets, quality testing, and election predictions. Next, it defines classification as the grouping of related facts into classes and describes four methods of classification: geographical, chronological, qualitative, and quantitative. Finally, it lists three limitations of statistics, which are that it concerns quantitative data, does not study individuals but aggregates, and requires experts to properly handle statistical data.