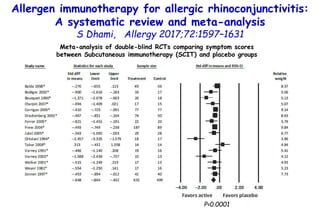
1) Several studies reviewed found that allergen immunotherapy (AIT) can improve symptoms, medication use, and quality of life for patients with allergic asthma and rhinoconjunctivitis.
2) Subcutaneous immunotherapy was more effective than sublingual immunotherapy at improving quality of life and decreasing allergen-specific airway hyperactivity for asthma.
3) The evidence suggests AIT may help prevent new allergen sensitizations, though more high-quality studies are still needed to better determine its efficacy in preventing new sensitizations.