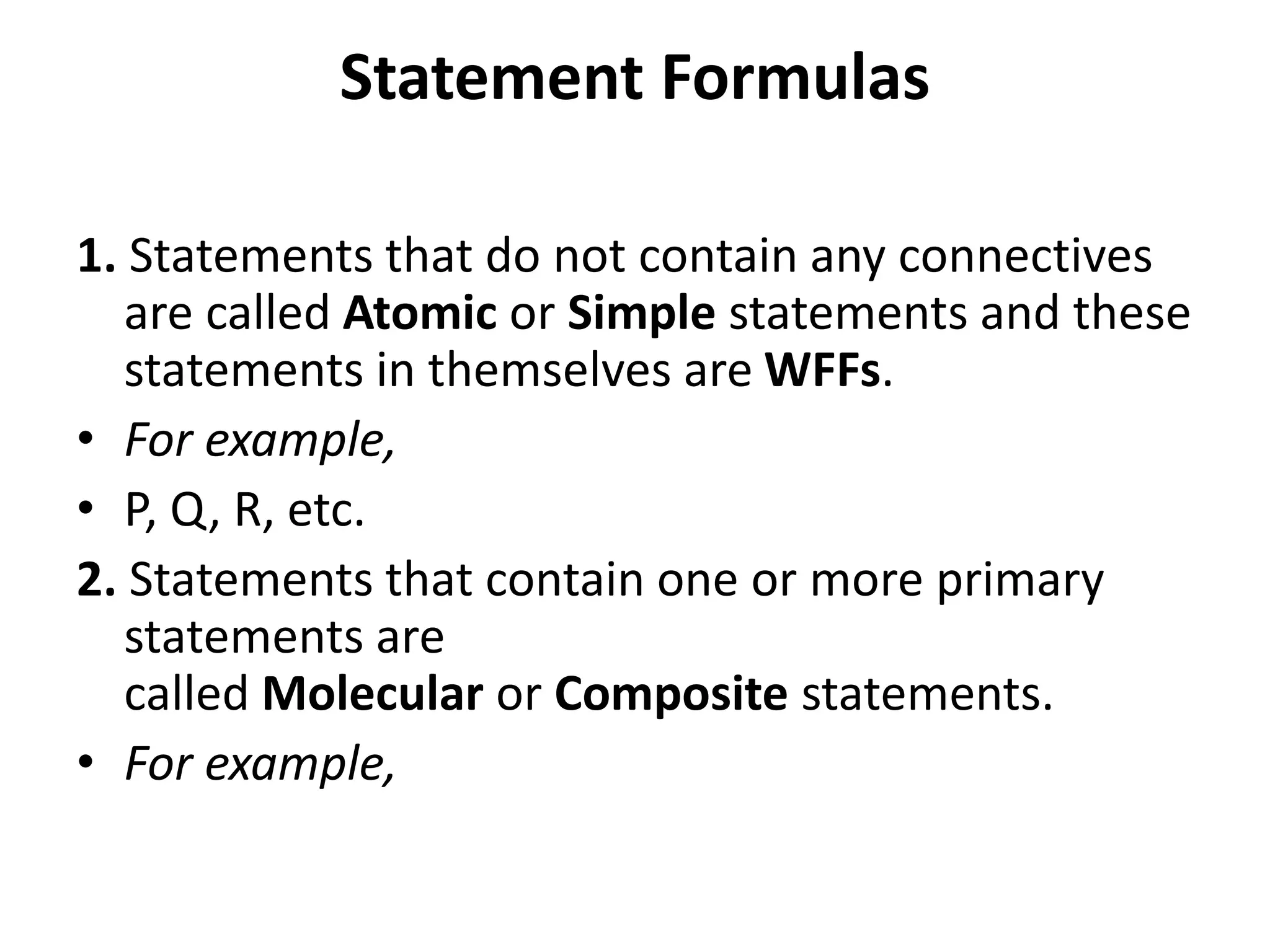
A well-formed formula (wff) is an expression made up of variables, parentheses, and connective symbols, which include negation, conjunction, disjunction, and implication. Atomic statements are simple statements without connectives, while molecular statements consist of one or more atomic statements, with specific rules that define valid wff structures. Parentheses must be used correctly in composite statements, as improper placement or ambiguity can lead to invalid formulas.