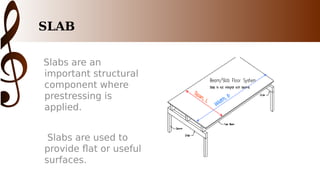
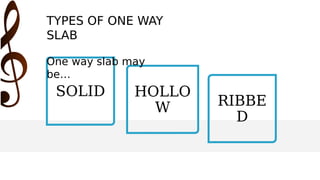
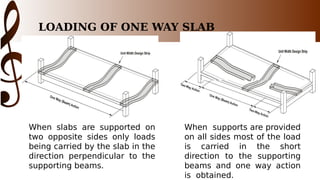
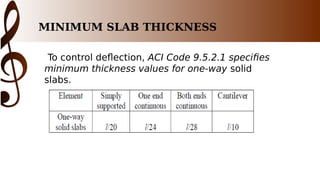
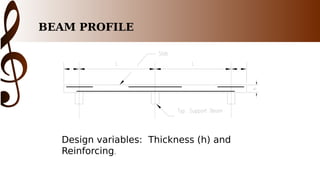
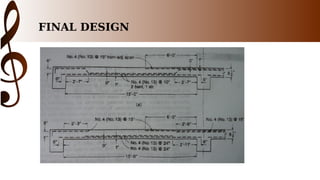
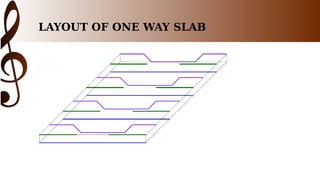
The document provides an overview of one-way slab design. It defines one-way slabs as having an aspect ratio of 2:1 or greater, with bending primarily in one direction. Types of one-way slabs include solid, hollow, and ribbed slabs. The document discusses applications of the L/B ratio, loading conditions, analysis approach by considering strips as beams, and ACI code specifications for one-way slab design including minimum thickness, reinforcement ratios, and an example problem solution.