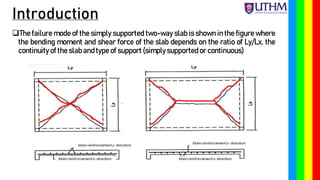
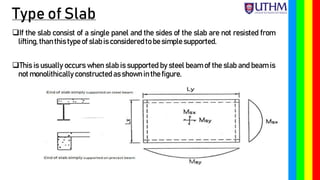
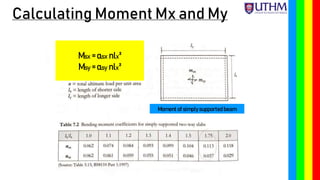
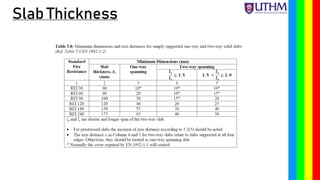
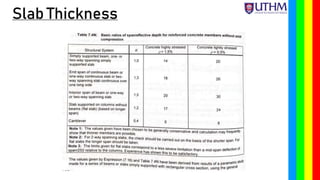
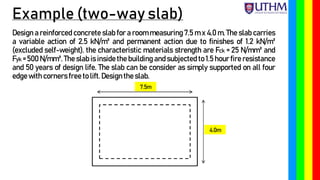
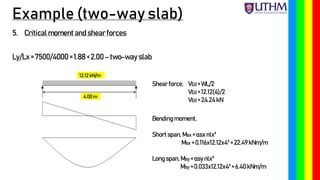
Chapter 6 discusses the design principles of two-way reinforced concrete slabs, focusing on their reinforcement in both directions when supported on all four edges. An example is provided for designing a slab with specific measurements and loads, including calculations for moment, shear force, and reinforcement requirements. Key factors such as minimum thickness, durability, and fire resistance are also considered in the design process.