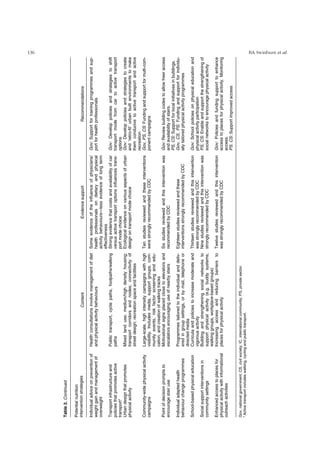
This review paper examines evidence on dietary and other factors that influence weight gain and obesity at the population level. It finds convincing evidence that regular physical activity and high fiber intake protect against obesity, while sedentary lifestyles and consumption of calorie-dense, nutrient-poor foods increase obesity risk. It recommends a range of strategies to address obesity, including making healthy foods more available, limiting marketing of unhealthy foods to children, promoting active transportation, and improving health services and messaging around nutrition and physical activity. Comprehensive programs are needed to reverse obesity epidemic trends affecting both rich and poor countries.