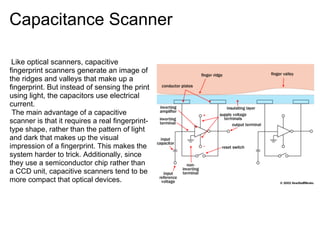
Fingerprint scanners work by obtaining an image of a fingerprint and analyzing the unique pattern of ridges and valleys. There are two main types of scanners - optical scanners use cameras to take a picture of the print, while capacitive scanners use electrical current to sense the print's shape. The scanner software then analyzes features called minutiae (ridge endings and bifurcations) to match fingerprints by measuring the relative positions of multiple minutiae. Fingerprint analysis is useful for security and identification because each print is unique, cannot be forgotten or easily stolen like passwords, and is very difficult to forge.