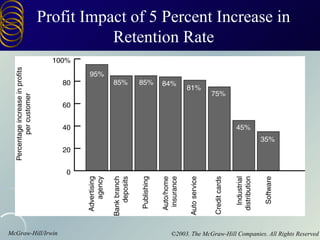
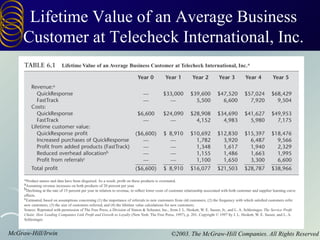
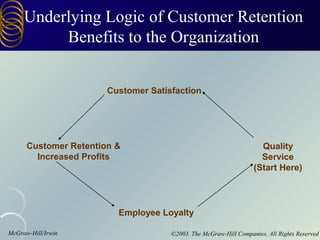
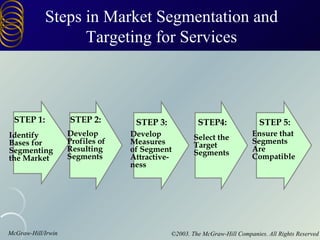
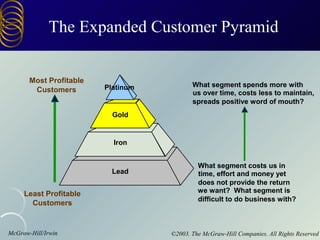
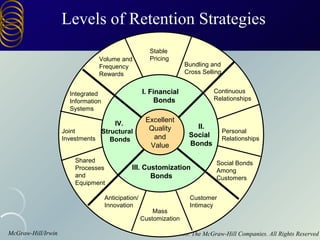
The document discusses building customer relationships through relationship marketing. It emphasizes retaining current customers rather than acquiring new ones since retaining customers is typically cheaper. It discusses segmenting customers into tiers based on profitability and focusing on the most profitable segments. Building strong customer relationships involves developing different types of bonds with customers like financial, social, structural, and customization bonds along with providing excellent quality and value.