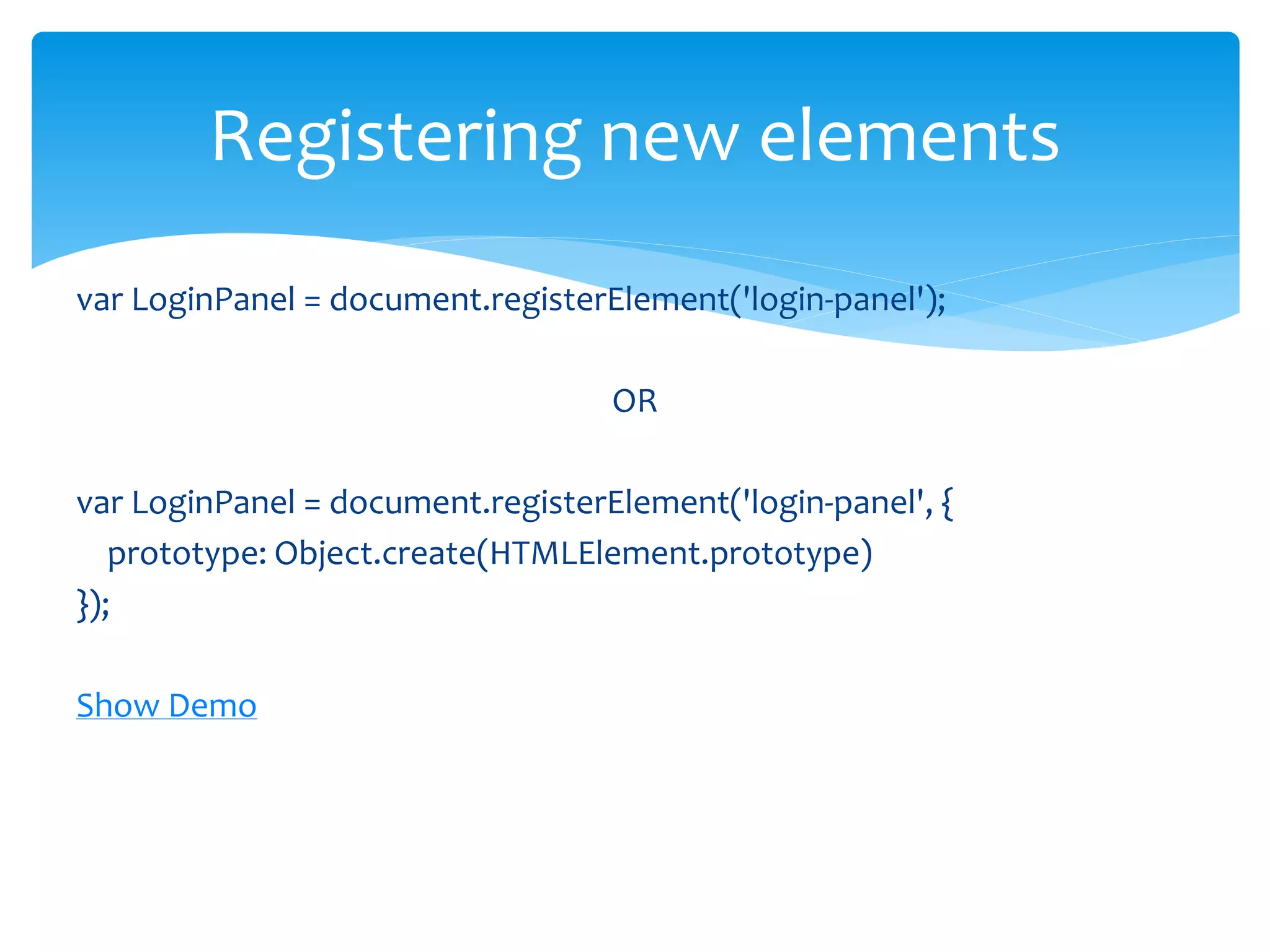
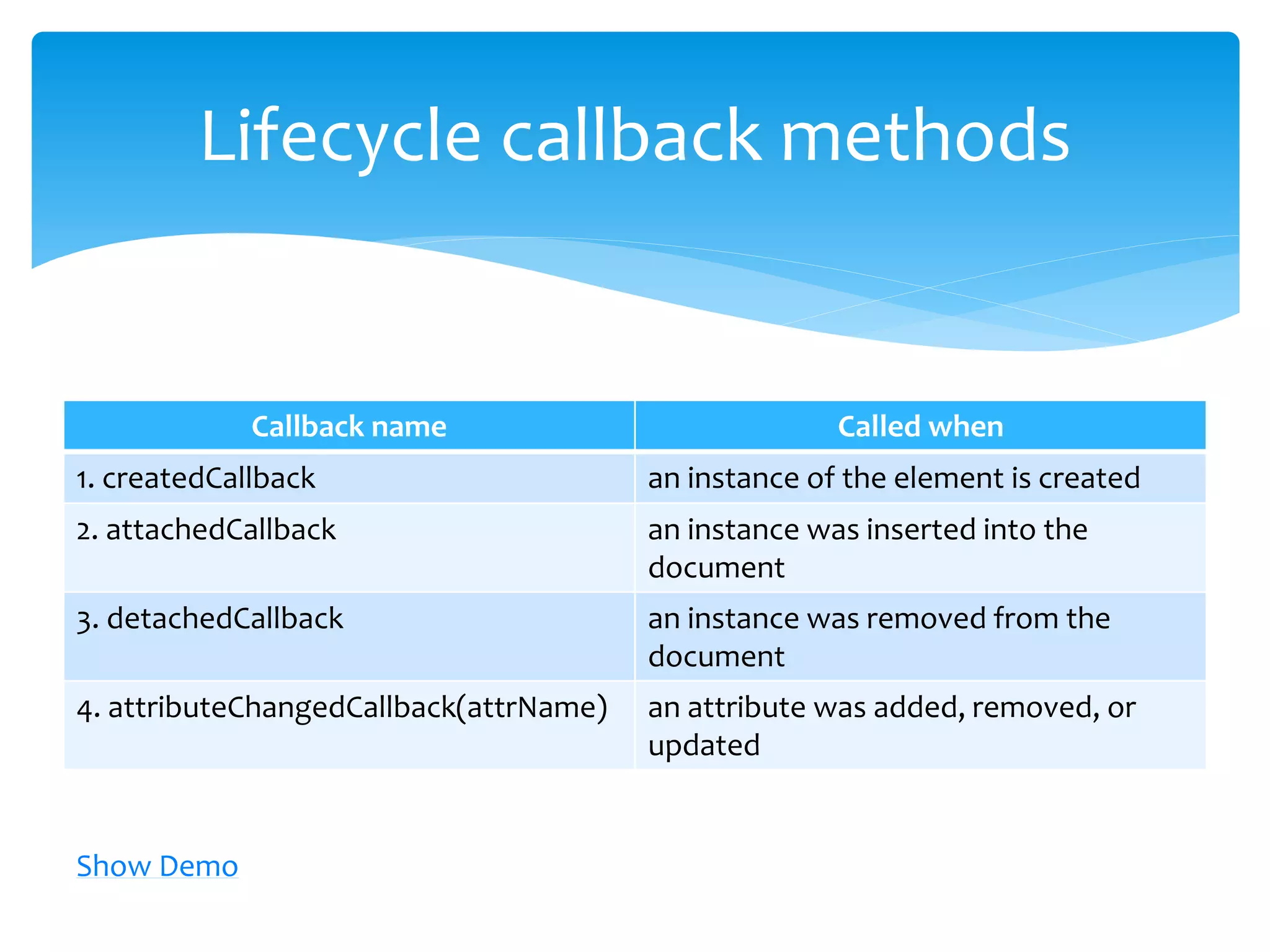
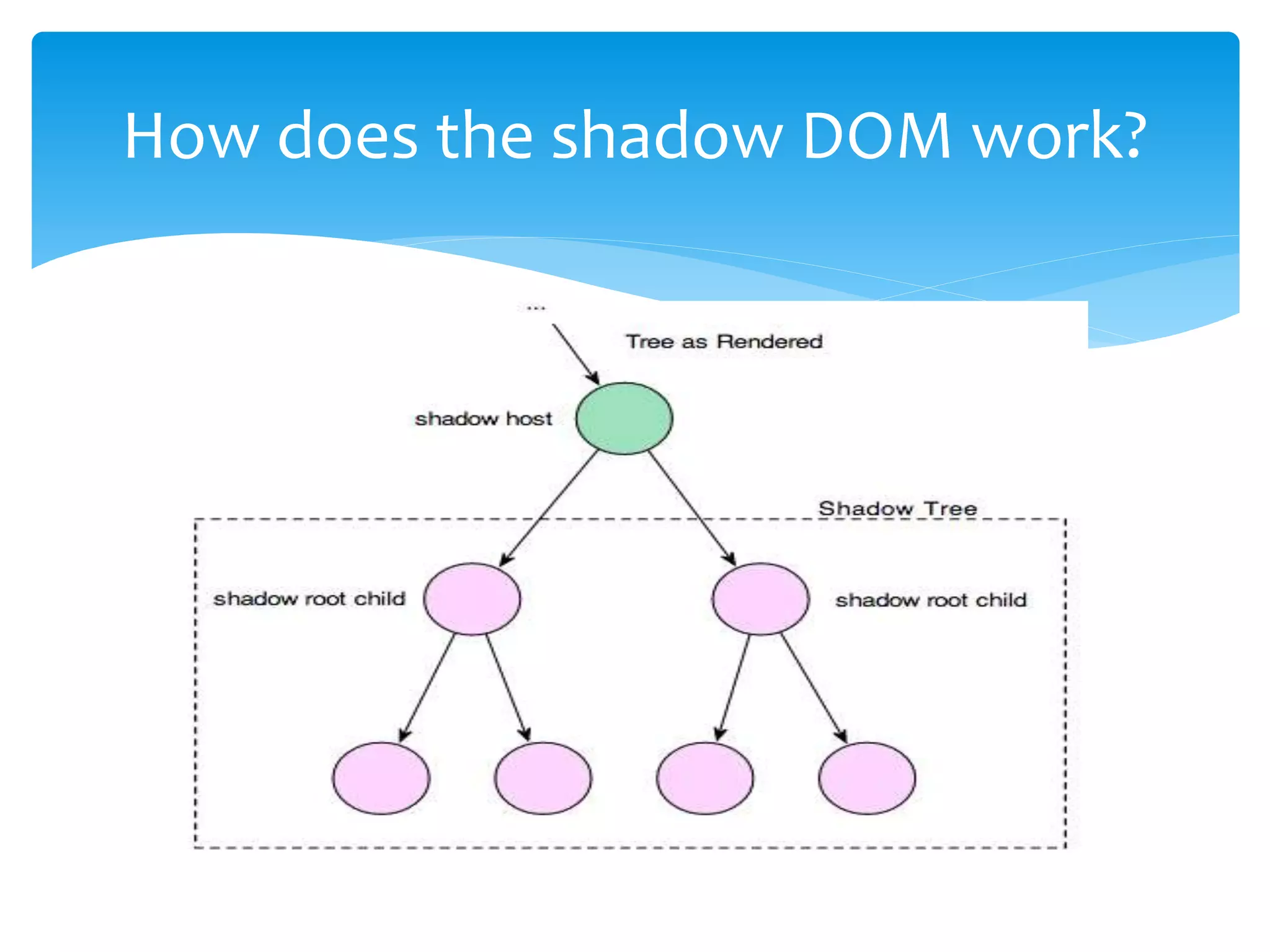
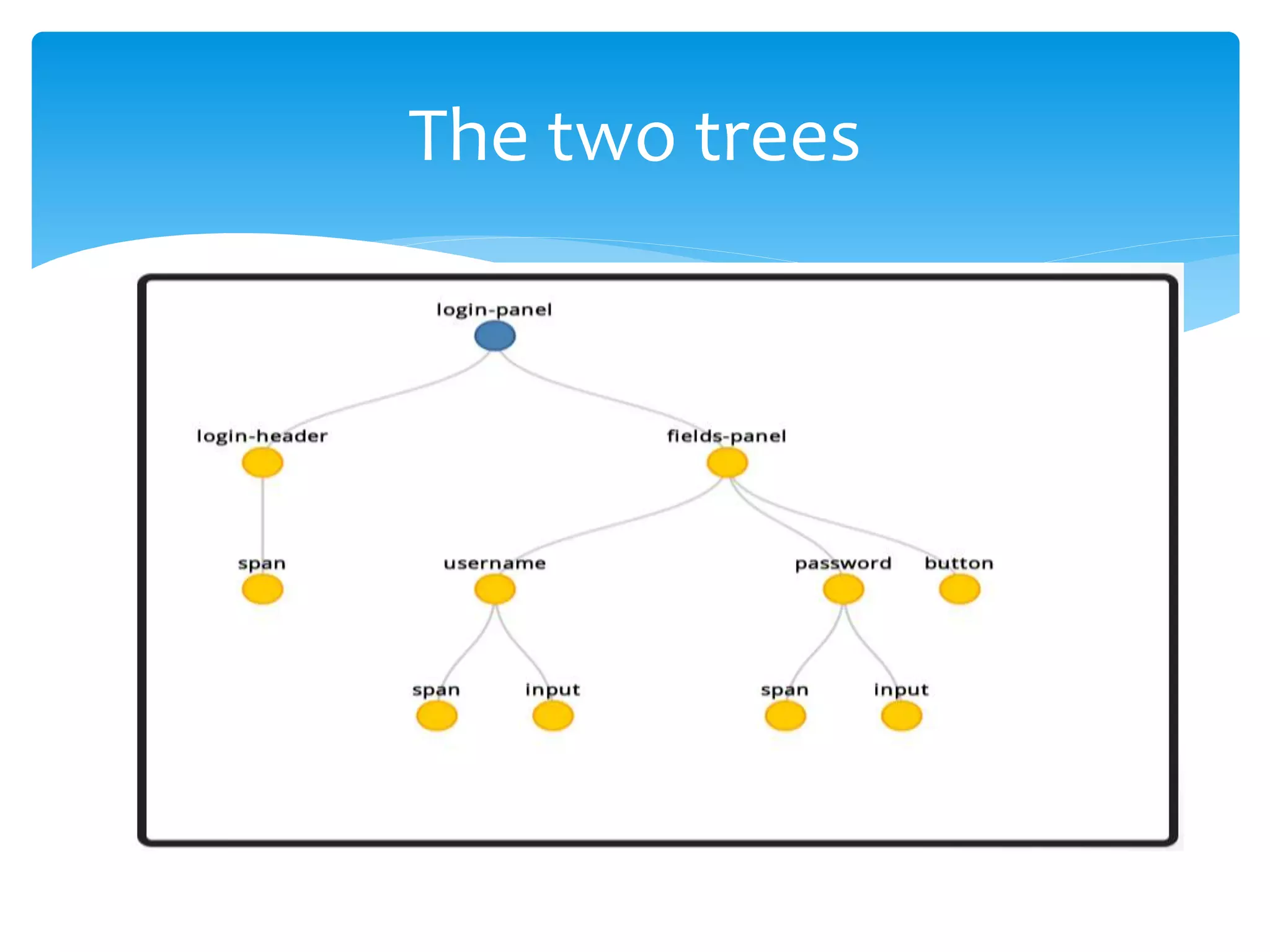
Web Components are a new set of web platform features that enable developers to build applications in a declarative, composable way. Shadow DOM is an emerging web standard that gives developers access to style and DOM scoping. It establishes a boundary between the host element and the rest of the DOM tree. Some key features of web components are custom elements, shadow DOM, templates, and HTML imports. Shadow DOM provides encapsulation by creating a boundary between the host element and the rest of the DOM tree. It has its own DOM tree that is attached to the host element.