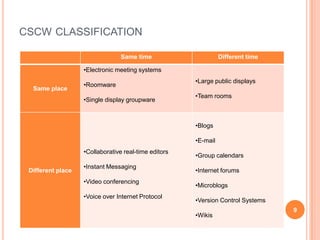
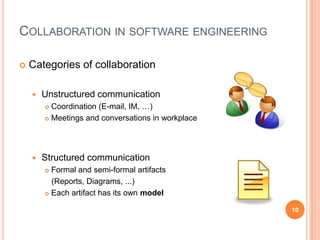
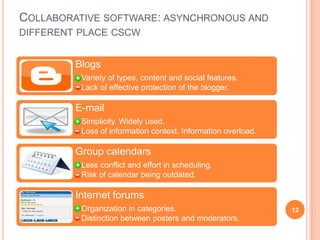
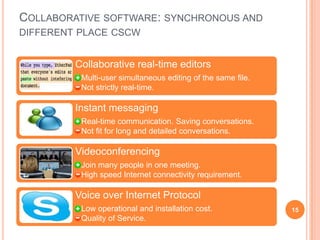
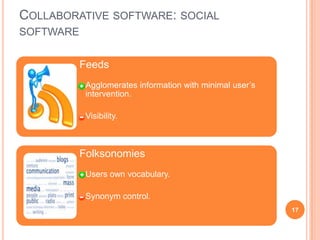
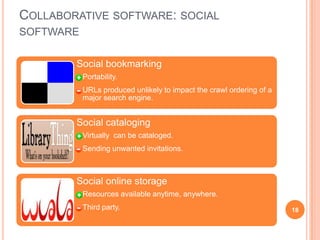
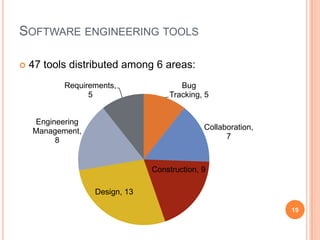
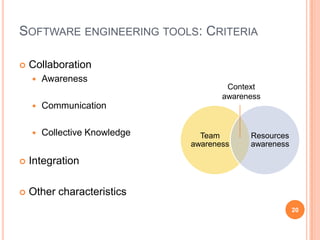
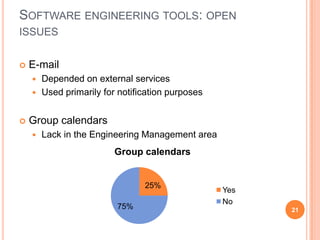
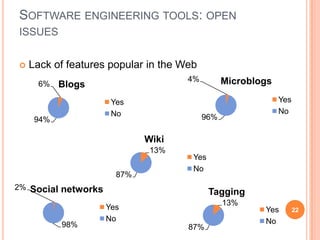
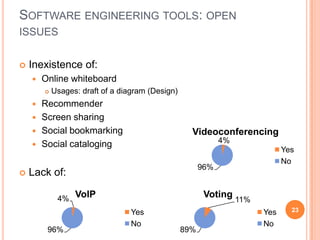
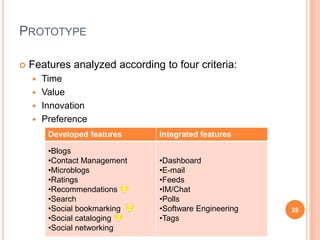
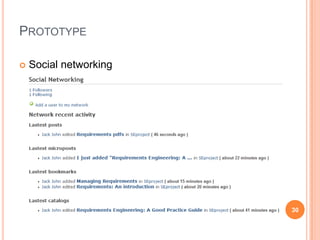
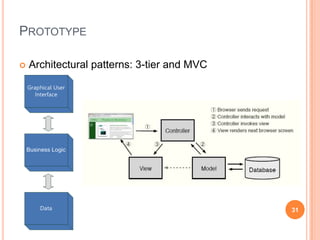
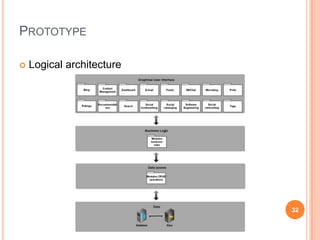
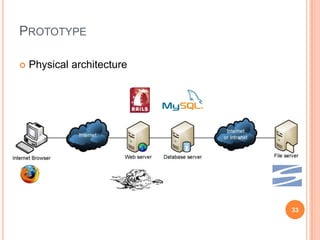
The document discusses the importance of collaboration in software engineering, outlining various collaborative software tools and their integration into project management processes. It identifies gaps in existing web-based tools and proposes a prototype that enhances collaboration features throughout a project's life cycle. Additionally, it highlights the necessity for further research to assess the effectiveness of these tools and address unresolved issues in the field.