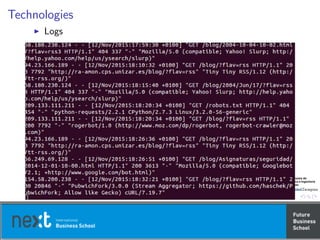
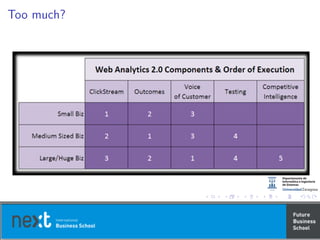
This document discusses web analytics and analytical techniques. It begins with some definitions of key terms related to web analytics, such as pageviews, visits, unique visitors, referrers, and conversions. It then covers topics like qualitative user research methods, testing and experimentation, and analyzing social, mobile, and video data. The document provides examples of metrics for blogs, Twitter, and video analytics. It emphasizes testing hypotheses and measuring multiple outcomes to drive continual improvement of the online experience.


















![Some definitions
[Page]
A page is an analyst definable unit of content.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-27-320.jpg)
![Some definitions
[Page]
A page is an analyst definable unit of content.
Flash, AJAX, media files, downloads, documents, and PDFs?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-28-320.jpg)
![Some definitions
[Pageviews]
The number of times a page (an analyst-definable unit of
content) was viewed.
Vendors do make different distinctions in deciding what should be
counted. Consult your tool provider for more information on your
implementation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-29-320.jpg)
![Some definitions
[Visit/Sessions]
A visit is an interaction, by an individual, with a website
consisting of one or more requests for an
analyst-definable unit of content (i.e. “page view”). If an
individual has not taken another action (typically
additional page views) on the site within a specified time
period, the visit session will terminate.
Visit → Several pageviews
Representation of the interaction of the visitor with the site](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-30-320.jpg)
![Some definitions
[Unique Visitors]
The number of inferred individual people (filtered for
spiders and robots), within a designated reporting
timeframe, with activity consisting of one or more visits
to a site. Each individual is counted only once in the
unique visitor measure for the reporting period.
Authentication, either active or passive, is the most accurate way
to track unique visitors.
Their activity will be over-represented unless they are
de-duplicated.
Blocked cookies!
Related → New Visitor, Repeat Visitor (reporting period),
Return Visitor (previous periods)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-31-320.jpg)

![Some definitions
[Entry Page]
The first page of a visit.
First page in the visit regardless of how the sessions are calculated](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-33-320.jpg)
![Some definitions
[Landing Page]
A page intended to identify the beginning of the user
experience resulting from a defined marketing effort.
Landing pages are often optimized for specific keywords, audiences,
or calls to action](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-34-320.jpg)
![Some definitions
[Exit Page]
The last page on a site accessed during a visit, signifying
the end of a visit/session.
In a tabbed or multi-window browser environment it should still be
the final page accessed that is recorded as the Exit Page though it
cannot be definitively known that this was the last page the visitor
viewed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-35-320.jpg)
![Some definitions
[Visit Duration]
The length of time in a session. Calculation is typically
the timestamp of the last activity in the session minus
the timestamp of the first activity of the session.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-36-320.jpg)
![Some definitions
[Referrer]
The referrer is the page URL that originally generated the
request for the current page view or object.
Internal Referrer
External Referrer
Search Referrer
Visit Referrer (session)
Original Referrer (all visits)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-37-320.jpg)
![Some definitions
[Click-through]
Number of times a link was clicked by a visitor.
Click-throughs are typically associated with advertising activities,
whether external or internal to the site. Note that click-throughs
measured on the sending side (as reported by your ad server, for
example) and on the receiving side (as reported by your web
analytics tool) often do not match.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-38-320.jpg)
![Some definitions
[Click-through Rate/Ratio]
The number of click-throughs for a specific link divided
by the number of times that link was viewed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-39-320.jpg)
![Some definitions
[Page Views per Visit]
The number of page views in a reporting period divided
by number of visits in the same reporting period.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-40-320.jpg)

![Some definitions
[Page Exit Ratio]
Number of exits from a page divided by total number of
page views of that page.
Page exit ratio should not be confused with bounce rate, which is
an indicator of single-page-view visits on your site. Page exit ratio
applies to all visits regardless of length.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-42-320.jpg)
![Some definitions
[Single-Page Visits]
Visits that consist of one page regardless of the number
of times the page was viewed.
For a single-page visit, the entry page and exit page are the same
page.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-43-320.jpg)
![Some definitions
[Single Page View Visits (Bounces)]
Visits that consist of one page-view.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-44-320.jpg)
![Some definitions
[Bounce Rate]
Single page view visits divided by entry pages.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-45-320.jpg)

![Some definitions
[Event]
Any logged or recorded action that has a specific date
and time assigned to it by either the browser or server.
An example is counting page views per day. The event count gives
the total number of page views loaded during the day, visit count
is the number of visits (that downloaded at least one page view)
during the day, and the visitor count gives the number of unique
visitors (that downloaded at least one page view) that visited the
site during the day.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-47-320.jpg)
![Some definitions
[Conversion]
A visitor completing a target action.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webanalytics-151124115008-lva1-app6891/85/Web-analytics-48-320.jpg)