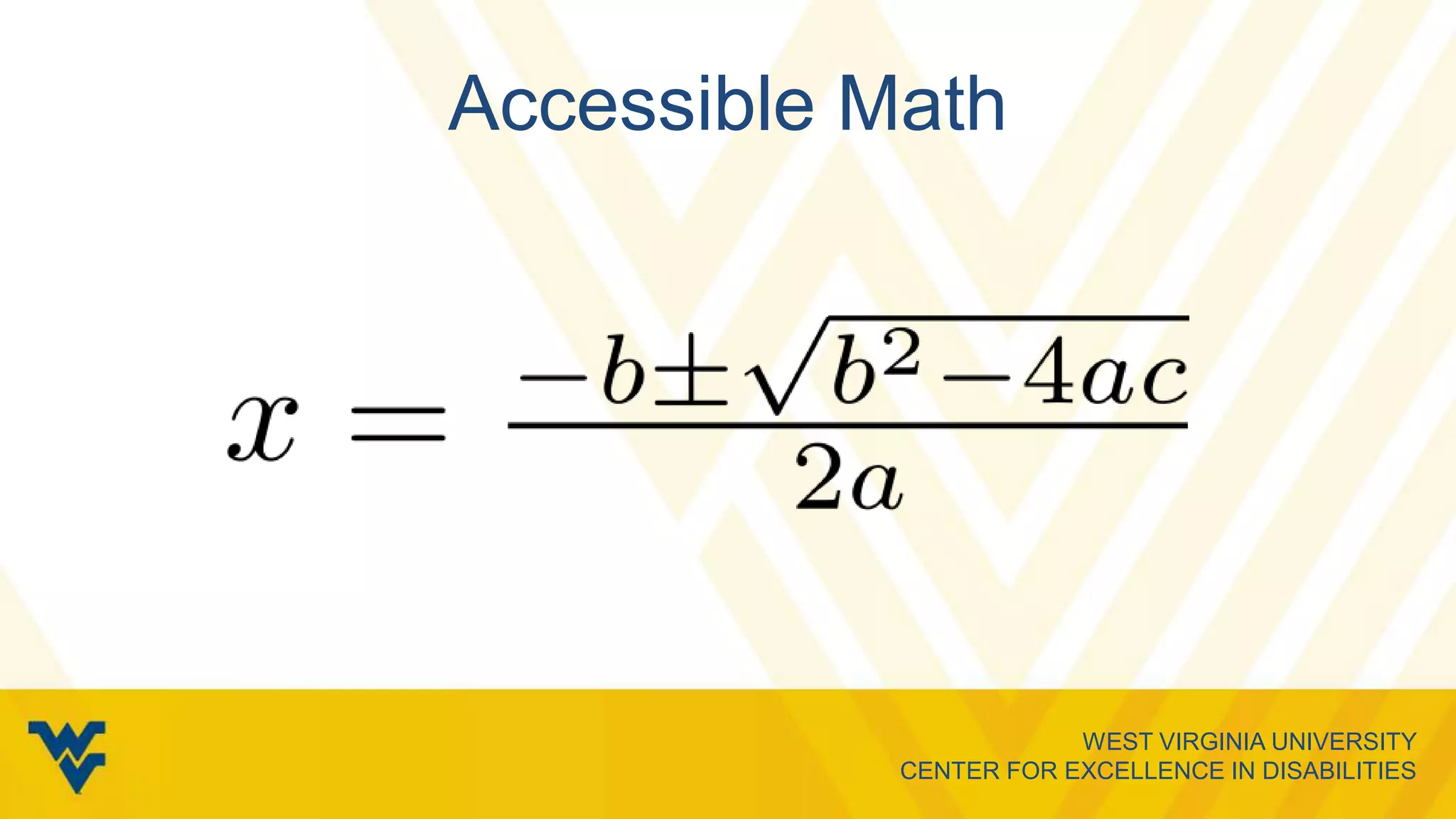This document provides an overview of web accessibility from a presentation given at West Virginia University. It defines web accessibility and why it is important, discusses considerations for various disabilities, and provides tools and resources for creating accessible content. The speaker aims to increase awareness of standards and best practices for developing websites that are usable by all people, including those with disabilities.