The document discusses CFO M&A strategies and experiences, including:
- How ICF sourced deal opportunities through investment bankers and expanding contacts.
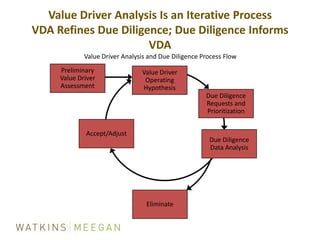
- ICF's reliance on internal due diligence of contracts/backlog and external experts for accounting/legal/HR reviews.
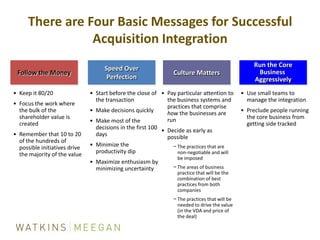
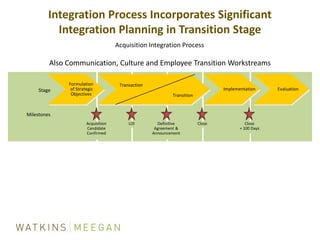
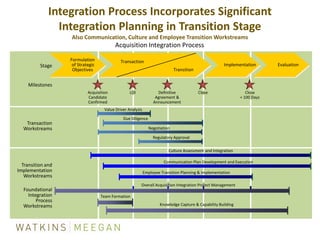
- ICF's M&A process of due diligence, negotiating deals to closing, and post-closing integration.
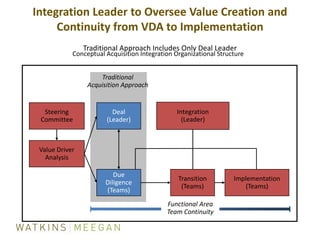
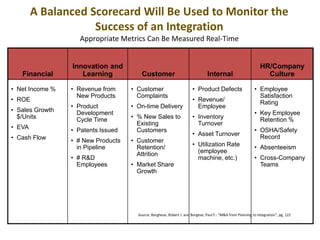
- Key aspects of ICF's integration process including identifying teams, addressing culture/communication, and focusing on value drivers.