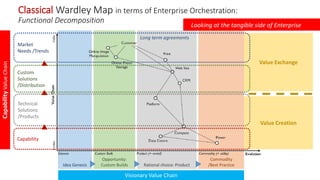
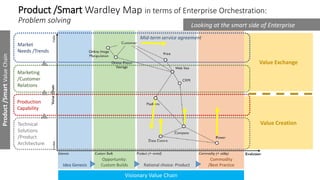
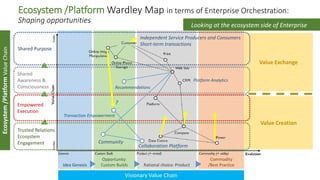
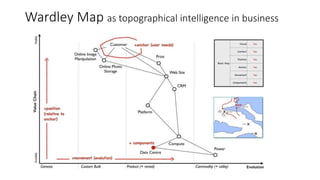
The document explains Wardley mapping as a strategic tool that can enhance enterprise orchestration by focusing on purpose, landscape, climate, doctrine, and leadership. It highlights the importance of understanding the environment and competitive landscape while applying strategic thinking through various engagement principles. Additionally, it discusses value creation and exchange through different business models, including pipelines and platforms.

![What is a map?
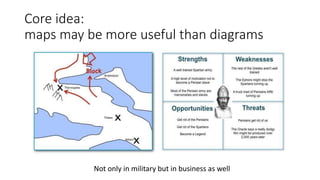
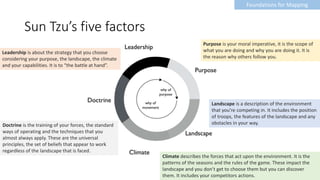
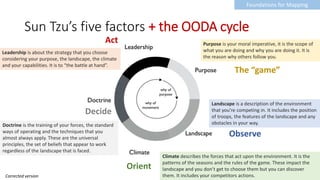
Landscape:
The image of
the environment
Climate:
The forces that impact
the landscape;
you don’t get to choose them
but you can discover them.
Purpose:
The scope +
your aspiration
[Your] Doctrine:
the training of your forces,
the standard ways
of operating and
the techniques that you
almost always apply.
Options you choose from.
[Your] Leadership:
Your choices and
applying your capabilities
to get them implemented
The map
The scope of the map
and its type
The arrows on the map
Your arrows on the map
Five Elements
Context =
Purpose
+ Your World
[Landscape
+ Climate]
+ You
[Your Doctrine
+ Your Capability]Your Intelligence](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wardleymapping-200925082516/85/Wardley-mapping-6-320.jpg)

![Basic Palette of Strategy Types and Org layers
Classical Top-Down Smart Solutions Ecosystem and Platform
Participants
BOSS-DRIVEN performers /
REQUIREMENT-DRIVEN customer
EXPERIENCE-DRIVEN experts /
PROBLEM-DRIVEN customer
INDEPENDENT PARTICIPANTS:
Producers and Consumers
Engagement
principles
PROCESS and instructions,
Long-term, Hierarchy, STABLE
Research and ARCHITECTURE,
Mid-term, Service, VARIABLE
Platform MATCHING,
Short-term, Platform, ADAPTIVE
Engagement
criteria
Skills fit job position,
Job ASSIGNMENT
Expert status is confirmed,
INVOLVEMENT into service pool
ENGAGEMENT, if ecosystem curation
principles fit personal preferences
Goal /Value type
Tangible RESULT,
Up-to-date skills & capabilities
Problem SOLVING,
Proven knowledge & expertise
New OPPORTUNITY,
Successful value exchange
Motivation
Follow technology processes and
best practices, master SKILLS
Invent, validate and implement
solutions, enrich EXPERTISE
QUICK WIN WITH NEW
OPPORTUNITY
Success definition
The work process is completed
(OUTPUT)
The Solution has resolved initial
problem (OUTCOME)
The interaction is initiated and
closed with ACHIEVING PURPOSE
Lifecycle principle
Time to RESULTS ACCEPTANCE
OODA cycle
(Observe<-Orient<-Decide <-Act)
Time from Goal to MARKET
Design Thinking ([Empathize]->
Define->Ideate->Prototype->Learn)
Time from Goal to LEARN
Adaptive Thinking (Shared Purpose->
Trusted Partners-> Quick Wins-> Learn &Adapt)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wardleymapping-200925082516/85/Wardley-mapping-9-320.jpg)
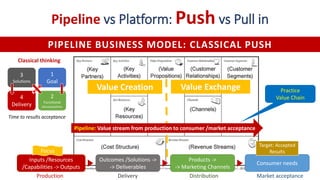
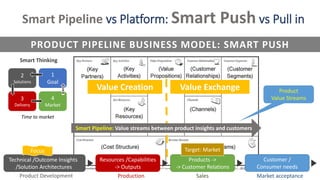
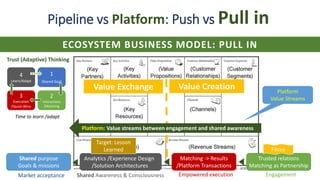
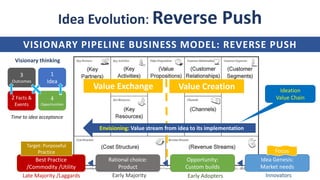
![Basic Palette of Strategy Types and Org layers
Classical Top-Down Smart Solutions Ecosystem and Platform
Participants
BOSS-DRIVEN performers /
REQUIREMENT-DRIVEN customer
EXPERIENCE-DRIVEN experts /
PROBLEM-DRIVEN customer
INDEPENDENT PARTICIPANTS:
Producers and Consumers
Engagement
principles
PROCESS and instructions,
Long-term, Hierarchy, STABLE
Research and ARCHITECTURE,
Mid-term, Service, VARIABLE
Platform MATCHING,
Short-term, Platform, ADAPTIVE
Engagement
criteria
Skills fit job position,
Job ASSIGNMENT
Expert status is confirmed,
INVOLVEMENT into service pool
ENGAGEMENT, if ecosystem curation
principles fit personal preferences
Goal /Value type
Tangible RESULT,
Up-to-date skills & capabilities
Problem SOLVING,
Proven knowledge & expertise
New OPPORTUNITY,
Successful value exchange
Motivation
Follow technology processes and
best practices, master SKILLS
Invent, validate and implement
solutions, enrich EXPERTISE
QUICK WIN WITH NEW
OPPORTUNITY
Success definition
The work process is completed
(OUTPUT)
The Solution has resolved initial
problem (OUTCOME)
The interaction is initiated and
closed with ACHIEVING PURPOSE
Lifecycle principle
Time to RESULTS ACCEPTANCE
OODA cycle
(Observe<-Orient<-Decide <-Act)
Time from Goal to MARKET
Design Thinking ([Empathize]->
Define->Ideate->Prototype->Learn)
Time from Goal to LEARN
Adaptive Thinking (Shared Purpose->
Trusted Partners-> Quick Wins-> Learn &Adapt)
OODA cycle is important,
but it’s just one of some
that are important](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wardleymapping-200925082516/85/Wardley-mapping-17-320.jpg)