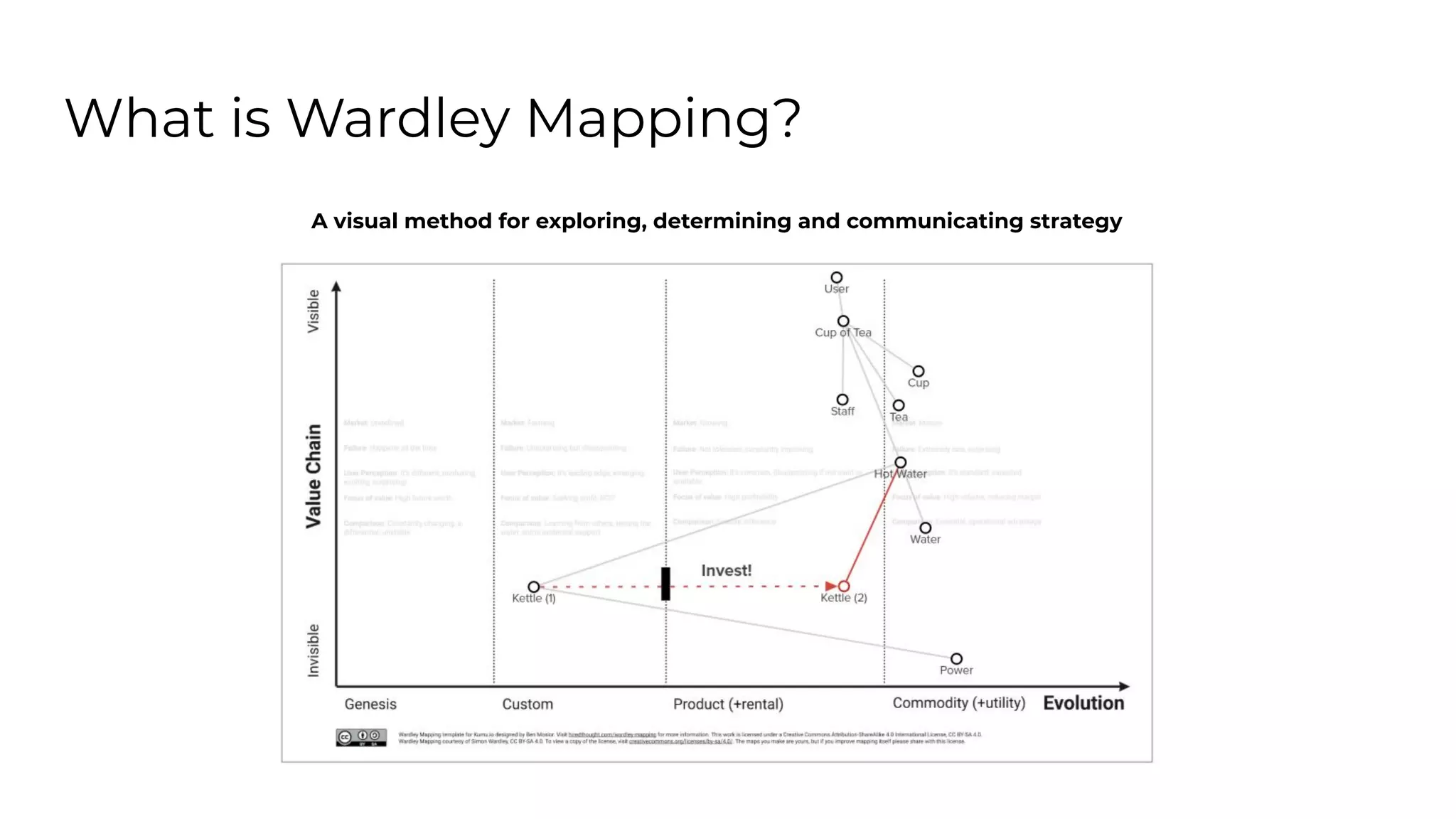
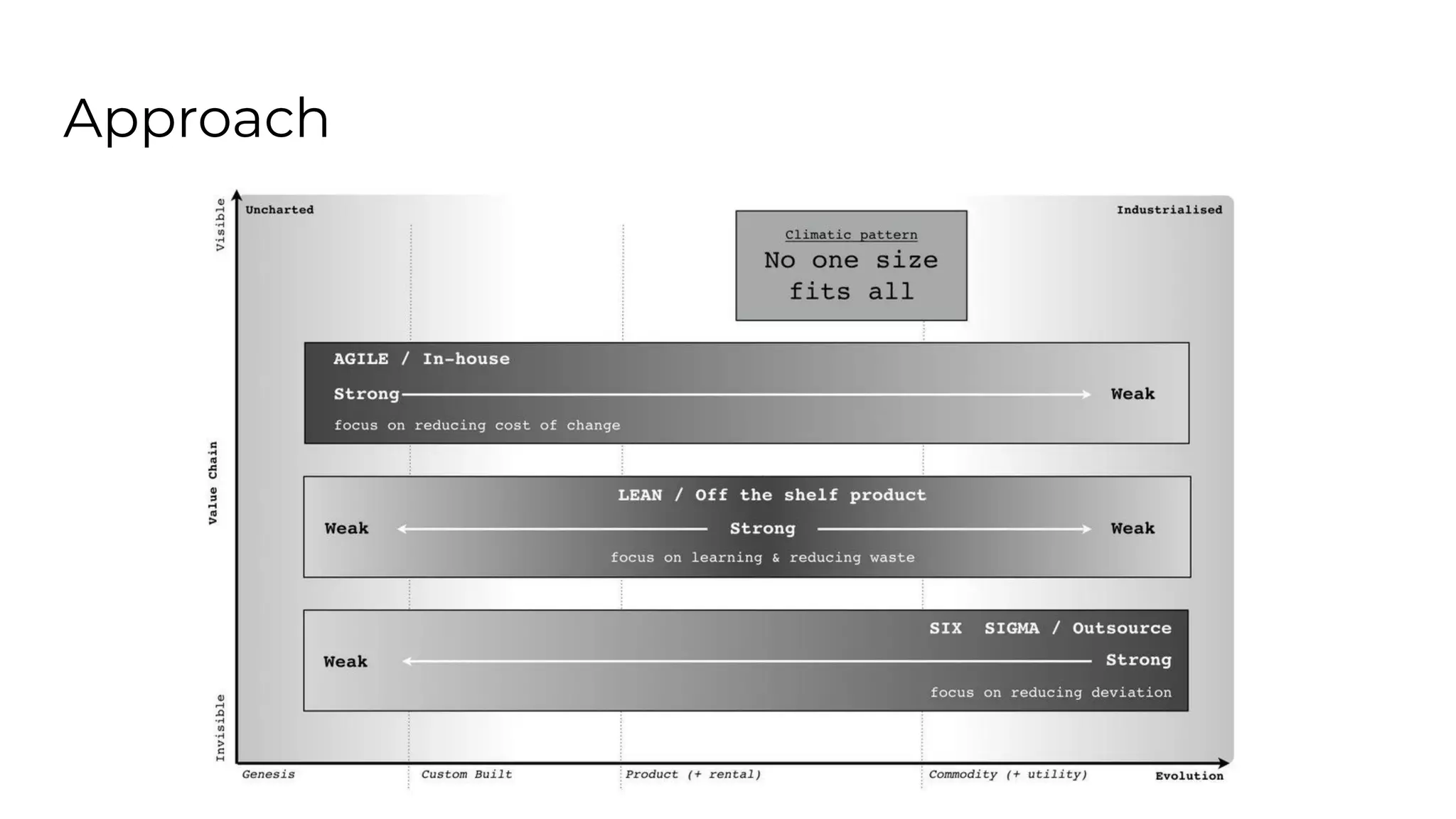
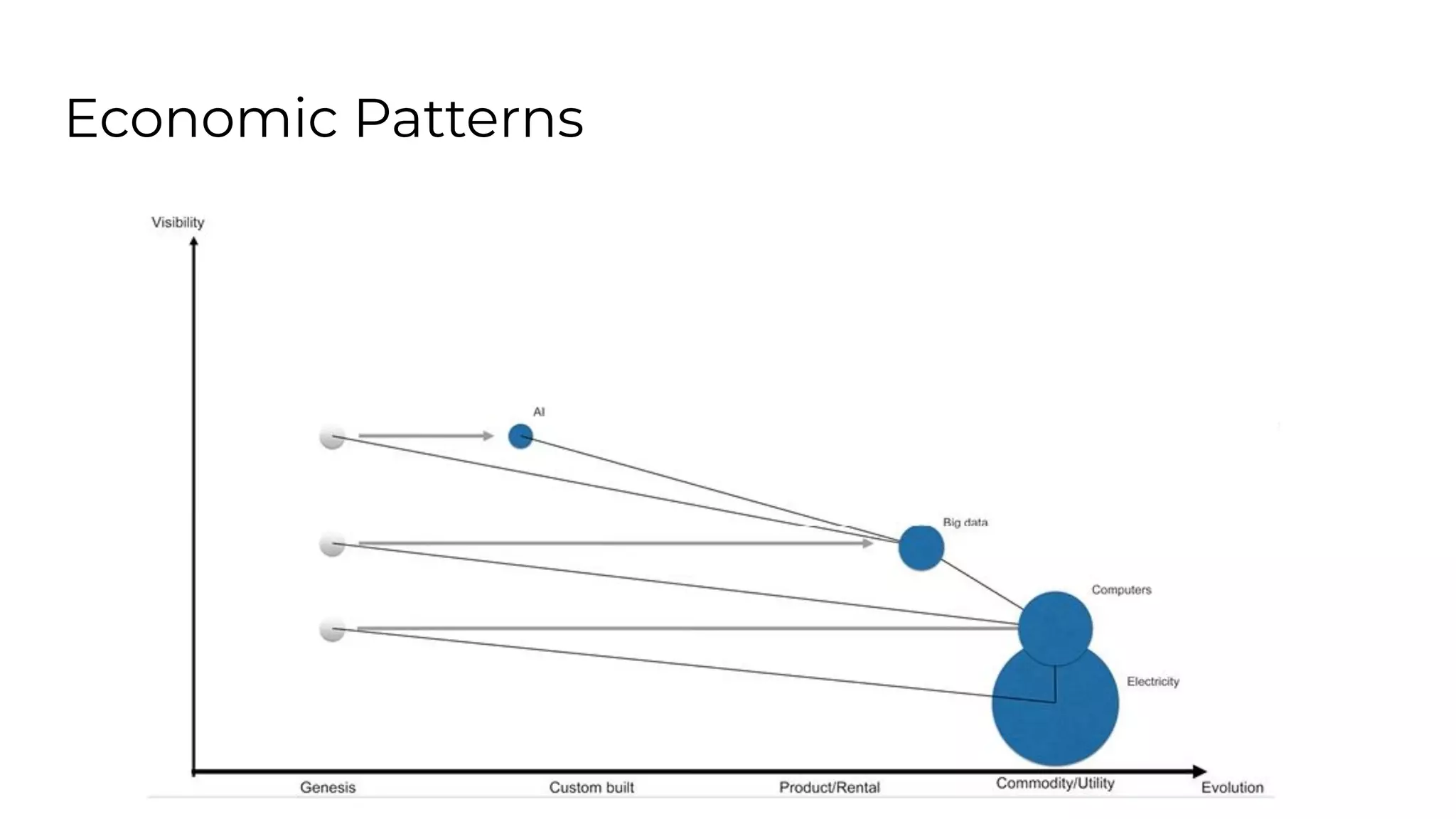
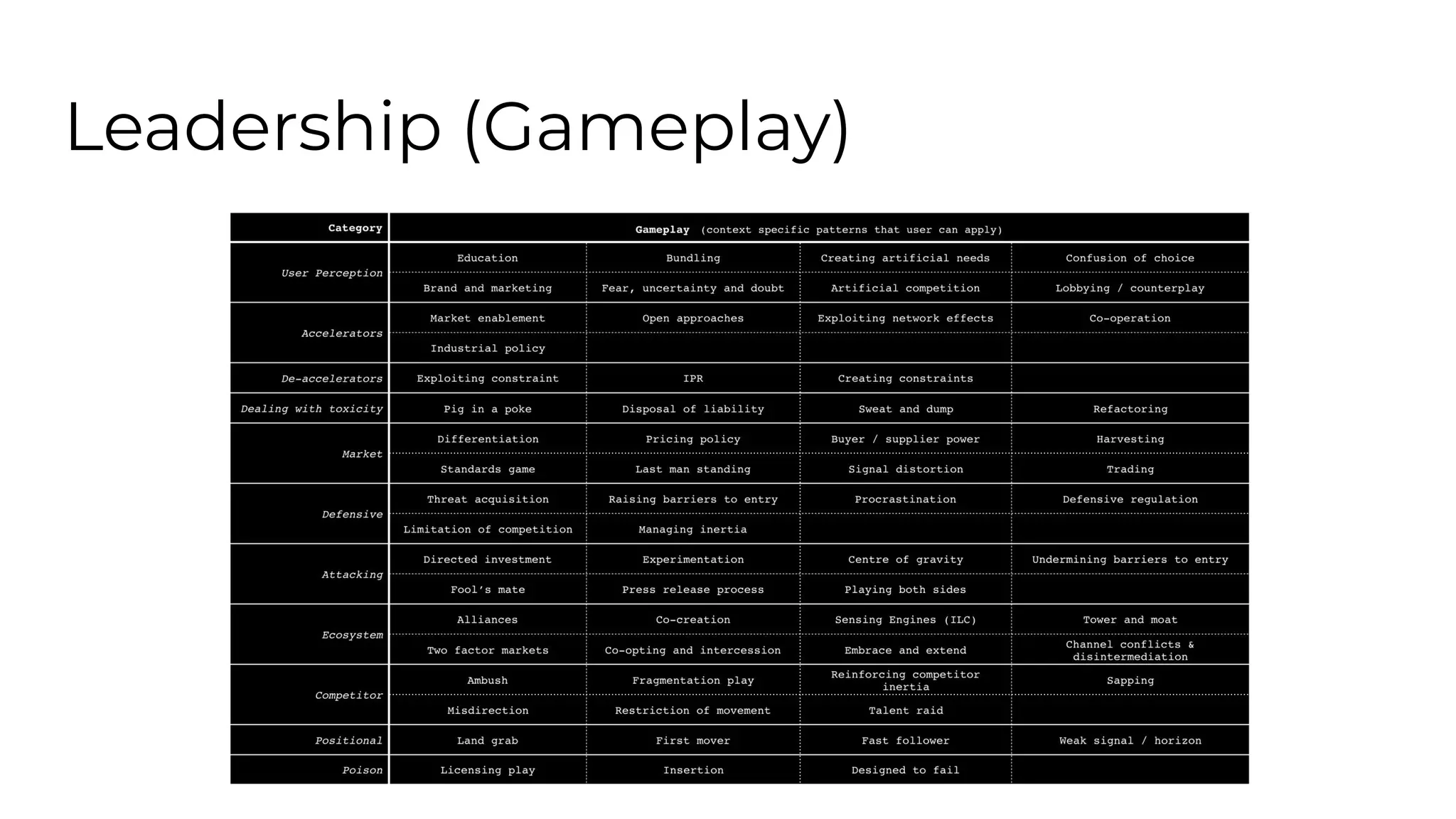
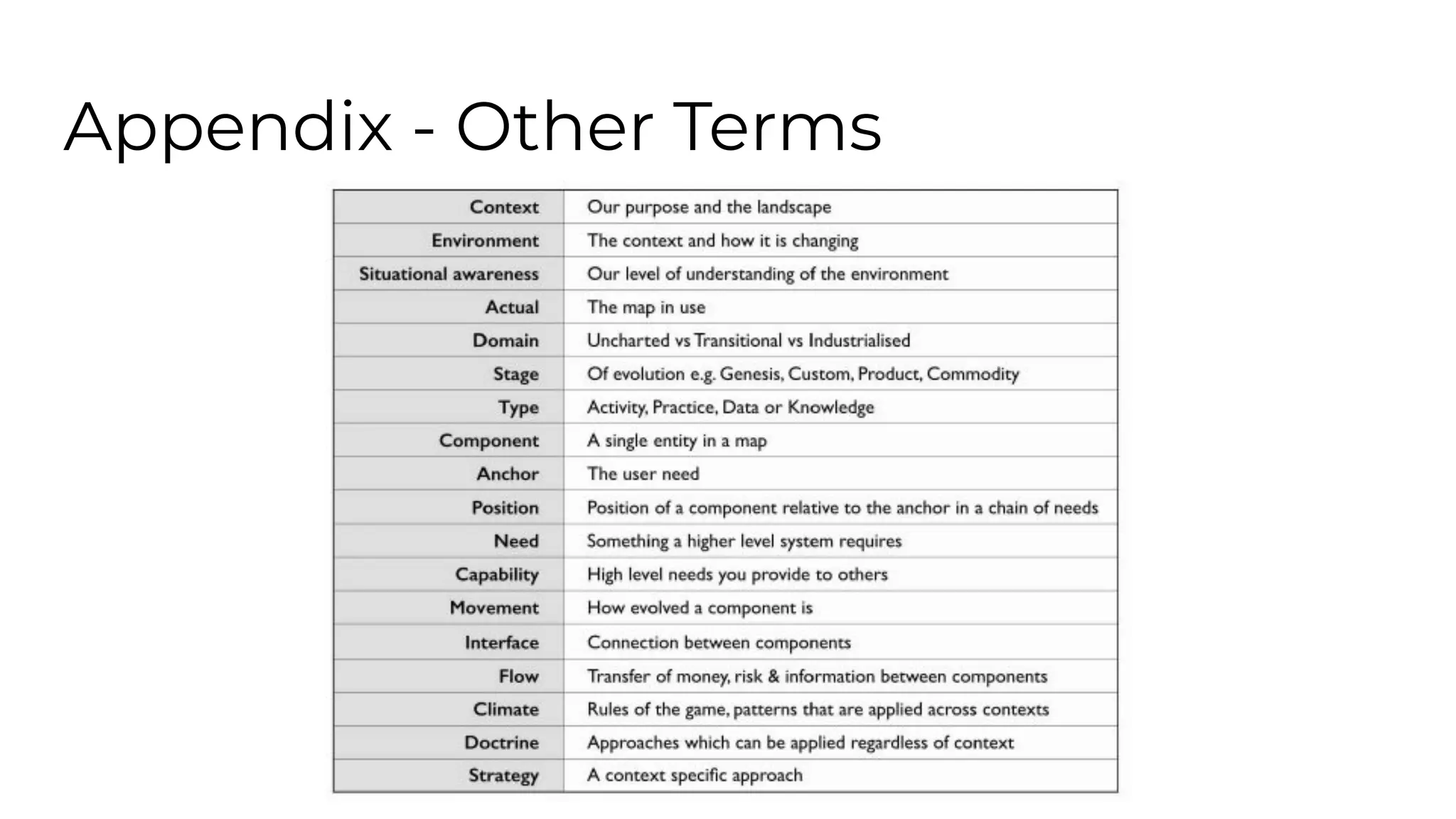
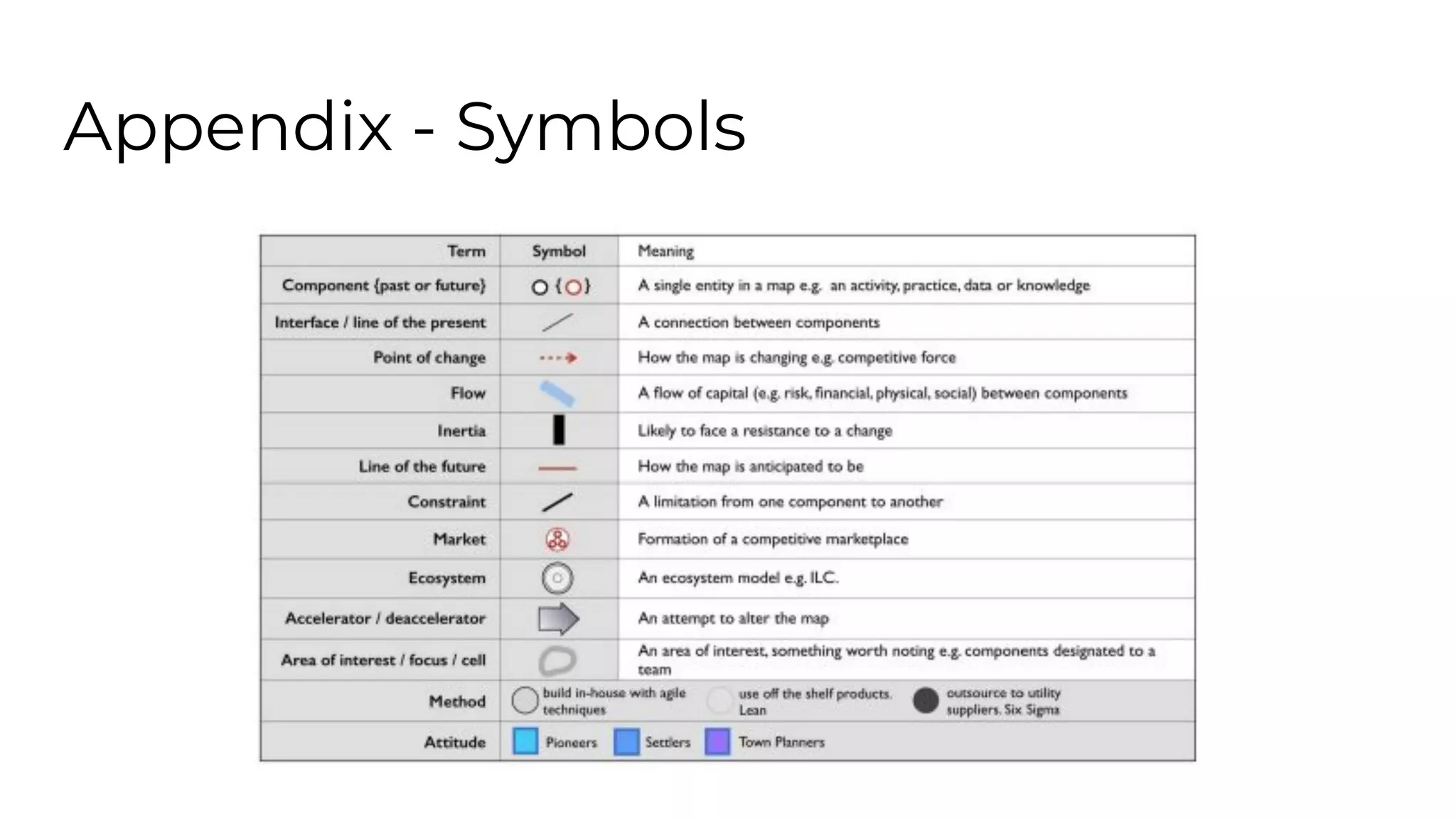
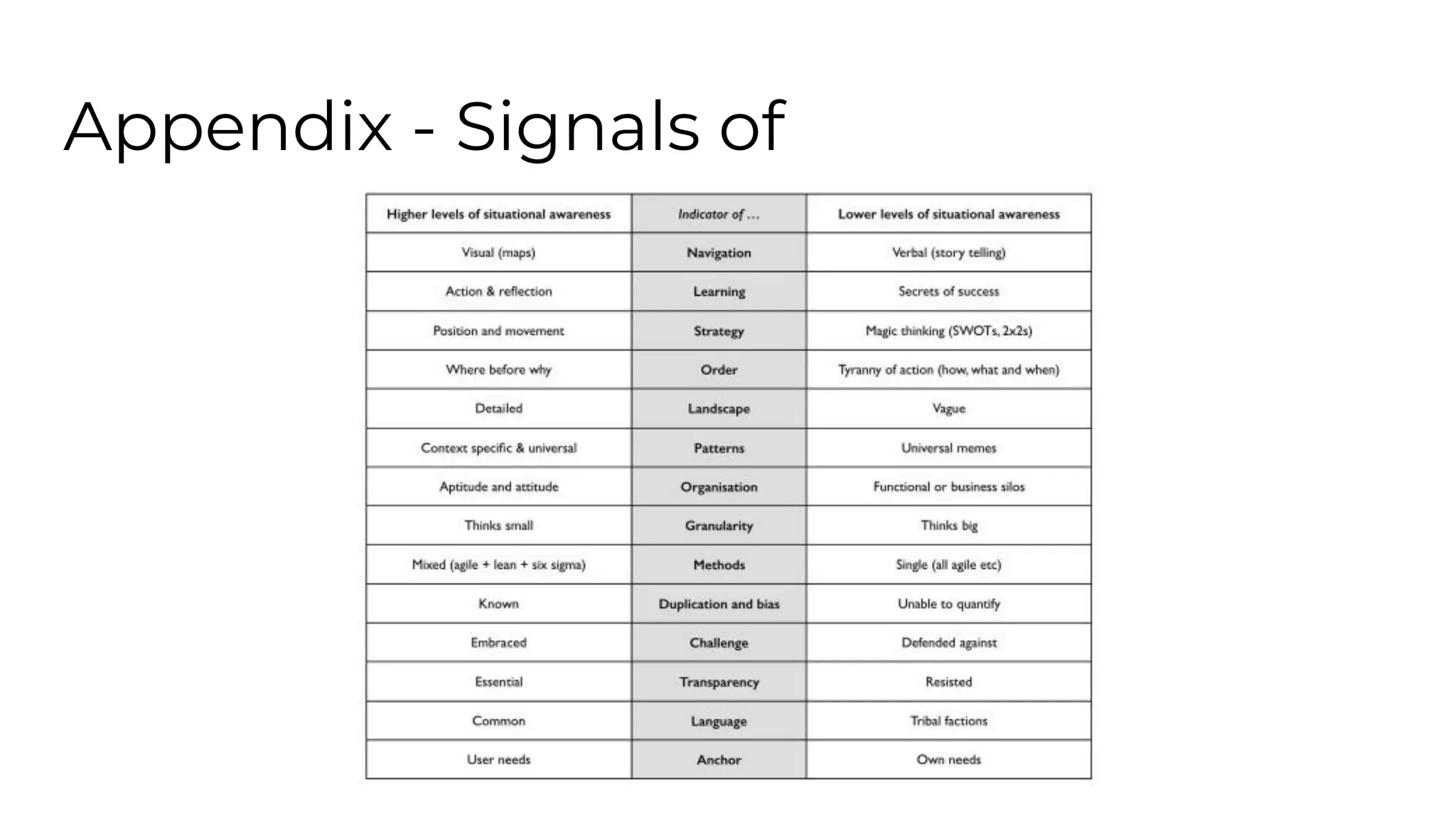
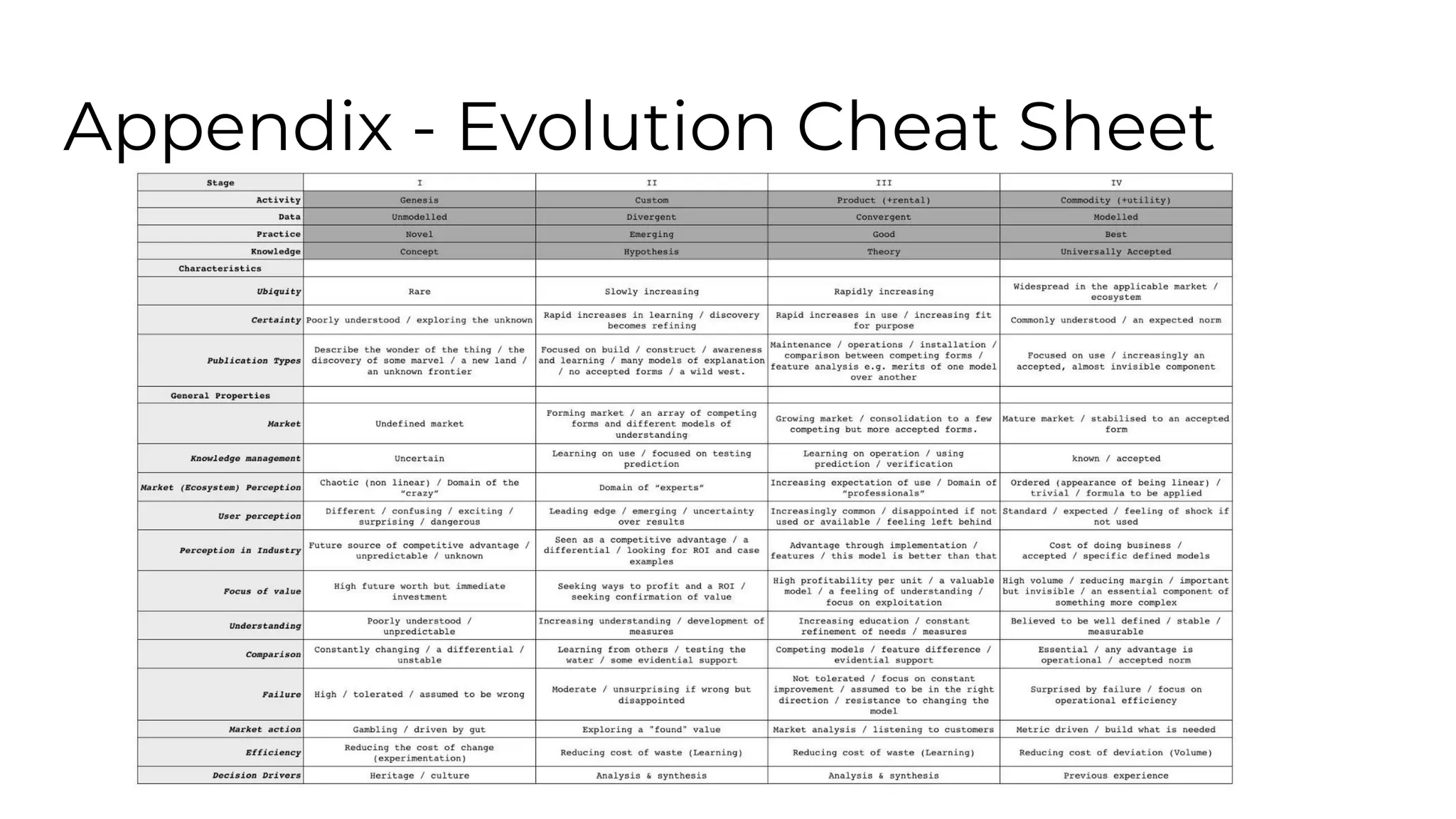
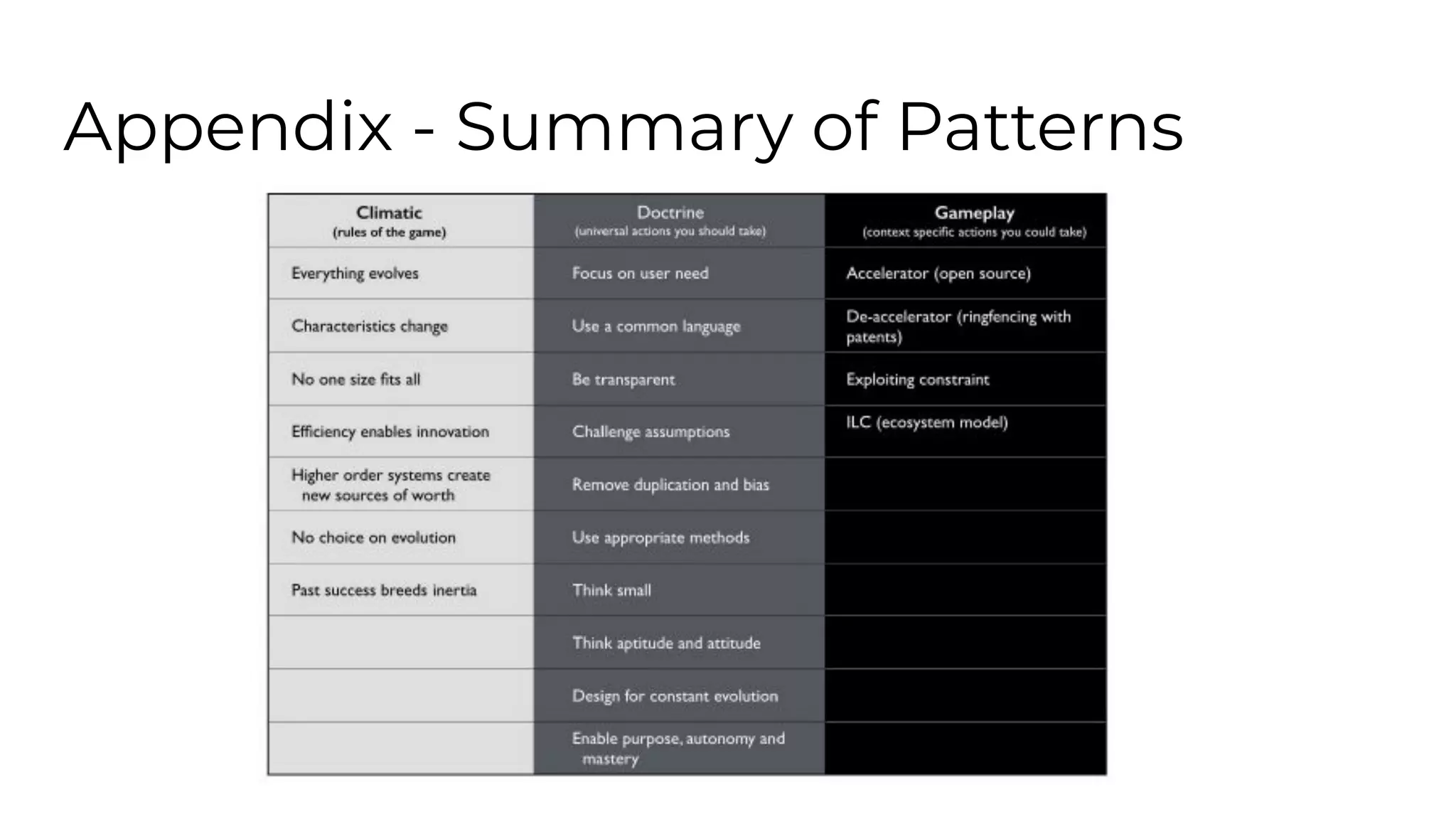
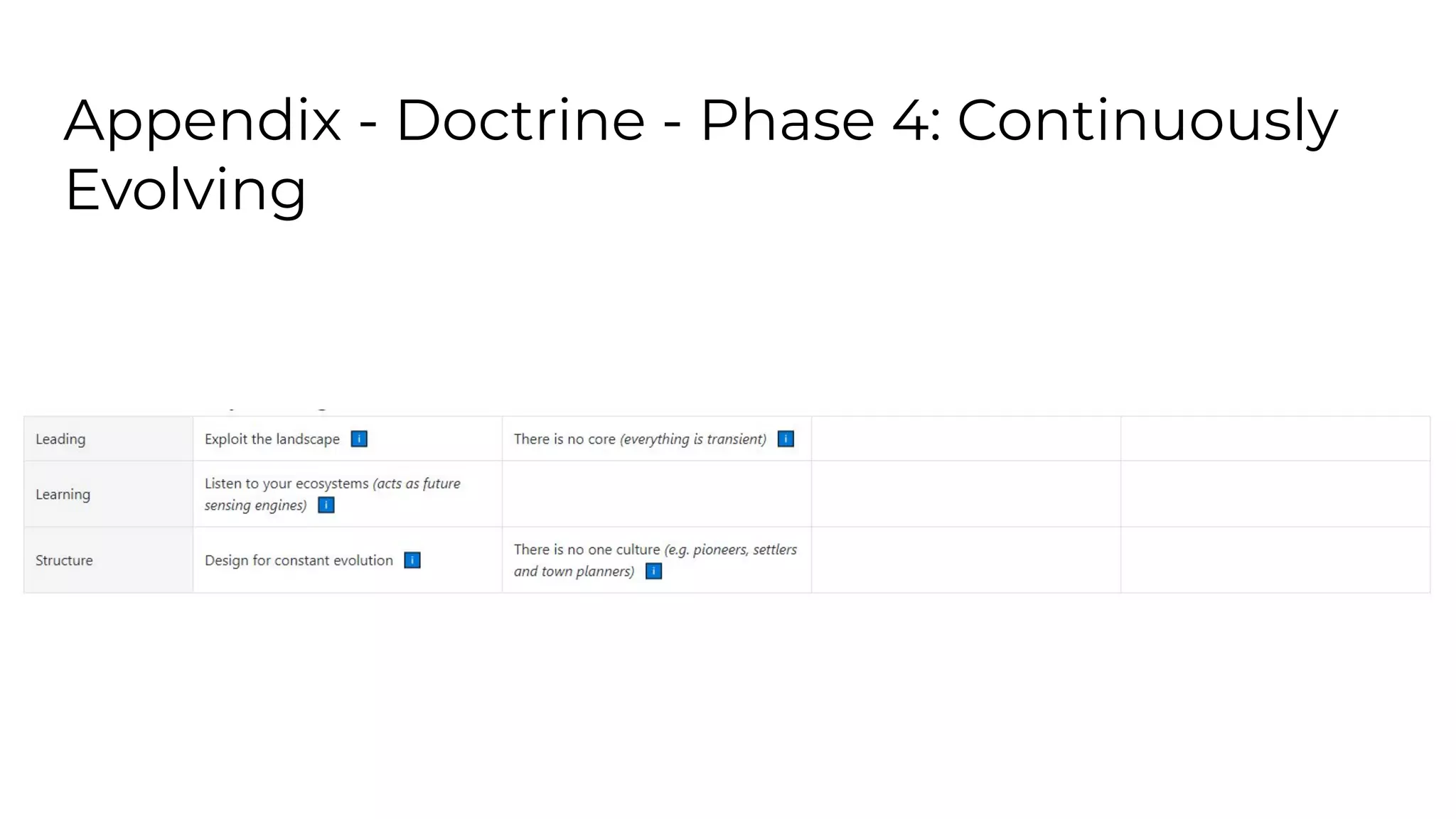
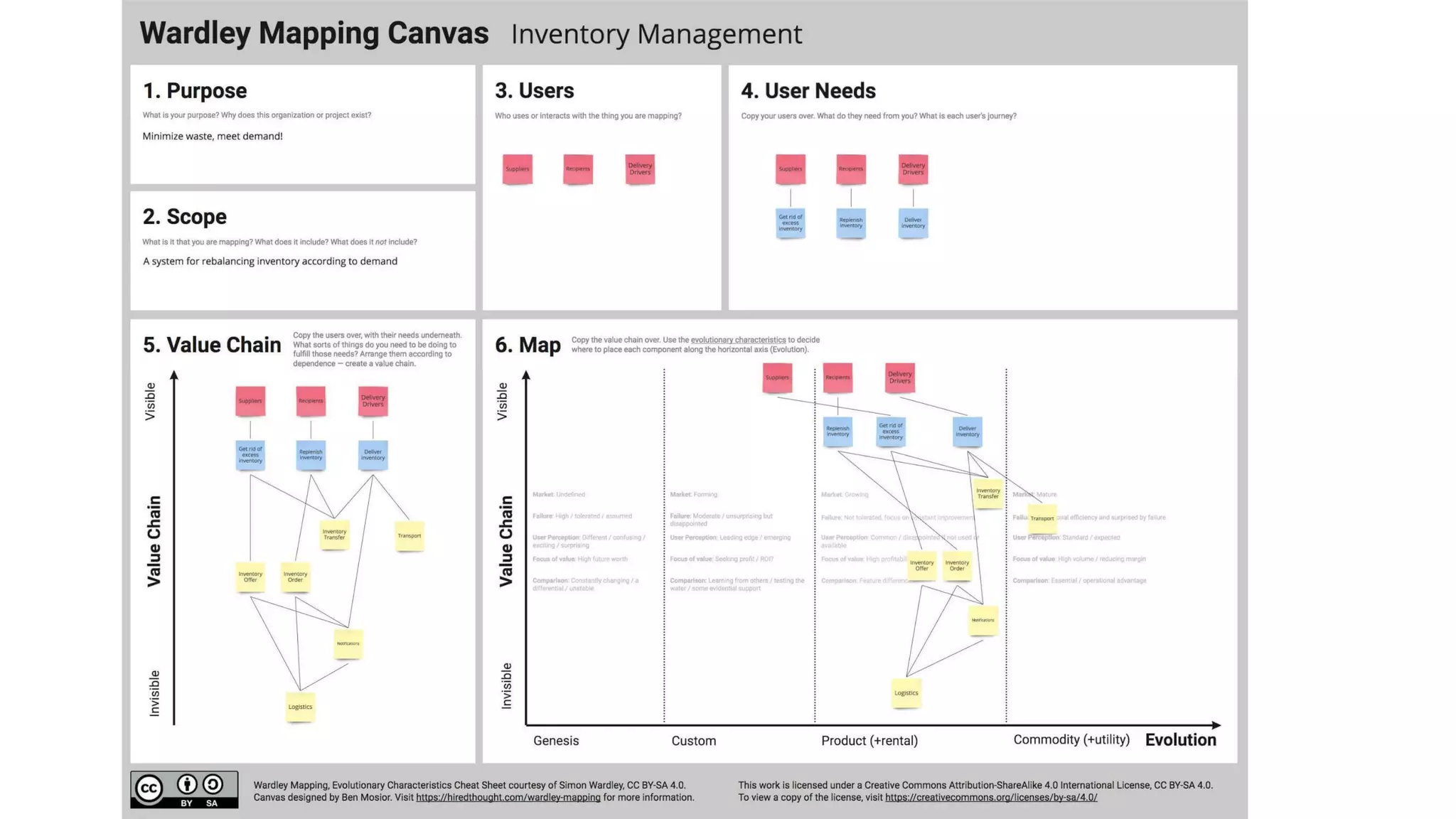
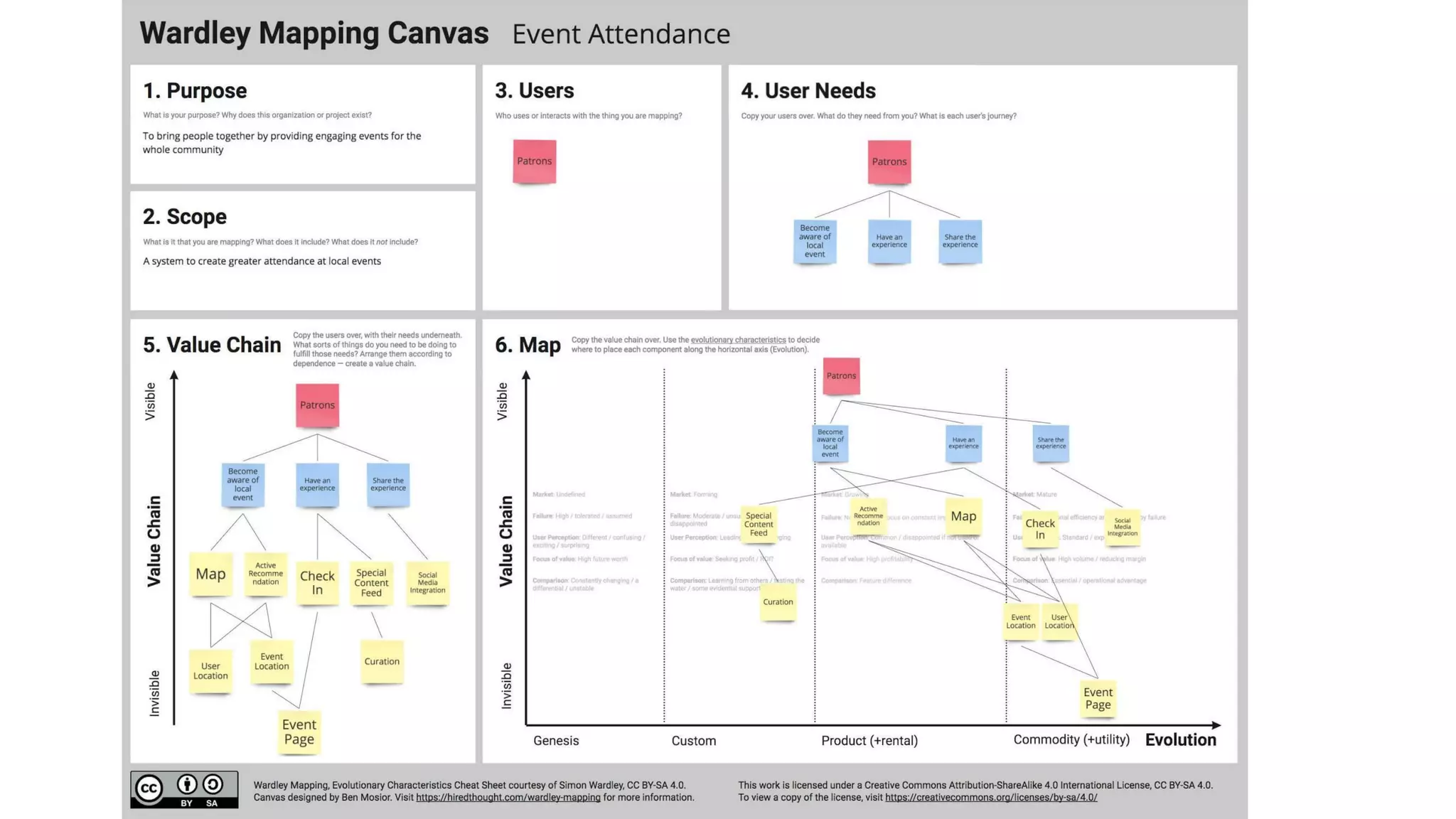
This document outlines an agenda for a lunch and learn on Wardley mapping. Wardley mapping is a visual method for exploring, determining and communicating strategy. It involves identifying user needs, mapping the value chain to meet those needs, and assessing how evolved each component of the value chain is. The agenda covers identifying scope, users and their needs, mapping the value chain, and assessing component evolution. It also discusses how to structure an organization based on component evolution, when to outsource components, and patterns like innovation types and economic patterns that impact components.