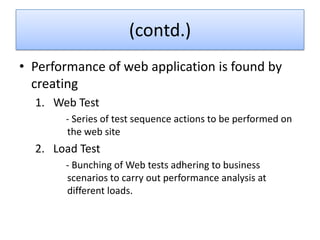
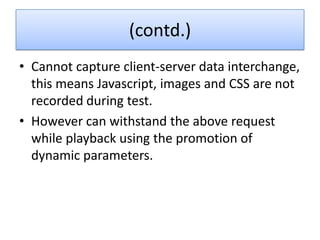
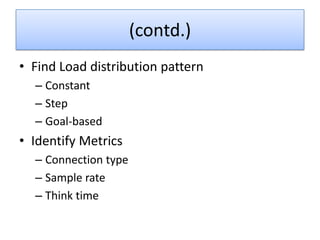
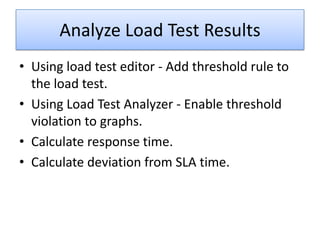
VSTS 2010 for Testers provides an overview of Microsoft's testing tools in Visual Studio 2010, including Test Manager for test planning and management, different types of tests like load testing and web performance testing, and how to perform tasks with the tools like creating test plans and cases, executing tests, and analyzing results. The goal is to provide an integrated testing solution across the entire product development and testing lifecycle within a single tool.