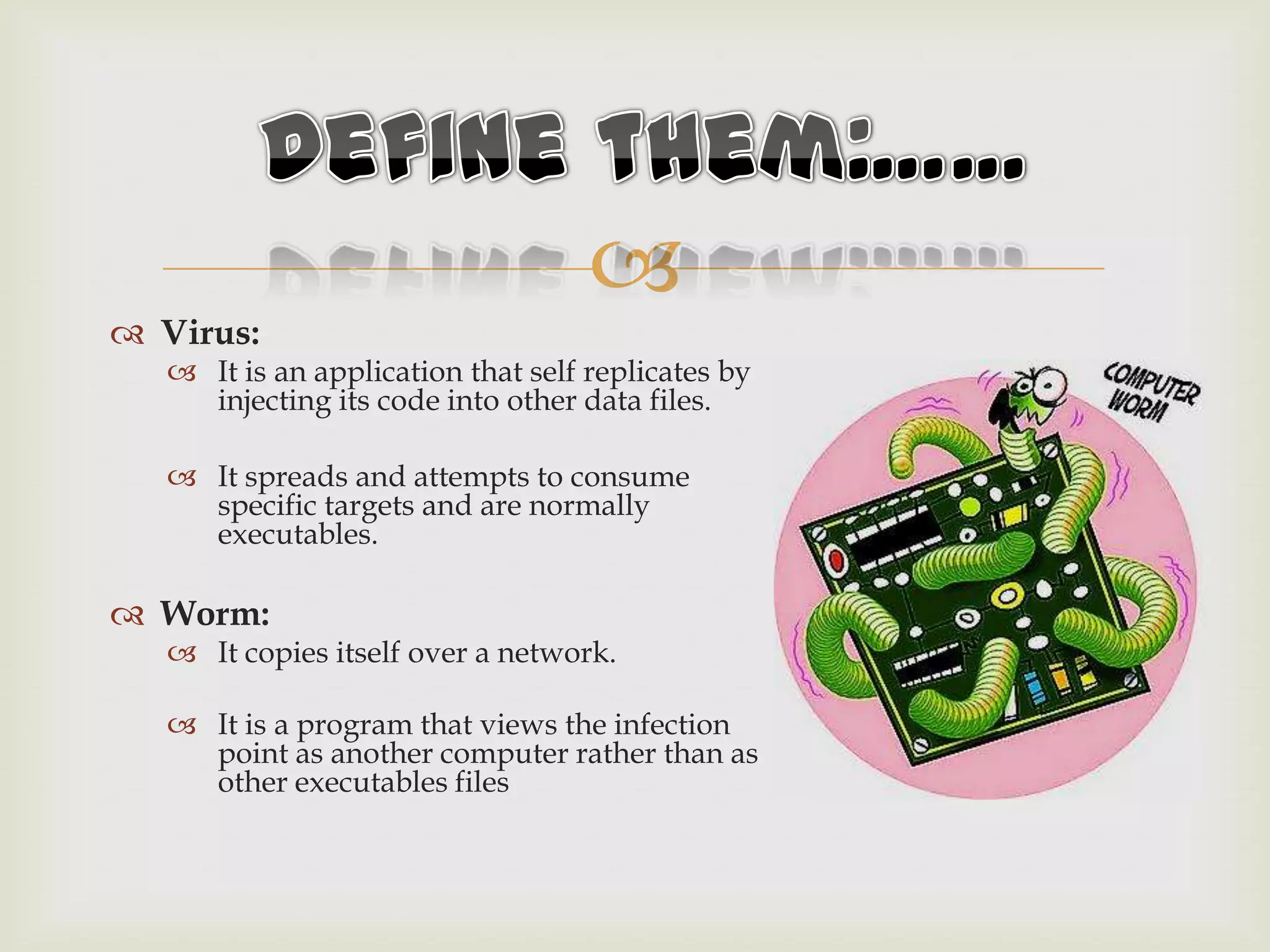
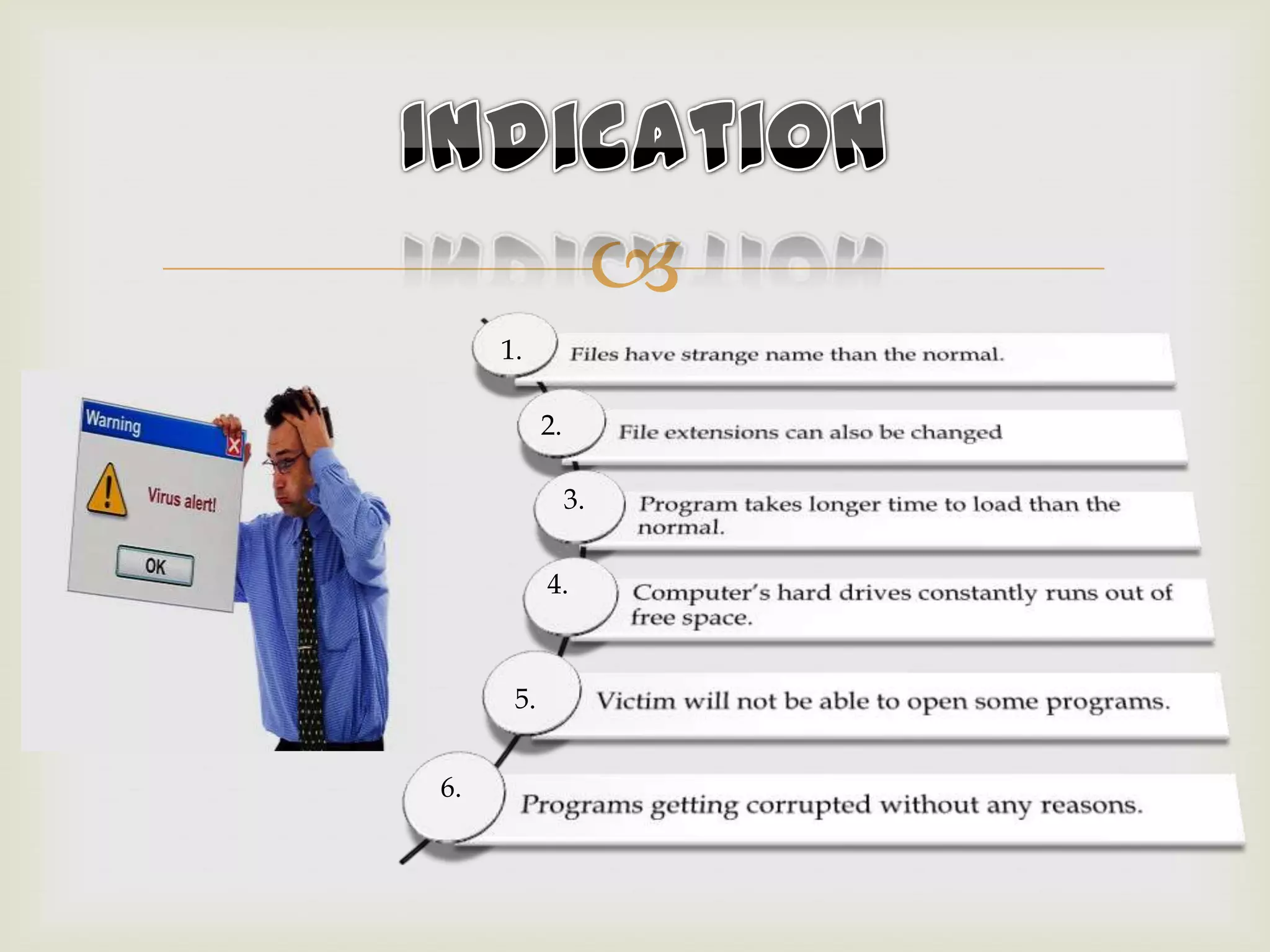
This document discusses viruses and worms, describing that viruses inject code into files while worms copy themselves over a network. It then lists common infection methods like email attachments and browser exploits. The document outlines virus characteristics like remaining hidden, carrying other viruses, and persisting after formatting. It describes the infection process and payload delivery. Finally, it lists different virus types and techniques used to avoid detection like maintaining file modification dates and encrypting code.