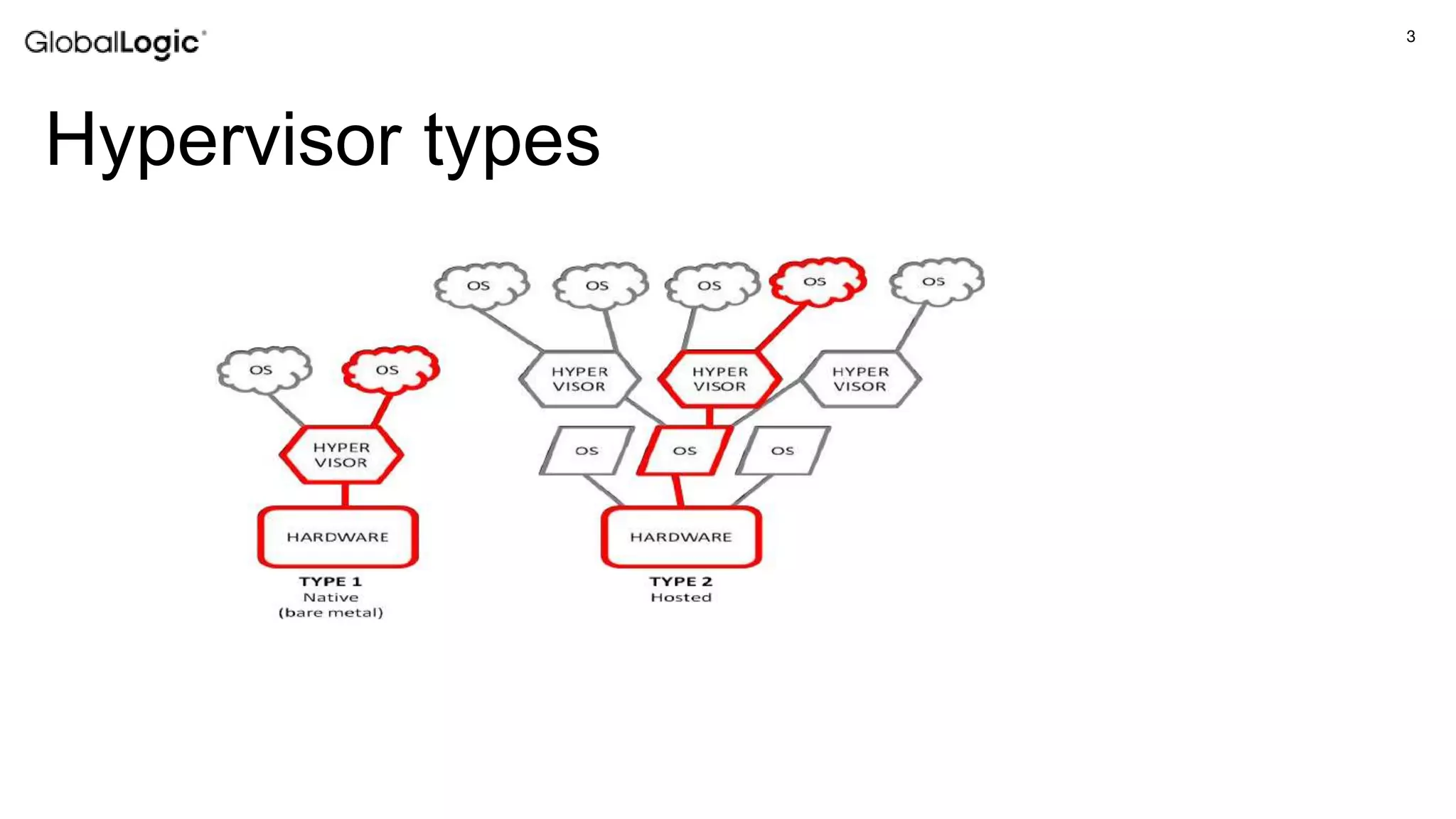
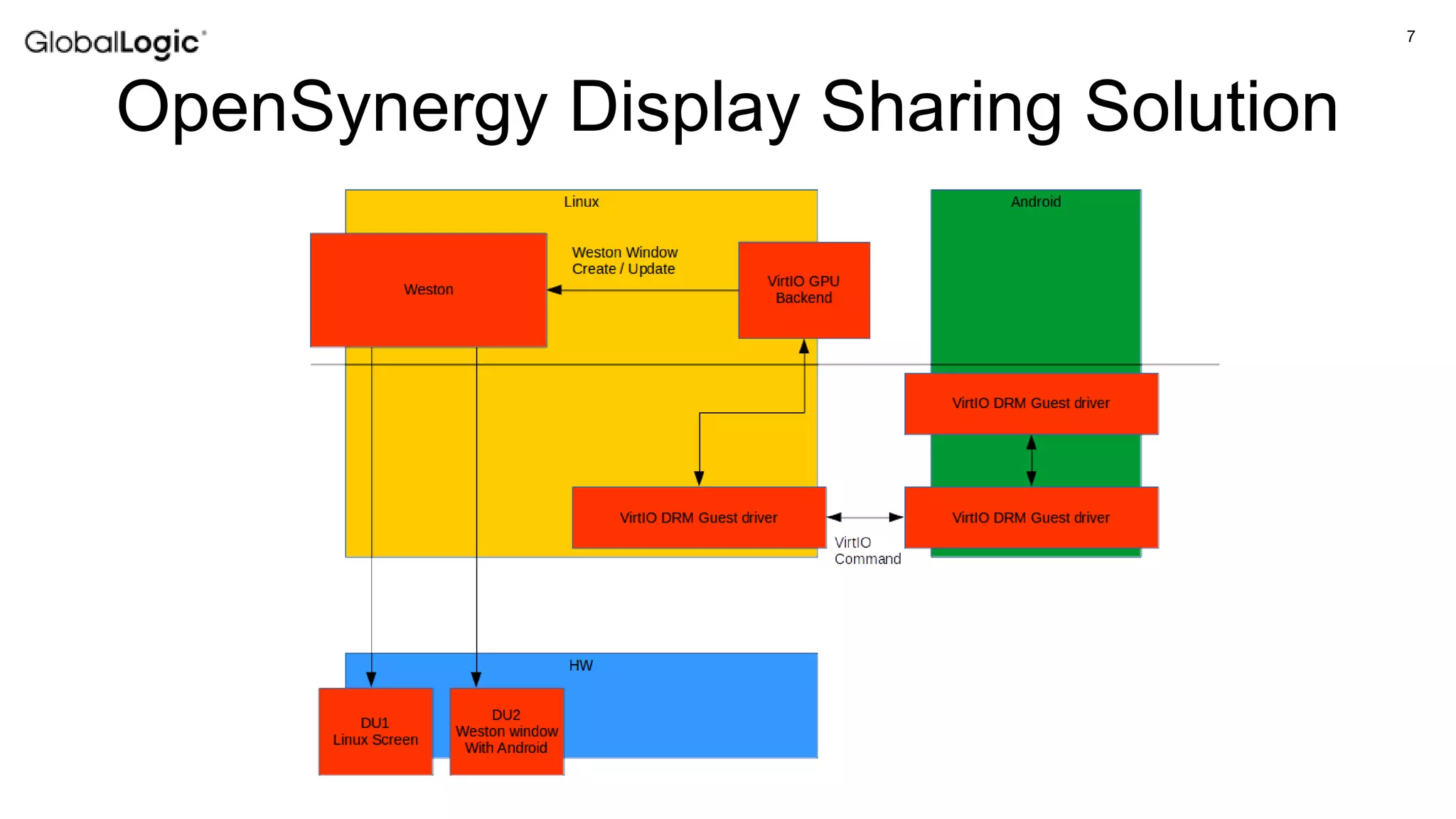
The document discusses the role of hypervisors in automotive applications, highlighting their ability to support mix-criticality systems by integrating software with varying safety, security, and real-time requirements. It addresses challenges related to virtualization of I/O devices in automotive, particularly the lack of standardized interfaces compared to desktop and cloud applications. The document also mentions the virtio standard for virtual I/O devices and presents a shared display solution, while acknowledging limitations in the current automotive ecosystem.