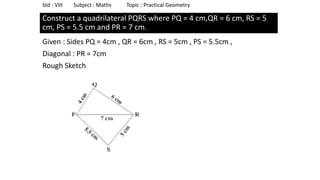
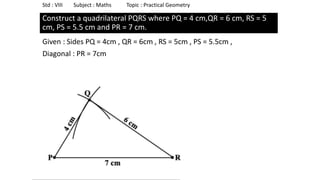
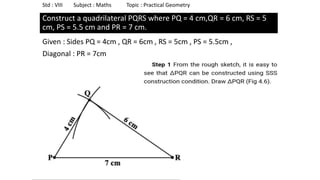
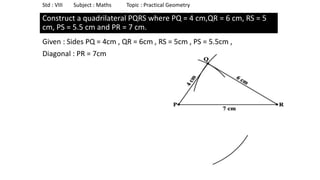
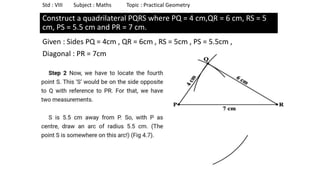
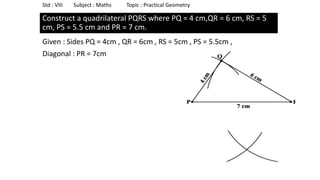
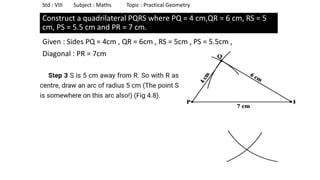
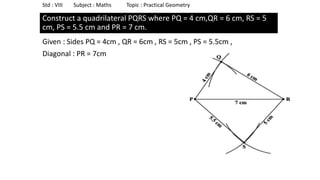
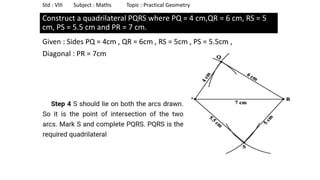
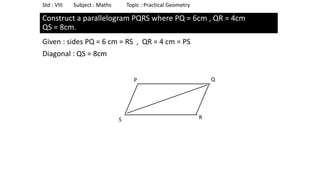
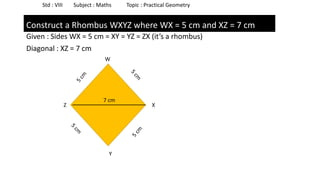
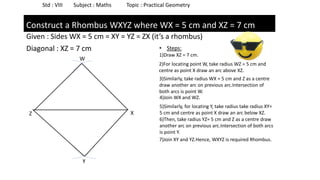
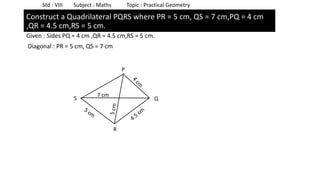
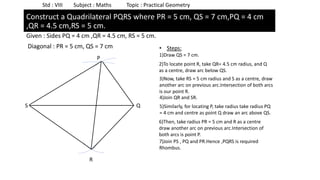
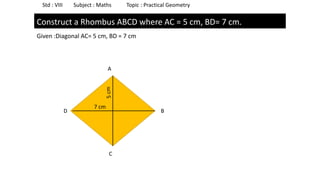
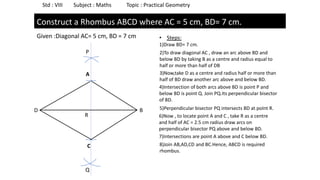
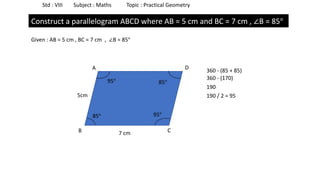
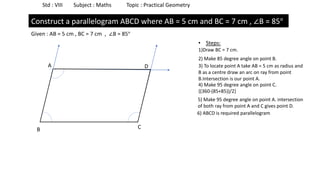
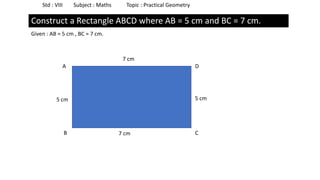
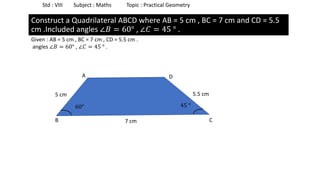
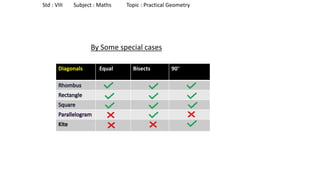
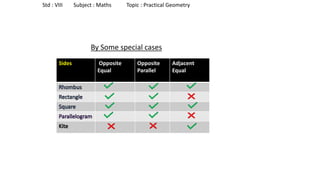
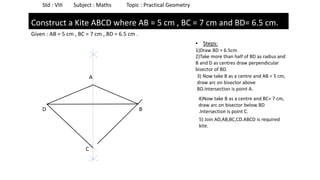
The document provides instructions for constructing several geometric shapes given specific measurements of sides and angles. It includes steps to construct a quadrilateral given five side lengths, a parallelogram given three sides and a diagonal, and several other shapes defined by various combinations of side lengths and angles. The steps generally involve drawing arcs using compasses based on the defined side lengths and angles and intersecting the arcs to locate the vertices of the shapes.