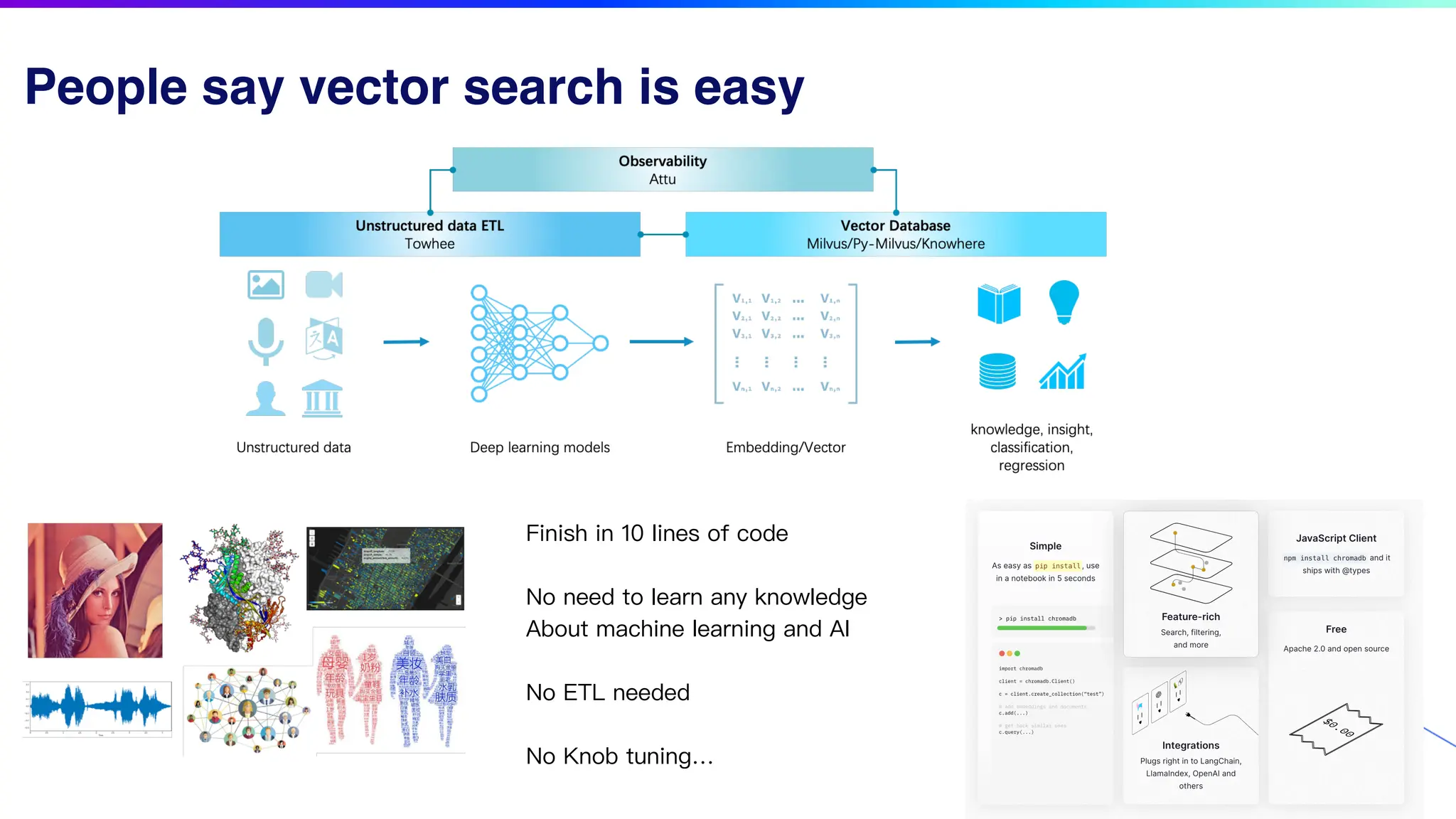
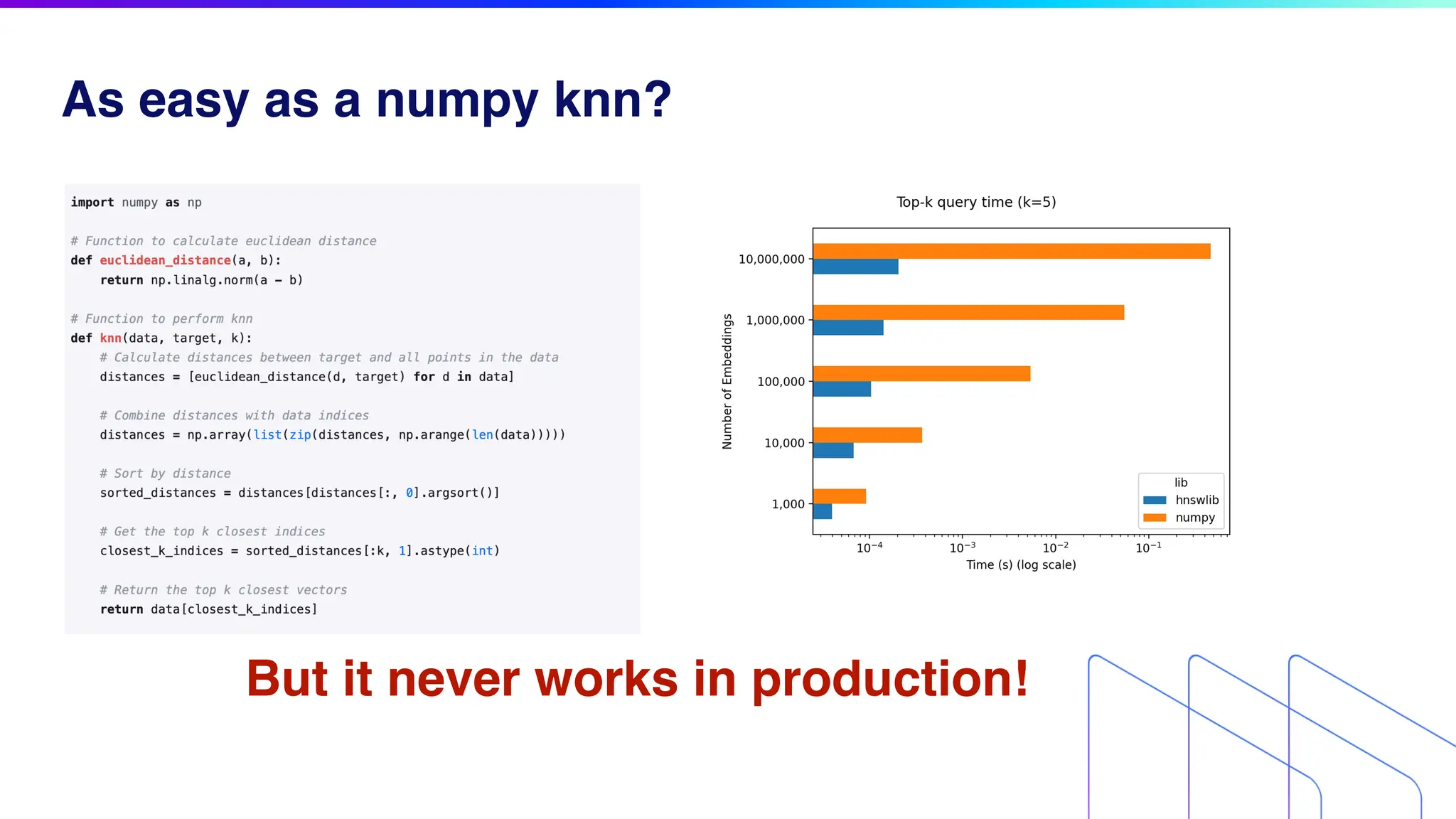
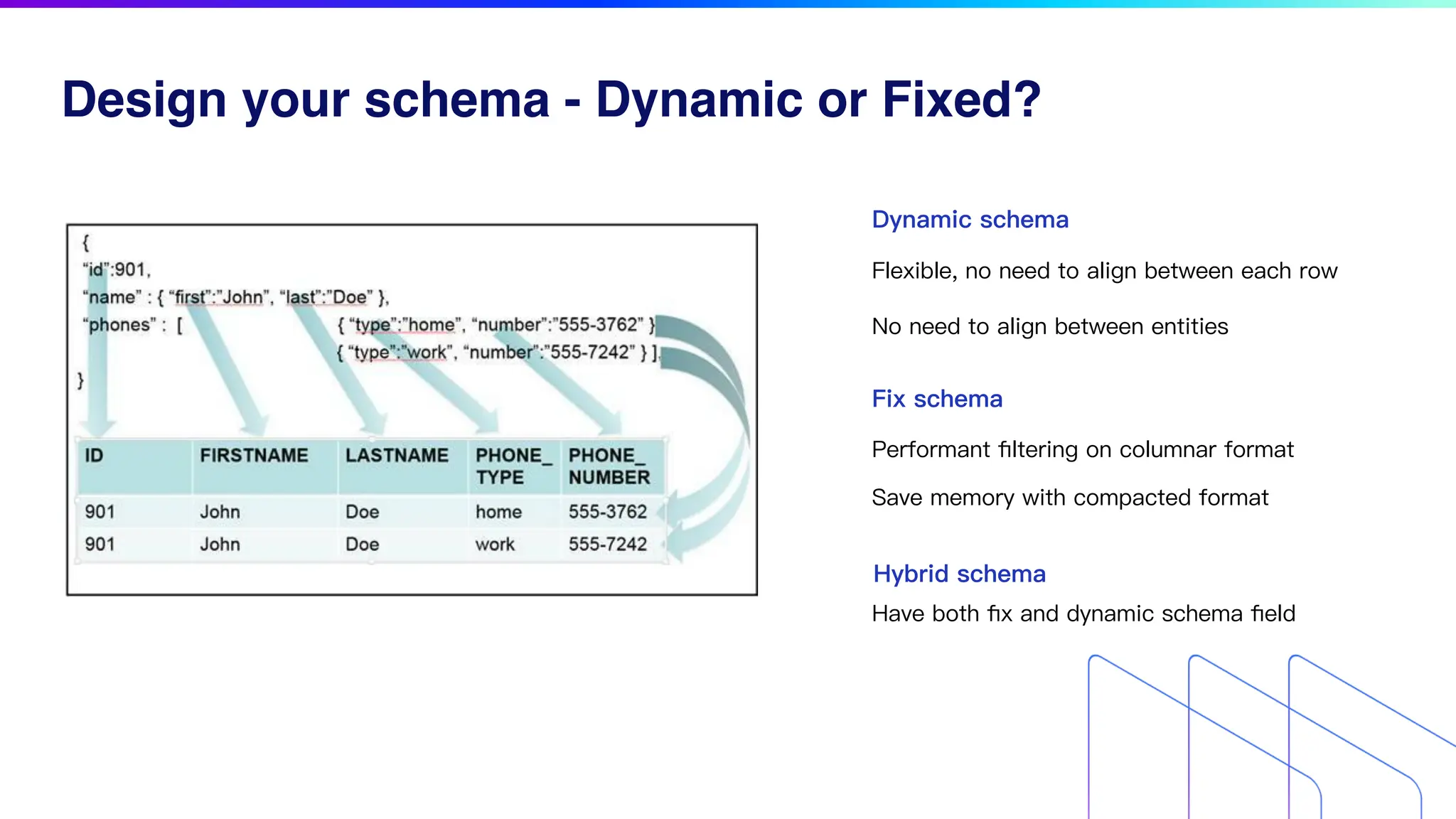
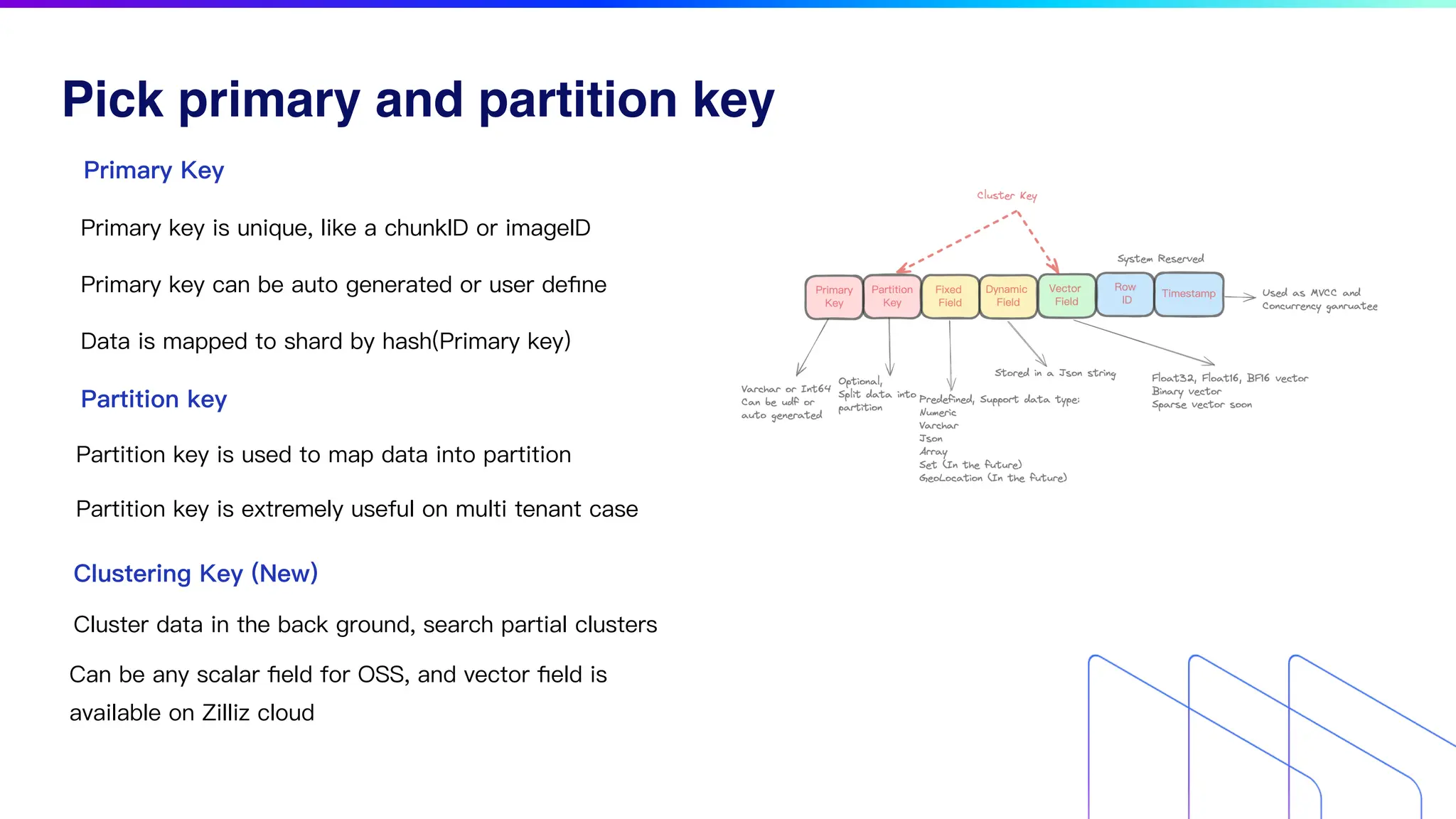
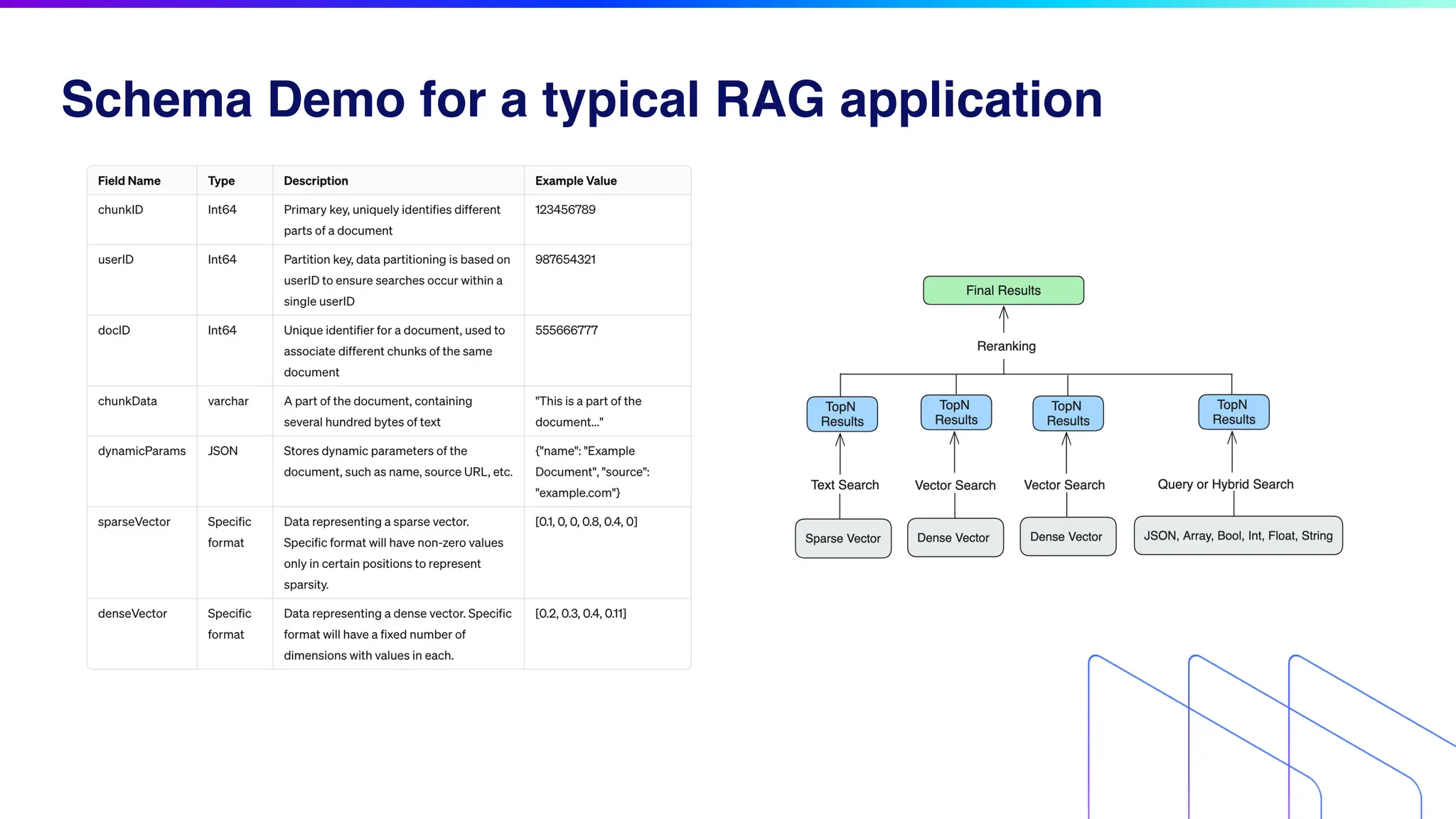
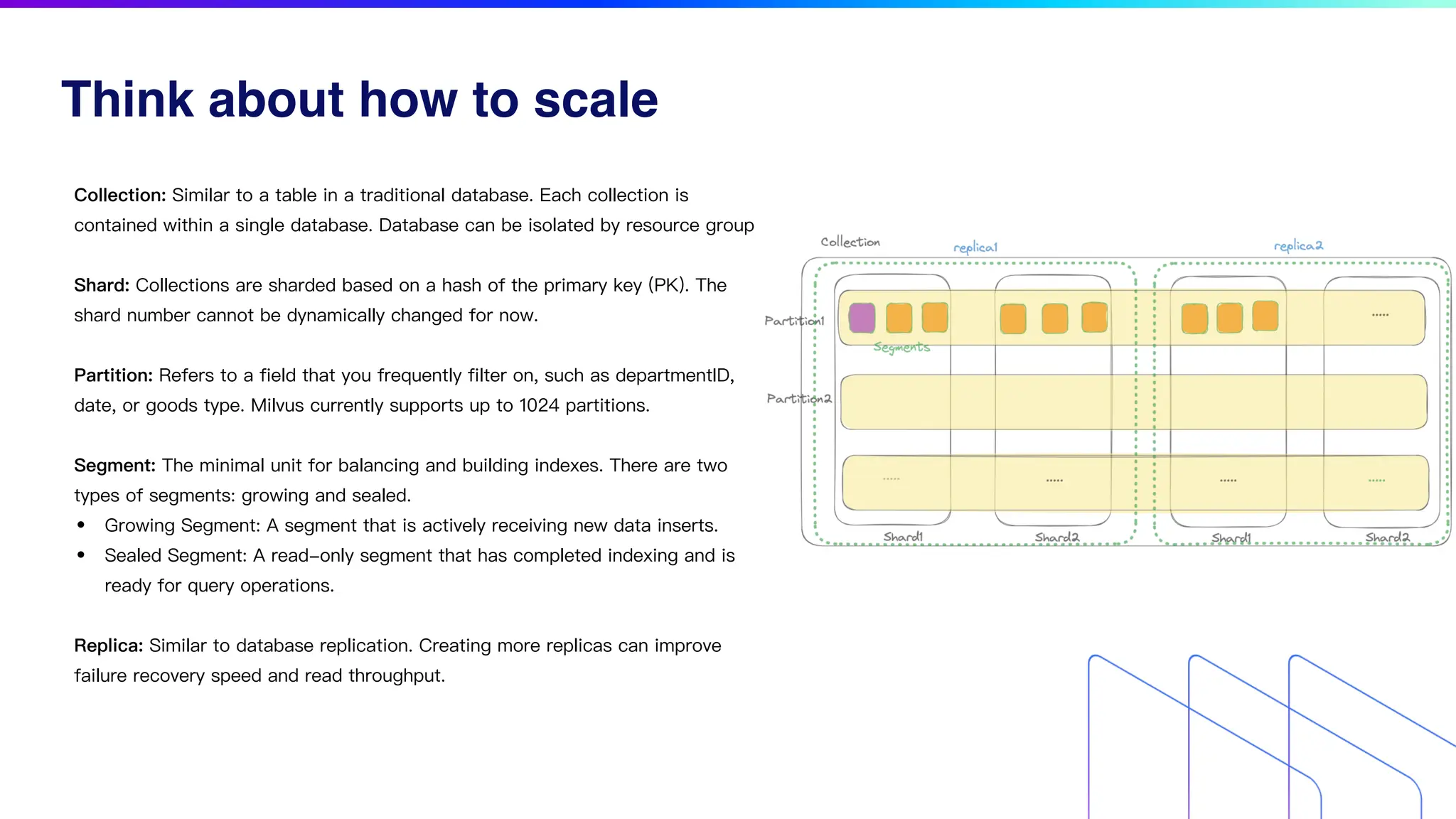
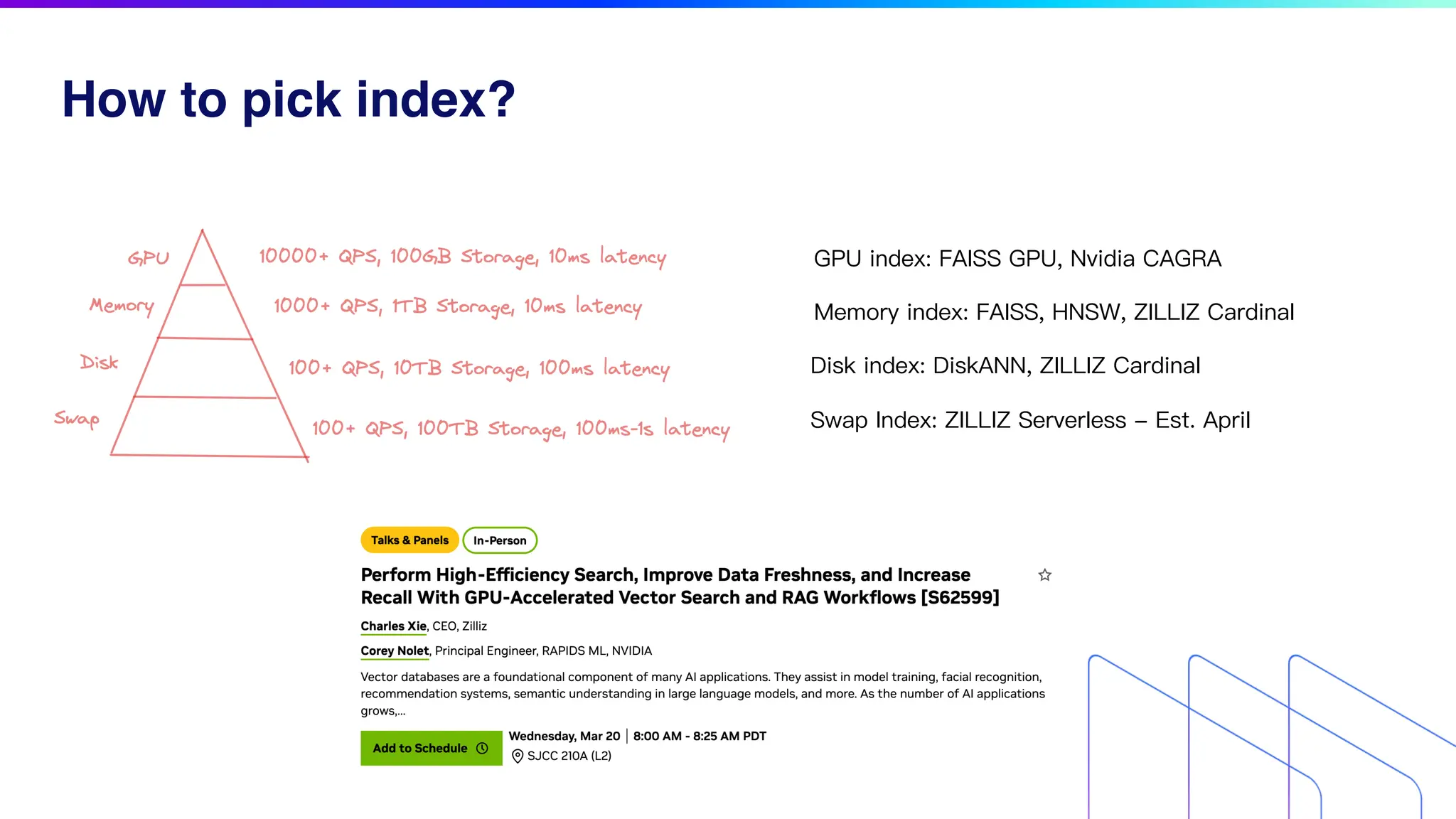
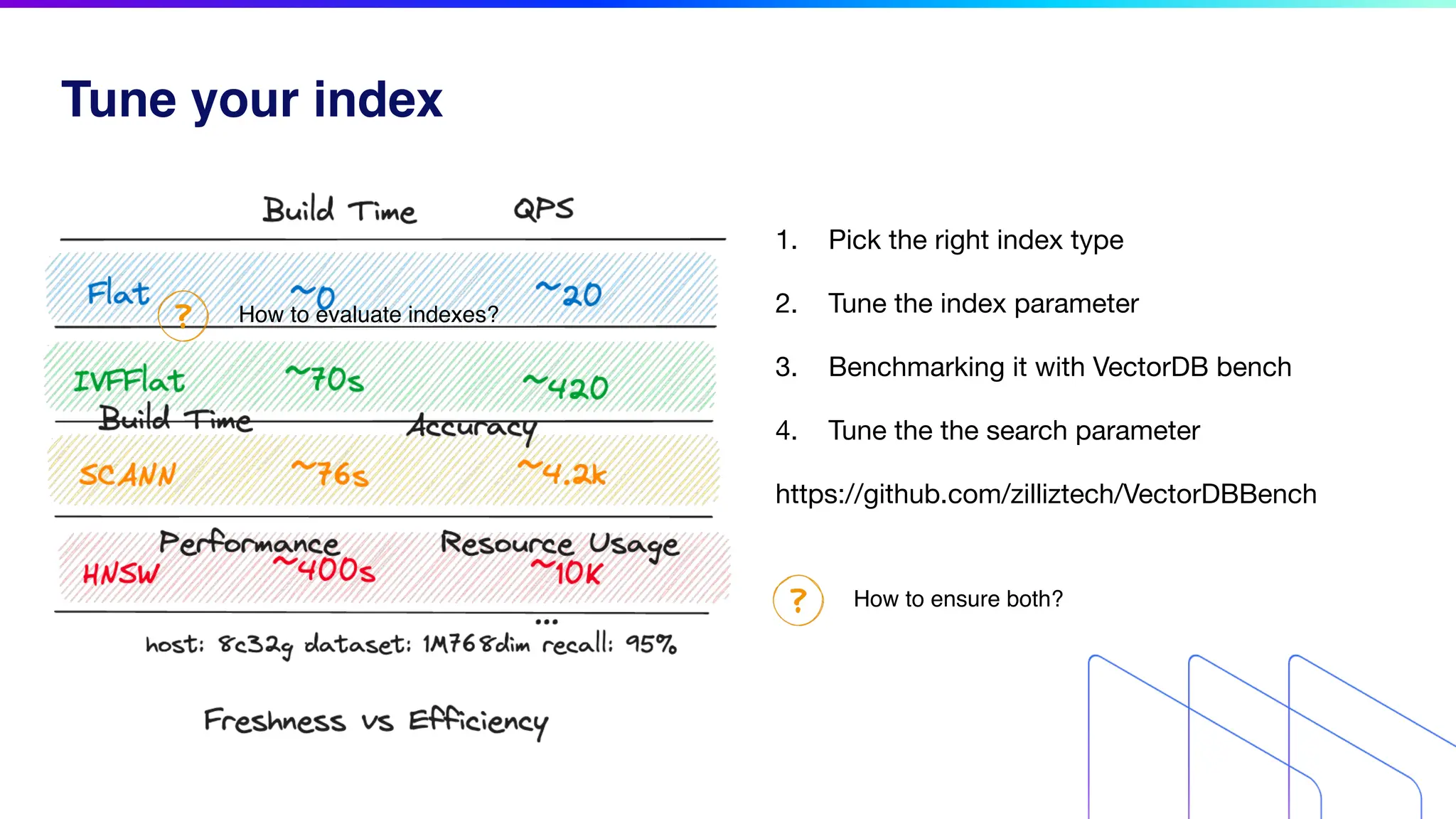
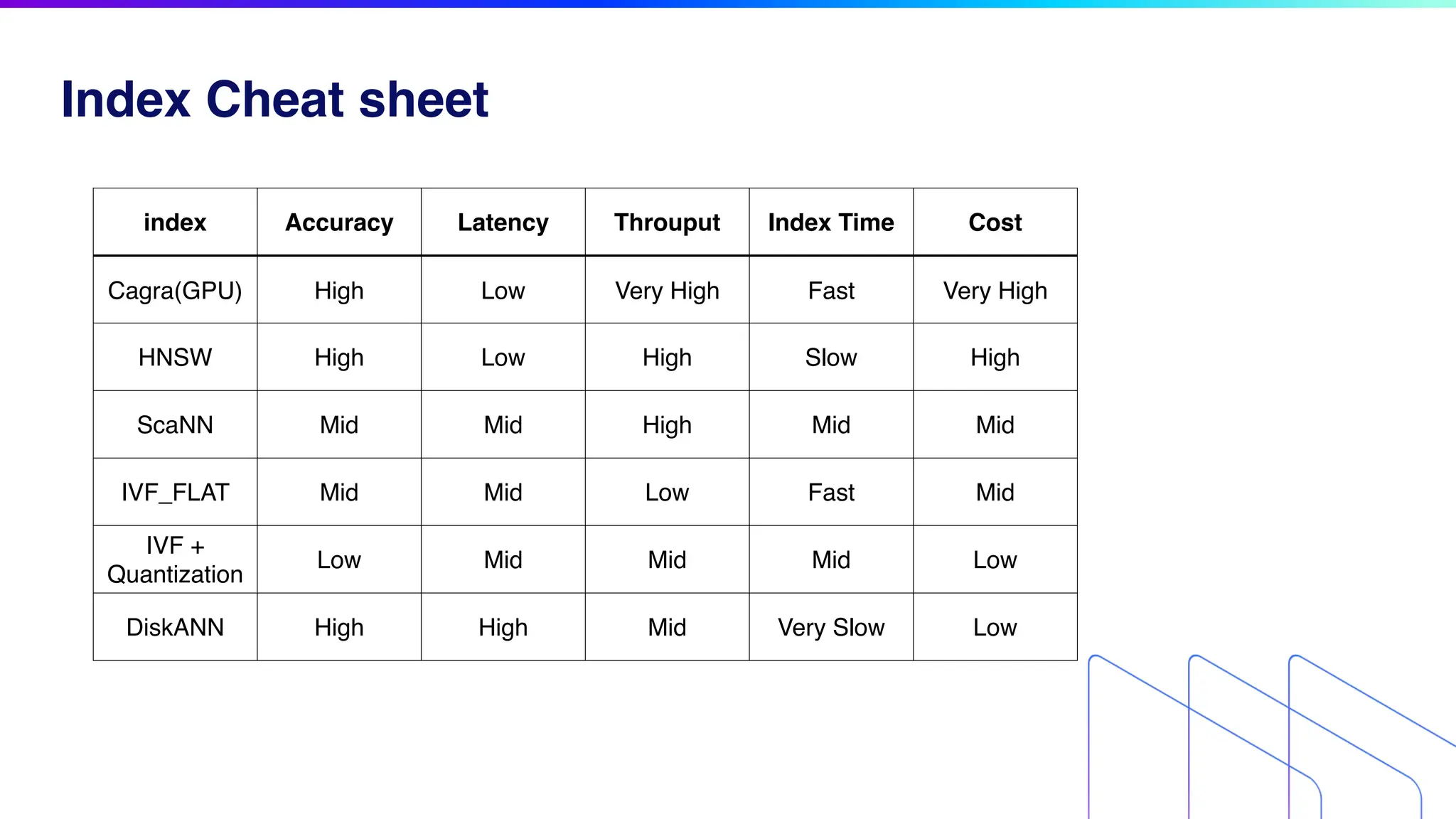
The document discusses key factors for optimizing performance in scalable vector search applications, emphasizing the importance of search quality, scalability, multi-tenancy, cost, and security. It outlines best practices for schema design, scaling collections, and index selection, providing practical examples and considerations for deploying vector databases in production. The document also highlights performance tuning and benchmarking techniques for different index types to enhance efficiency.