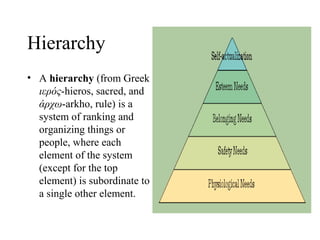
Values are ideals that guide personal conduct and involvement in career or life. They help distinguish right from wrong and provide meaning. Personal values like honesty define individuals, while cultural values sustain community connections. Beliefs are convictions without proof. Worldviews attempt to explain social and physical worlds. Rituals are symbolic actions performed regularly. Hierarchy ranks elements in a system with each below the one above. Myths are traditional stories explaining natural phenomena.










![MYTHS
• [Webster's]
• a traditional story of
unknown authorship,
ostensibly with a
historical basis, but
serving usually to
explain some
phenomenon of nature,
the origin of [humanity],
or the customs,
institutions, religious
rites, etc. of a people;
myths usually involve
the exploits of gods and
heroes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/values-130219070445-phpapp01/85/Values-12-320.jpg)



