1. The document discusses how to choose and use a digital camera and incorporate digital imaging into the curriculum. It provides an overview of the basics of digital photography and its educational benefits.
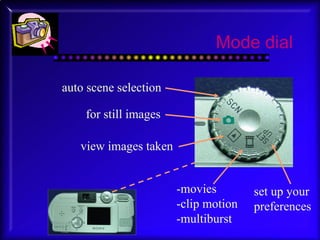
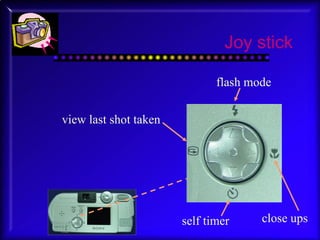
2. Details are given on choosing a digital camera, including factors like resolution, storage options, lens type, and additional features. The anatomy of the Sony Cybershot P71 camera is described.
3. Educational activities that can be done with digital images are listed, and standards that digital photography addresses are mentioned. Students are then instructed to take practice photos and upload them to share online.