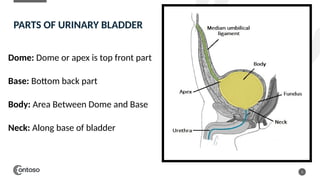
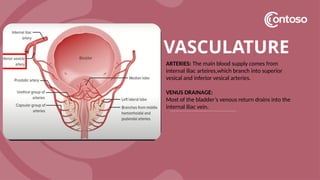
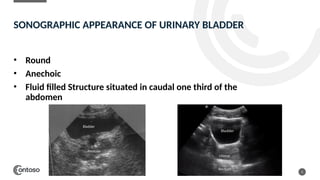
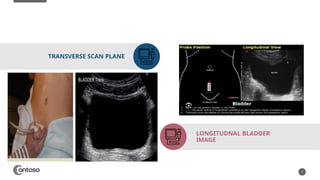
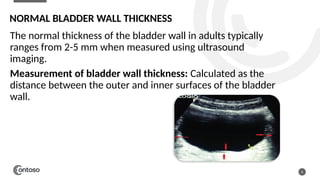
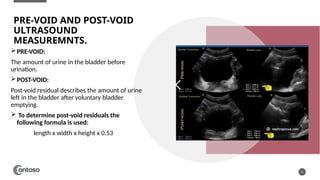
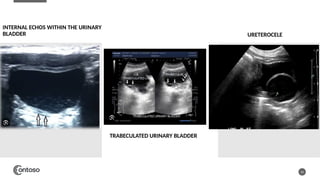
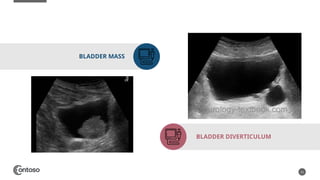
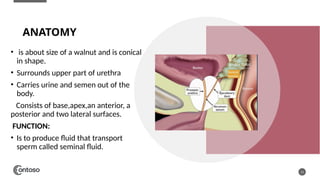
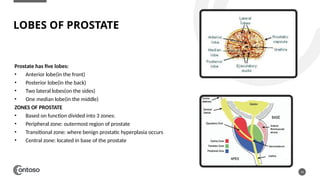
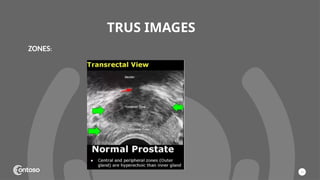
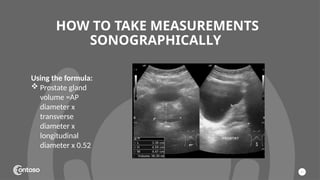
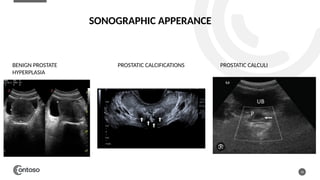
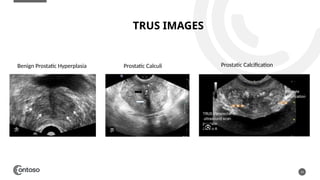
The document details the anatomy of the urinary bladder and prostate, explaining their locations, structures, and sonographic techniques for assessment. It describes the urinary bladder as a muscular organ that serves as a reservoir for urine and provides details on measuring bladder wall thickness and post-void residuals. Additionally, it outlines the structure and function of the prostate, including its lobes and zones, along with relevant sonographic measurement techniques.