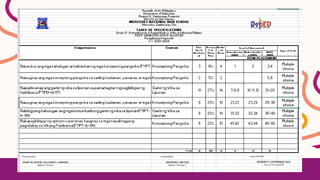
The document outlines the importance of the table of specifications in test construction for the K to 12 basic education program, emphasizing its role in aligning assessment with learning objectives. It provides guidelines for preparing tests, including tips on question distribution, characteristics of good tests, and types of test formats. Additionally, it highlights factors to consider when constructing tests, such as the purpose, time, student number, teacher skill, and available resources.