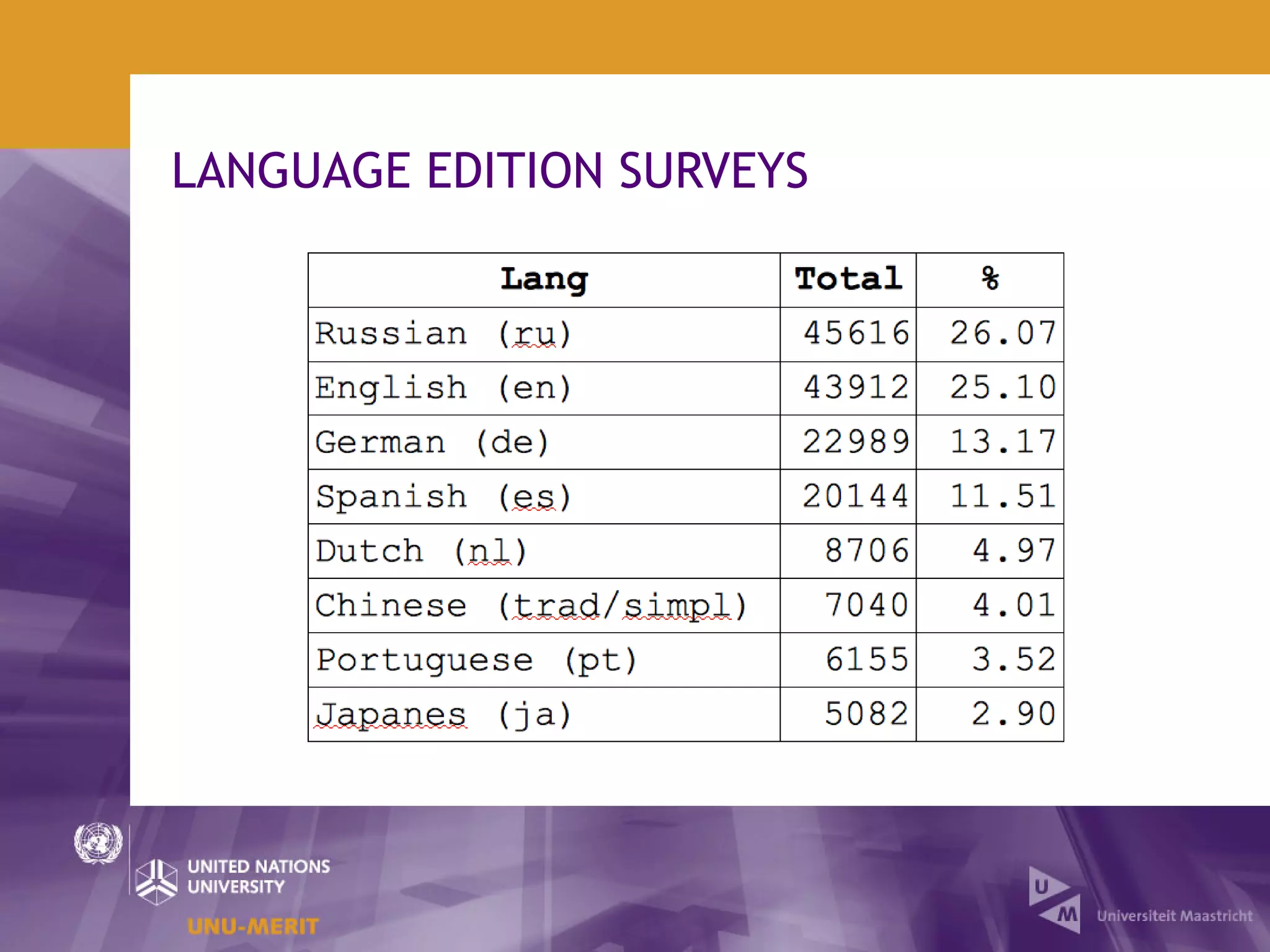
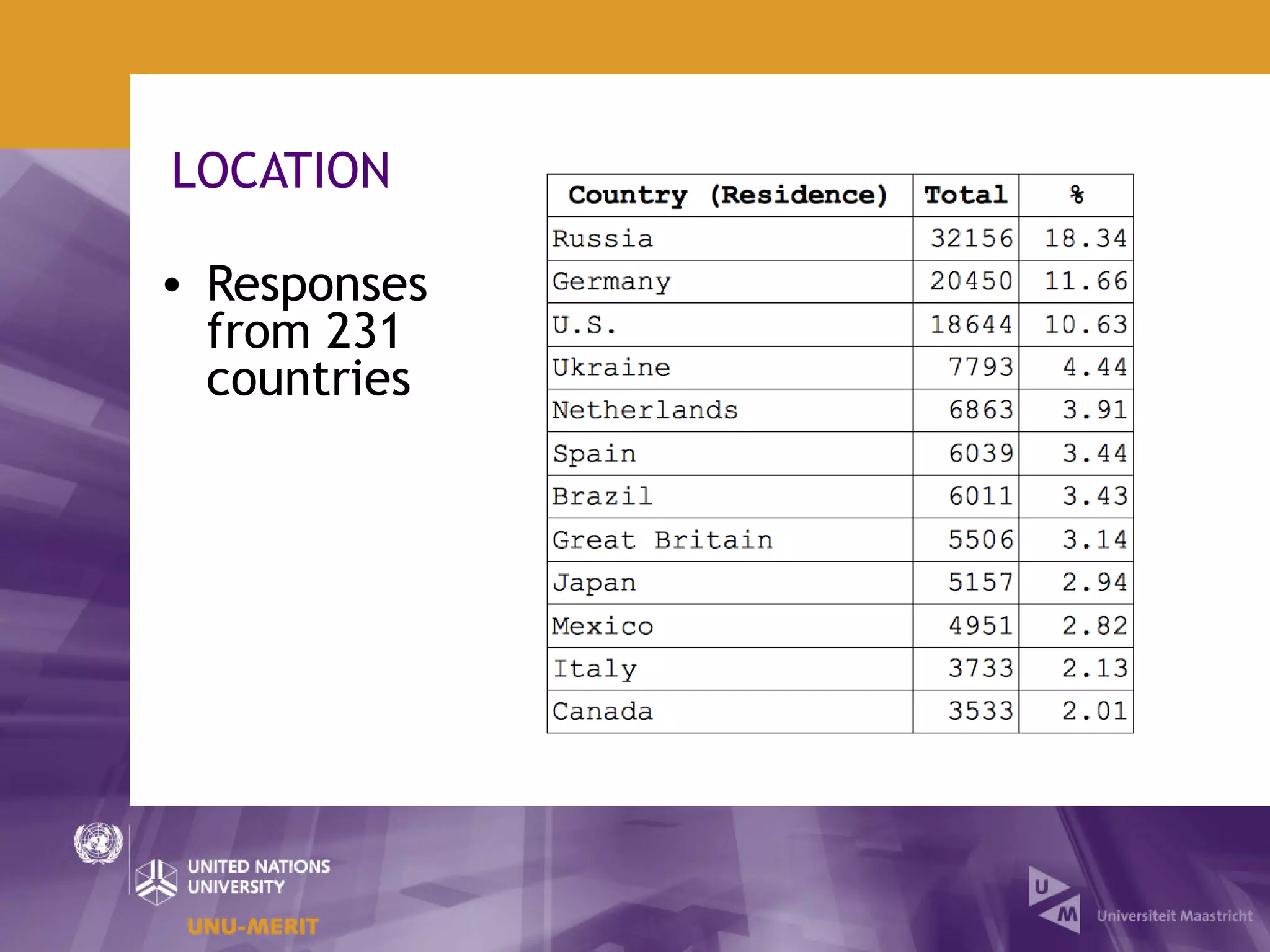
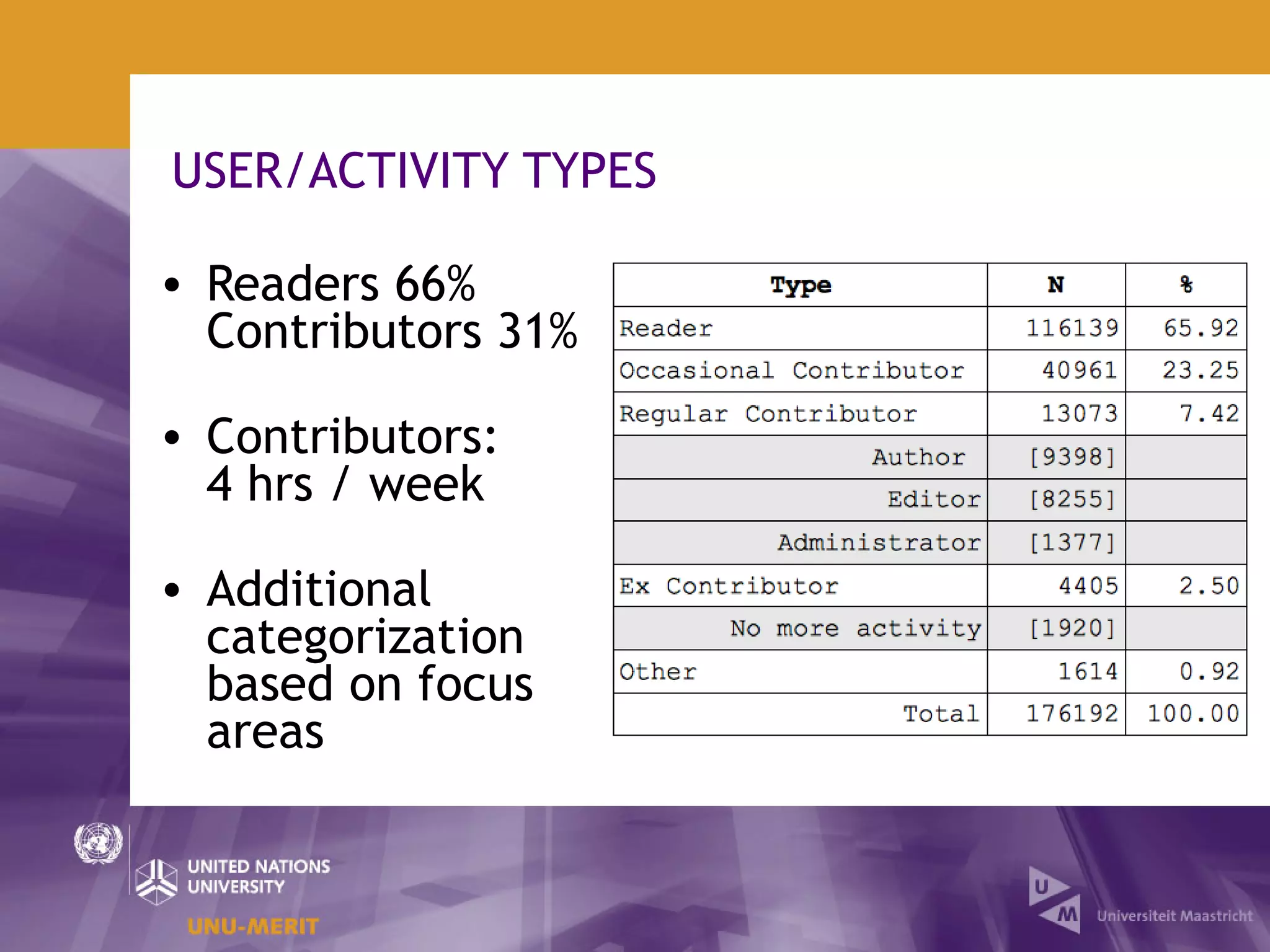
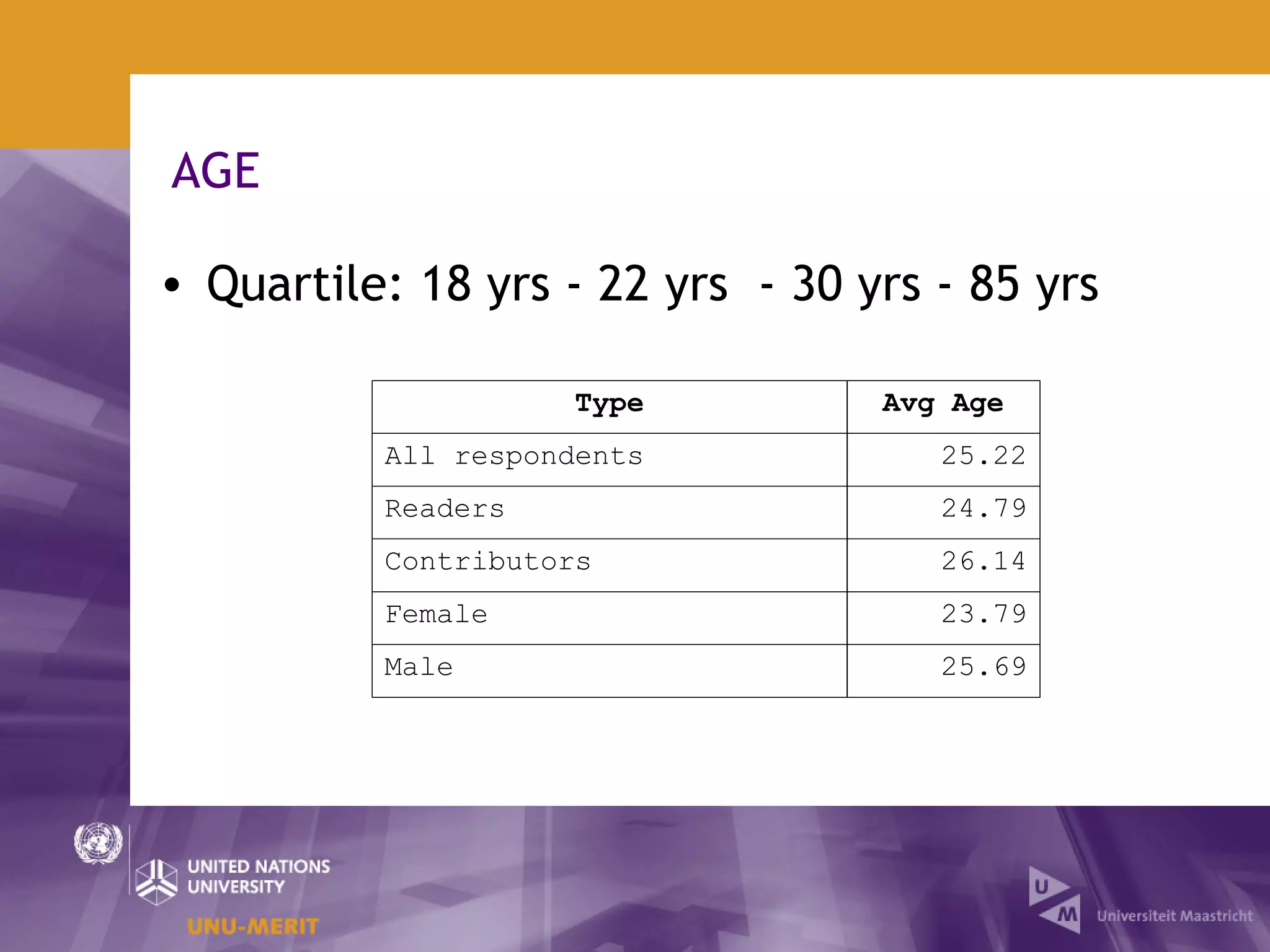
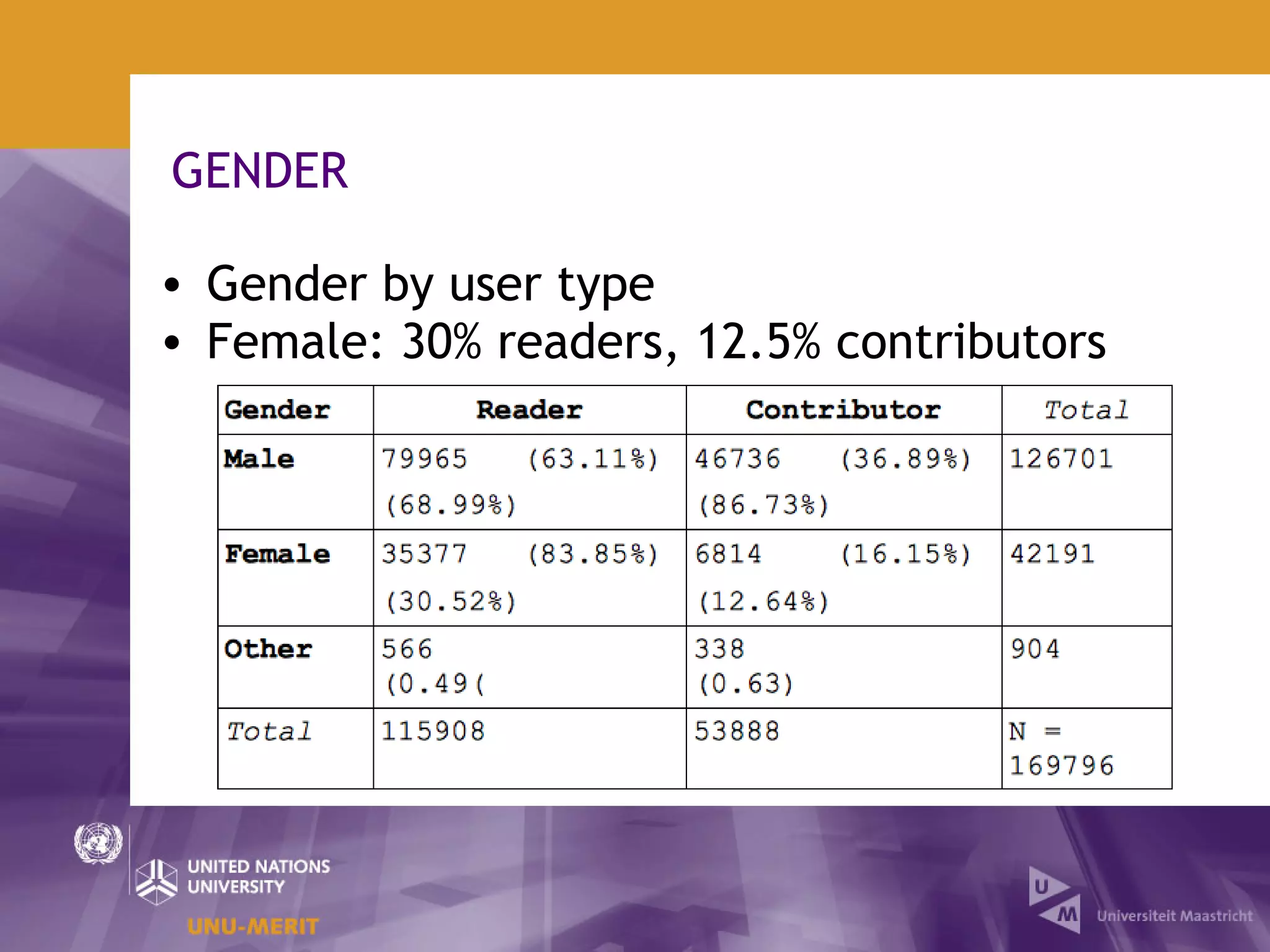
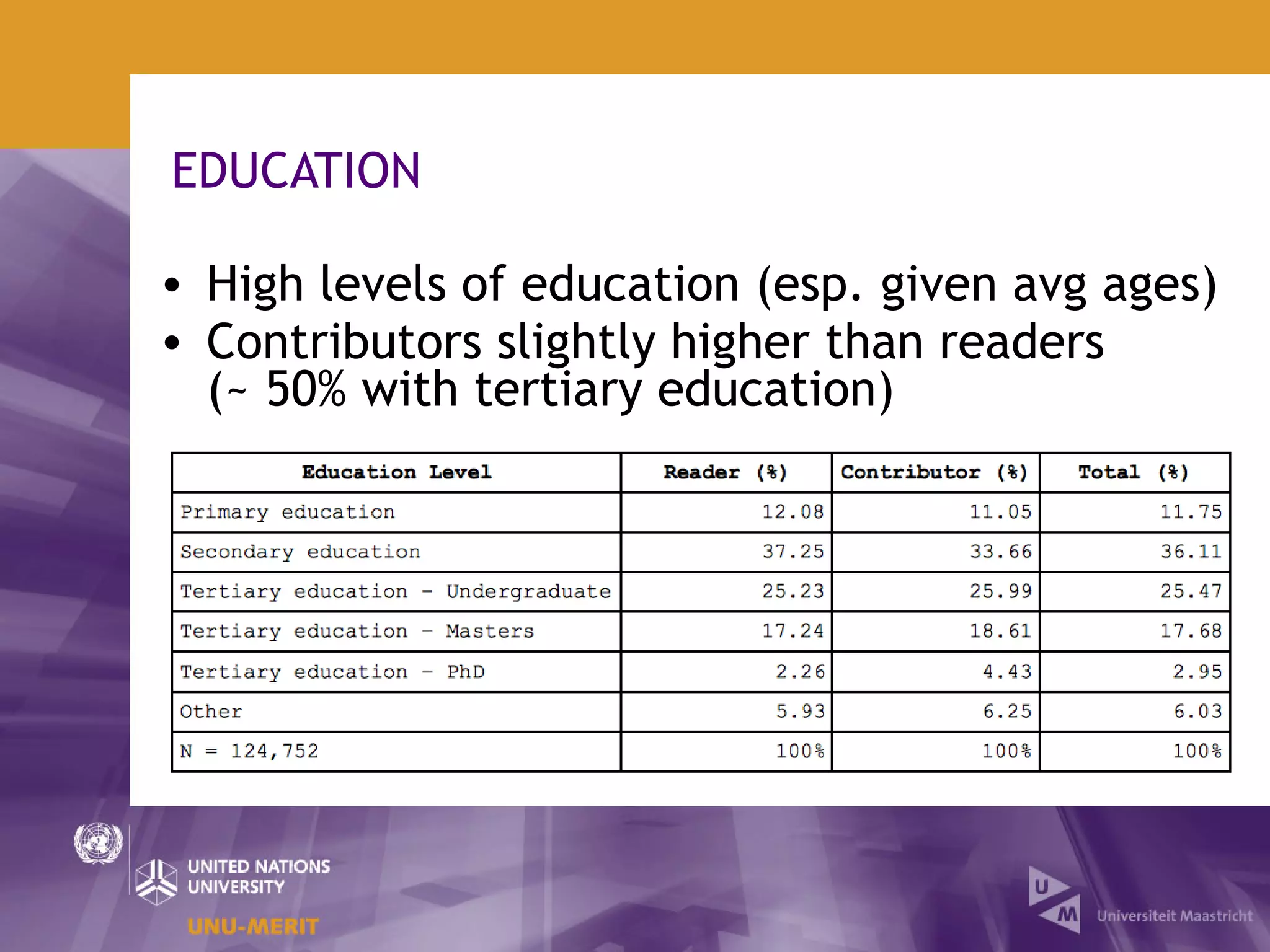
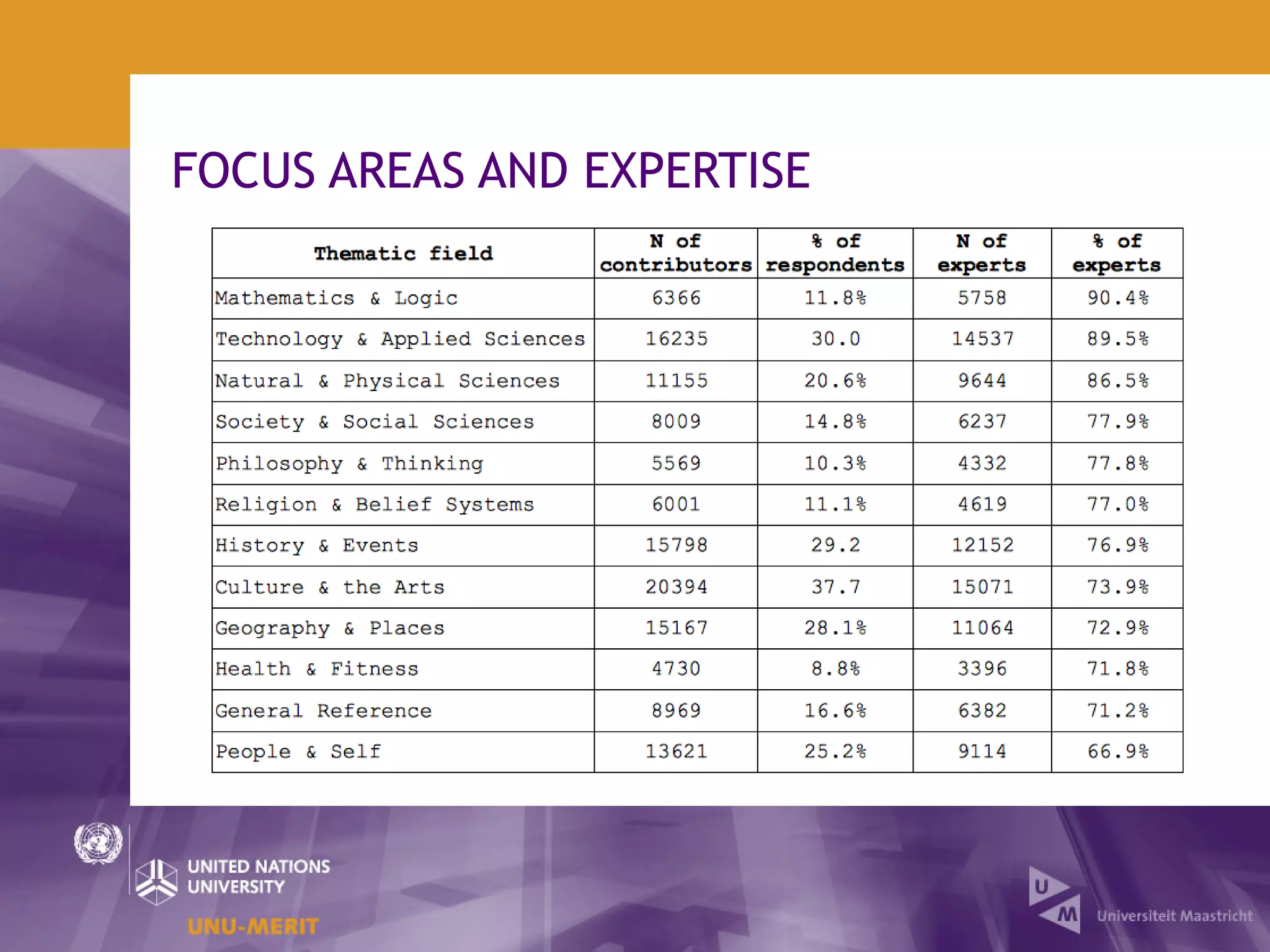
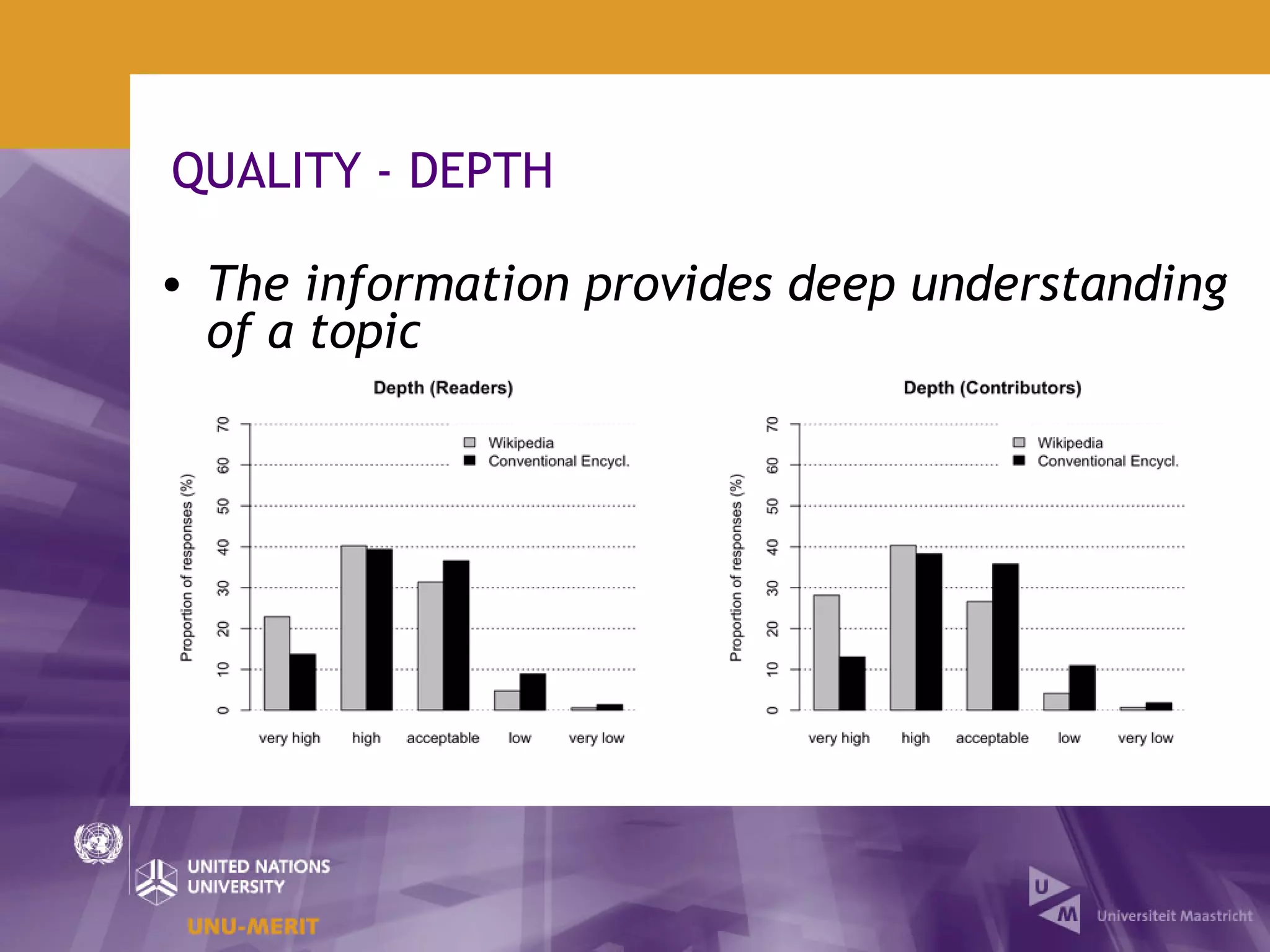
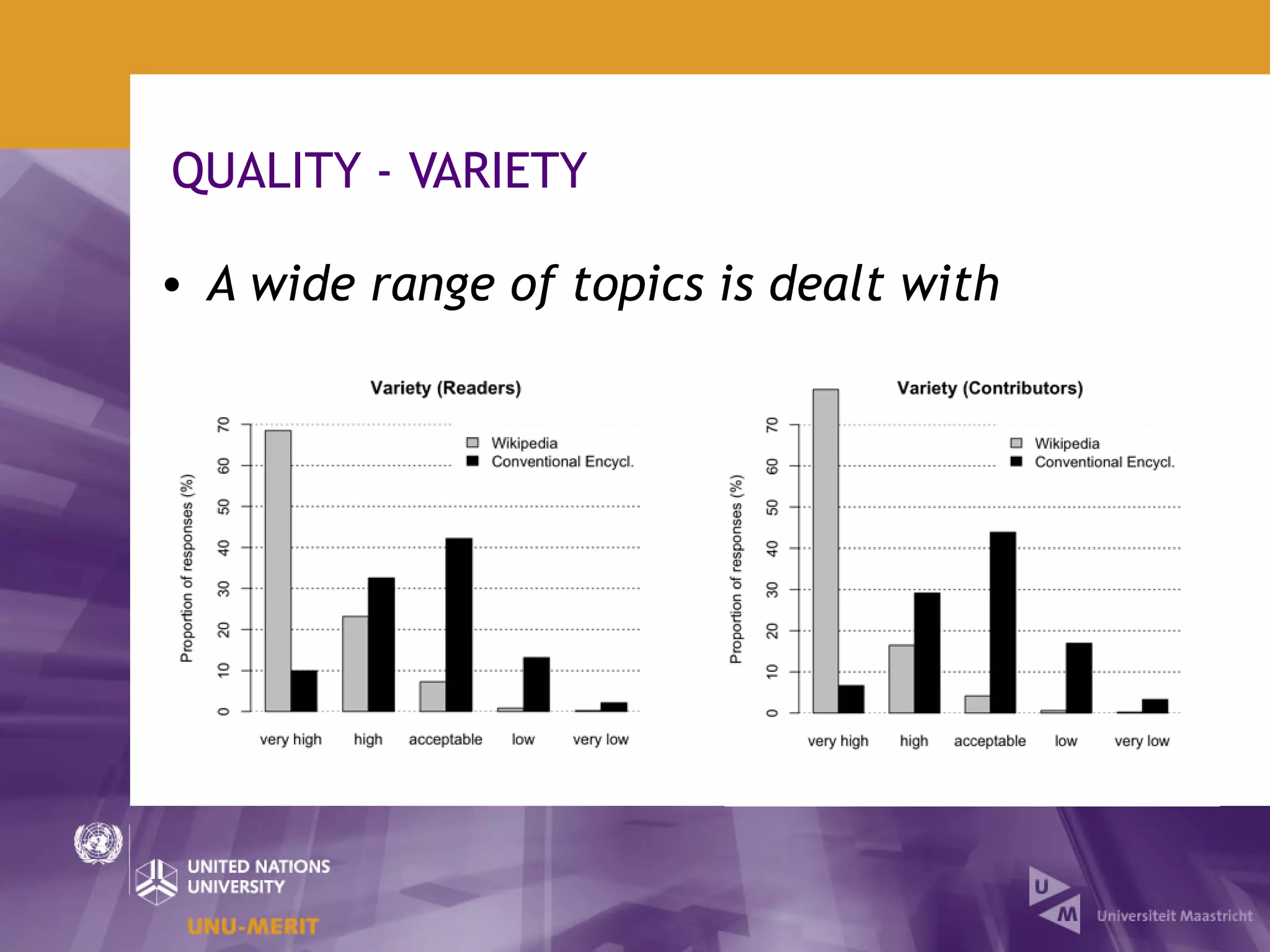
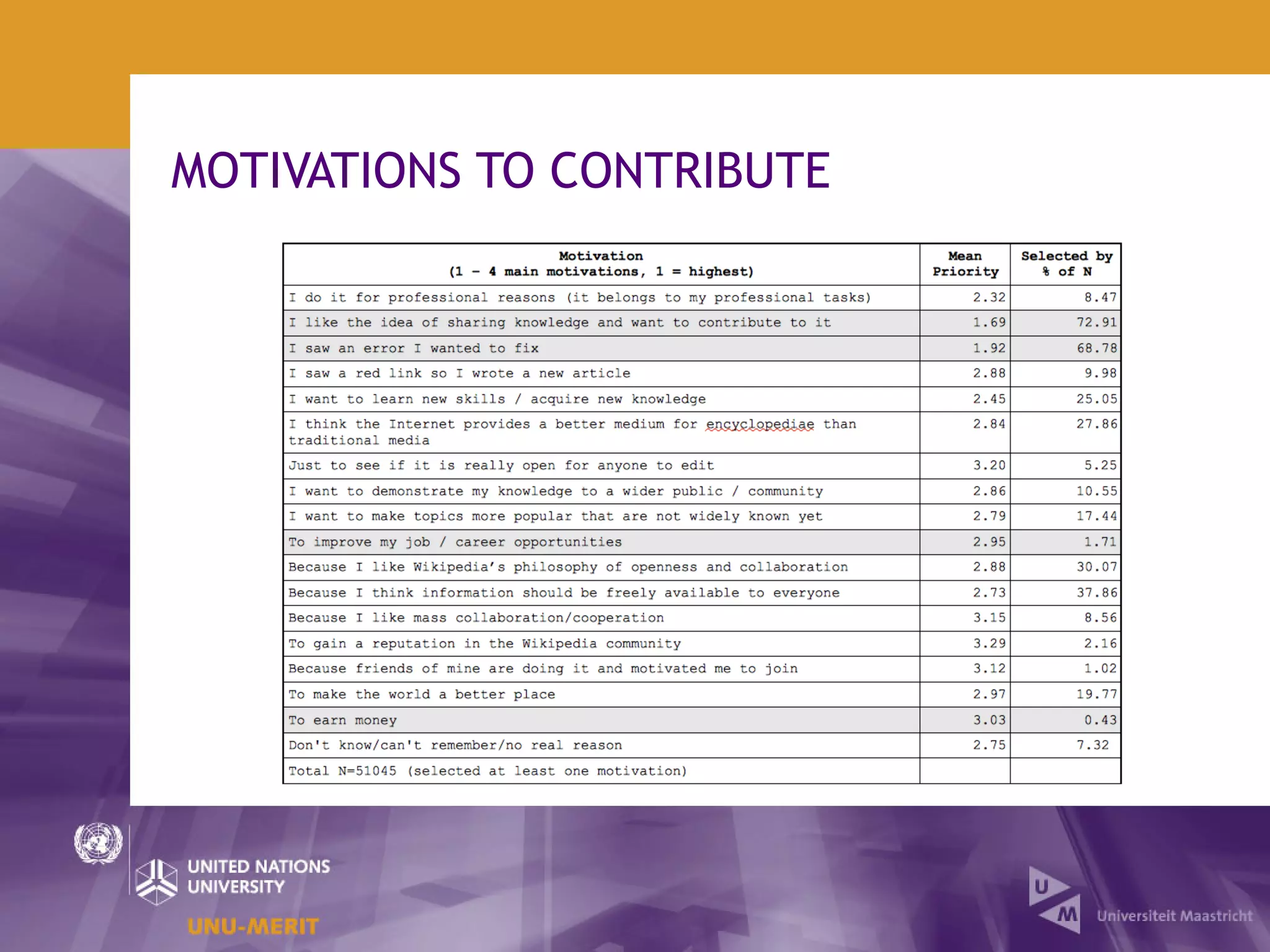
The document outlines the first official Wikipedia survey conducted in partnership with the United Nations University, focusing on the demographics, contributions, and perceptions of users and contributors. It details the methodology, scope, and findings from over 310,000 survey respondents across 22 languages, highlighting contributors' motivations, expertise areas, and perceptions of content quality compared to traditional encyclopedias. The survey aims to provide insights for the Wikimedia Foundation to enhance user engagement and content quality.