Untitled4
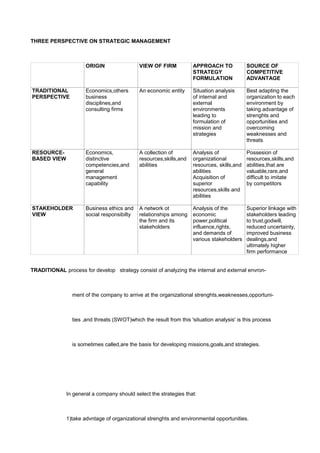
- 1. THREE PERSPECTIVE ON STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT ORIGIN VIEW OF FIRM APPROACH TO STRATEGY FORMULATION SOURCE OF COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE TRADITIONAL PERSPECTIVE Economics,others business disciplines,and consulting firms An economic entity Situation analysis of internal and external environments leading to formulation of mission and strategies Best adapting the organization to each environment by taking advantage of strenghts and opportunities and overcoming weaknesses and threats RESOURCE- BASED VIEW Economics, distinctive competencies,and general management capability A collection of resources,skills,and abilities Analysis of organizational resources, skills,and abilities Acquisition of superior resources,skills and abilities Possesion of resources,skills,and abilities,that are valuable,rare,and difficult to imitate by competitors STAKEHOLDER VIEW Business ethics and social responsibilty A network ot relationships among the firm and its stakeholders Analysis of the economic power,political influence,rights, and demands of various stakeholders Superior linkage with stakeholders leading to trust,godwill, reduced uncertainty, improved business dealings,and ultimately higher firm performance TRADITIONAL process for develop strategy consist of analyzing the internal and external envron- ment of the company to arrive at the organizational strenghts,weaknesses,opportuni- ties ,and threats (SWOT)which the result from this 'situation analysis' is this process is sometimes called,are the basis for developing missions,goals,and strategies. In general a company should select the strategies that: 1)take advntage of organizational strenghts and environmental opportunities.
- 2. 2)neutralizer or overcome organizational weaknesses and environmental threats. However,the traditional approach to strategy development also brought with it some ideas that strategic management schoolars have had to reevaluate. External Analysis (External Environment) Strategic Control Direction setting Vision Mission values Generate Evaluate and Select Strategies Allocate and Manage Resources Build Relationship Design Structures Develop Control System Measure and Evaluate Performance Internal Analysis (Internal Environment) Strategy Formulation Strategy Implementation and Evaluation The traditional supported the view of Deliberate strategy versus Emergent strategy. Deliberate Strategy implies that the manager plan to pursue an intended strategic course.In some cases strategy simply emerge from astream of dicision.Managers learns as they go. Emergent Strategy is one that was not planned or intended.According to this perspective,managers learn what will work through a process of trial and error.
- 3. RESOURCE-BASED VIEW=is a way of viewing the firm and in turn of approaching strategy. Funadamentally,this theory formulates the firm to be a bundle of resources.It is the resources and the way that they are combined.which make firms different from one another.It is considered as taking an inside out approach,while analysing the firm.This means that the starting point of the analysis in the in the internal environment of the organization. The resource -based view of the firm has it's roots in the work of the earliest strategic management theorists.General management capability is one ot first competencies identified.This led to the proposi- tion that firms with high quality general managers will outperform their rivals.Clearly.effective leadership is important to organizational performance,but it is difficult to specify what makes an effective leader.Edith Penrose she viewed firms as an administrative framework that coordinated the activities of numerous groups and individuals,and also as a bundle of productve resources.She studied the effect of various skills and abilities possessed by organization,concluding that a wide range of skills and resources could influence competitive performance.In which this this bundle of resources has fall into general five categories: STAKEHOLDERS VIEW:
- 4. Stakeholders a group or individual who can significantly affect or significantly affected by an organi- tion's activities.Stakeholders approach to strategic management=envision the firm at the center of a net- work of contituencies called stockholders:firm can gain competitive advantage through superior stake- holder management.It was developed as a direct response to the concerns of the managers who were being buffetted by increasing levels of complexity and change in the external environment.Stockholder were the only important constituency of the modern for-profit corporation.A firm has internal stake- holders,such as employees,who are considered a part of the internal organization.In addition,the firm has frequent interactions with stakeholders in what is called the operating (or task)environment. STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT PROCESS = meaning steps and component.or defining the organi- zation's strategy.It also define as the process by which managers make a choice of a strategies for the organization that will enable it to achieve better performance.Strategic management is a continous pro cess that appraises the business and industries in which the organization is involved appraises its com- petitors and fixes goals to meet all the present and future competitors and then reassesses each strategy. Four steps of straegic management process
- 5. Environmental scanning=refers to a process of collecting,scrutunizing and providing information for strategic purposes.It helps in analyzing the internal and external factors in- fluencing in organization. Strategy formulation= process of deciding best course of action for accomplishing organizational objectives and hence achieving organizational purposes. Strategy implementation=implies making the strategy works as intends or putting the organizations chosen strategy into action.includes designing organization structure distri- buting resources,developing dicision making process, and mnaging human resources. Strategy evaluation= is the final steps of strategy management process.The key strategy evaluation activities are:appraising internal and external factors that are the root of presenst strategies,measuring performannce,and taking remedial/corrective actions.Evaluation makes sure that the organization strategy as well as it's implementation meets the organization objectives. .
- 6. FINANCIAL=it is referred to as the money available to any business or te organization for spending or to transact in the form of cash,liquid and securities and credit lines.It is the basic supply and used for the circulation of te business.Financial resources, is the main sources in operating or managing a business.It is stated above that it may be liquid meaning to say it has the ability to convert asset to cash quickly.And the most liquid of all is cash itself. But take note that the more it is liquid the greater the risk.Cash coud be in the hand or in bank. Example: You will buy a specific equipment to enhance the speed of the operation like machine and other facilities,the owner of the company will use his/her check in paying the one he/ she purchased. Money is also used to pay liabilities in bank if the company borrowed from the bank or any loan type of business.Among the five resources,financial resources is the most important because it is the one used in acquiring all of the other resources.Before entering
- 7. a business,the owner must ensure and provide the capital or investments and expenses.It must also suffecient in order to be able to operate effeciently and suuffeciently to promote success and to achieve its mission.These are also used in payment to the laborers and em- loyees,to the supplies needed,to the raw materials needed in the production,to the mache- neries and equipments that helps shorten the production time and to the distribution of the processed goods that will be available to the market.Not only that,money is also used in advertisement the product to attract the consumers.And with that,it could easily be sold and greater profits will be generated.If the company gets a great profit and gives emplo- yees great benefits it will give a good reputation to the public,to the management team and to the overall business and will as well have a strong relationship with its current partners HERZBERG'S TWO FACTOR THEORY: A)Hygiene Factors- hygiene factors are those job factors which are essential your existence of moti vation at workplace.These do not lead to positive satifaction for long term.But if there's is factors factors are absent/if these factors are non-existant at workplace,then they led to dissatisfaction.In other words,hygiene factors are those factors which when adequate/reasonable in a job,pacify the
- 8. employees and do not make them dissatisfied.These factors are extrinsic to work.Hygiene Factors are also called as dissatisfiers or maintenance factors as they are required to avoid dissatisfaction. These factors describe the job enviroment/scenario. The hygiene factors symbolized the pyhsiolo gical needs which the individuals wanted and expected to be fullfilled. Hygiene factors includes: Pay – The pay or salary structure should be appropriate and reasonable.It must be equal and com petitive to those in the same industry in the same domain. Company Policies and Administrative Policies – The company policies should not be too rigid. They should be fair and clear.it should include flexible working hours,dress code,breaks,vacation, etc. Fringe Benefits – The employees should be offered health care plans (mediclaim)benefits for the family members,employee help programmes,etc. Pyhsical Working Condition – The working condition should be safe ,clean and hygienic.The equipments should be updated and well maintained. Status – The employees status within the organization should be familiar and retained. Interpersonal Relations – The relationship of the employees within his peers, superior and subor
- 9. dinates should be appropriated and acceptable.These should be no conflict or humiliation element present. Job Security – The organization must provide job security tp the employees... B) Motivational Factors – According Herzberg the hygiene factor cannot be regarded as motivators. The motivational factors yield positive satisfaction.These factors are inherent to work.These factors motivates employees for a superior performance.These factors called satisfier.These factors invol ved in performing the job.Employees find thid factors intrisincally rewarding.The motivators sym bolized the psychological needs that were perceived as an additional benefit. Motivators Factors Include: Recognition – The employees should be praised and recognized for their accomplishments by the managers. Sense of Achievement – The employees must sense of achievement.This depends on the job.There must be a fruit of some sort in the job. Growth and Promotional Opportunities – There must be growth and advancement opportunities
- 10. in an organization to motivate the employees to perform well.. Responsibilty - The employees must hold themselves responsible for the work.The managers should give them ownership of the work.They should minimize control but retain accountability. Meaningfulness of the work – The work itself should meaningful,interesting and challenging for the employee to perform and to get motivated... The two factor theory is not free from limitation: • The two factor theory overlooked situational variables • Herzberg assumed a correlation between satisfaction and productivity.But the research conducted by Herzberg stressed upon satisfaction and ignored productivity. • The theory reliability is uncertain,analysis has to be made by the raters.The raters may may spoil the findings by analyzing same response in different manners. • No comprehensive measures of satisfaction was used.An employee may find his job acceptable despite the fact that he may hate/object part of his job. • The two factor theory is not free from bias as it is based on the natural reaction of emplo
- 11. yees when they are enquired the sources os satisfaction and dissatisfaction at work.They will blame dissatisfaction on the external factors such as salary structure,company policies, and peer relationshi.Also,the employees will give credit to themselves for the satisfaction factors at work. • The theory ignores blue-collar workers.Despite this limitation,Herzberg two factors theory is acceptable broadly. CONCLUSION: Therefore,The two factor theory implies that the manager must stress upon guaranteeing the ade quacy of the hygiene factors to avoid employee dissatisfaction.Also.the managers must make sure that the work is stimulating and rewarding so that the employee are motivated to work and per form harder and better.This theory emphasize upon-job enrichment sa as to motivate the employees. The job must utilize the employees skills and competencies to the maximum.Focusing on the motivational factors can improve work equality.
- 12. Assignment A. FIVE COMMON INTERVIEWING MISTAKES • FAILING TI RESEARC A COMPANY: You will put yourself at a disadvantage before you even walked into an interviewers office if you fail to prepare for the discussion in advance.Primarily,this means learning as much as possible about propective employee. Hiring manager will assume that you have at minimum,invistigated their organization's web site,so expand the score of your research efforts.Use your professional network and industry publication to determine the company's priorities.Competitors and market position this will help you translate your expertise into concrete examples of how you can make difference
- 13. at the firm. • SAYING TOO LITTLE/TOO MUCH: As you respond to interview questions,you do not want to gloss over vital information but you also do not want to go into too much detail.Both extremes can create a negative impre ssion with hiring managers.If your response is to brief,interviewers may wonder if you are hiding something.If they are too lenthly,people may tune you out. Here Again,the key to achieving the right balance is advance preparation and practice.Be fore interviewer,think about your answer to question on interviewer is likely to ask about your background.Be prepared to support broader statement with specific examples that showcase your accountingand leadership skills. Consider practicing your responses with friends,family and trusted colleagues.They can pro vide candid feedback that can help you refine your answers and ensure they are the appro priate length. • IGNORING CUES FROM THE INTERVIEWER: One of the most valuable,and under rated,interviewing skills is the ability to listen, pay
- 14. attention to, understand and absorb what the other person is saying.If you concentrate too instantly on forming your responses,you can miss critical information offered by the hiring managers. Throughout the discussion,interviewer may provide useful clues as to what they are looking for candidates,allowing you to tailor yur answer to their requirements. For example,a chief financial officer might mention that the company is undergoing rapid growth-which can indicate a need for employees who adopt easily to afast-paced environ ment and assume challenging demand. • NOT BEING YOURSELF: Even though you want to customize your answer based on what you learn from the inter viewer to emphasize skills must applicable to the position,be careful not to overstate your case.Not only do you want avoid strethching the truth,but the hiring manager may not reveal every aspect that is important for the winning candidates to posses.In other words don't get so focused on saying the “right thing” that you do not give an accurate portrayal of your skills and interests.
- 15. For instance, exaggerated your role in analyzing operating metrics because you think that is what the job calls for,while failing to place emphasis on your proven ability to identify cost saving opportunities- acompetency the firm may actually value more Remember,it become both yu and the hiring manager if you present an accurate picture of your qualification so an appropriate match can be made to the position. • FAILING TO TAKE THE OPPORTUNITY TO ASK QUESTION: Interviewer are two-way street,so be ready with your own questions at the end of the dis cussion.Prepare a few before you arrive and write down any additional issues that arise as the conversation progress. Make certain you ask specific question a company's mission and business practices and expectations to determine wether they are realistic and in line with your own preferences. Also,find out about the organizations long-term priorities and how your contributions would impact these plans..
