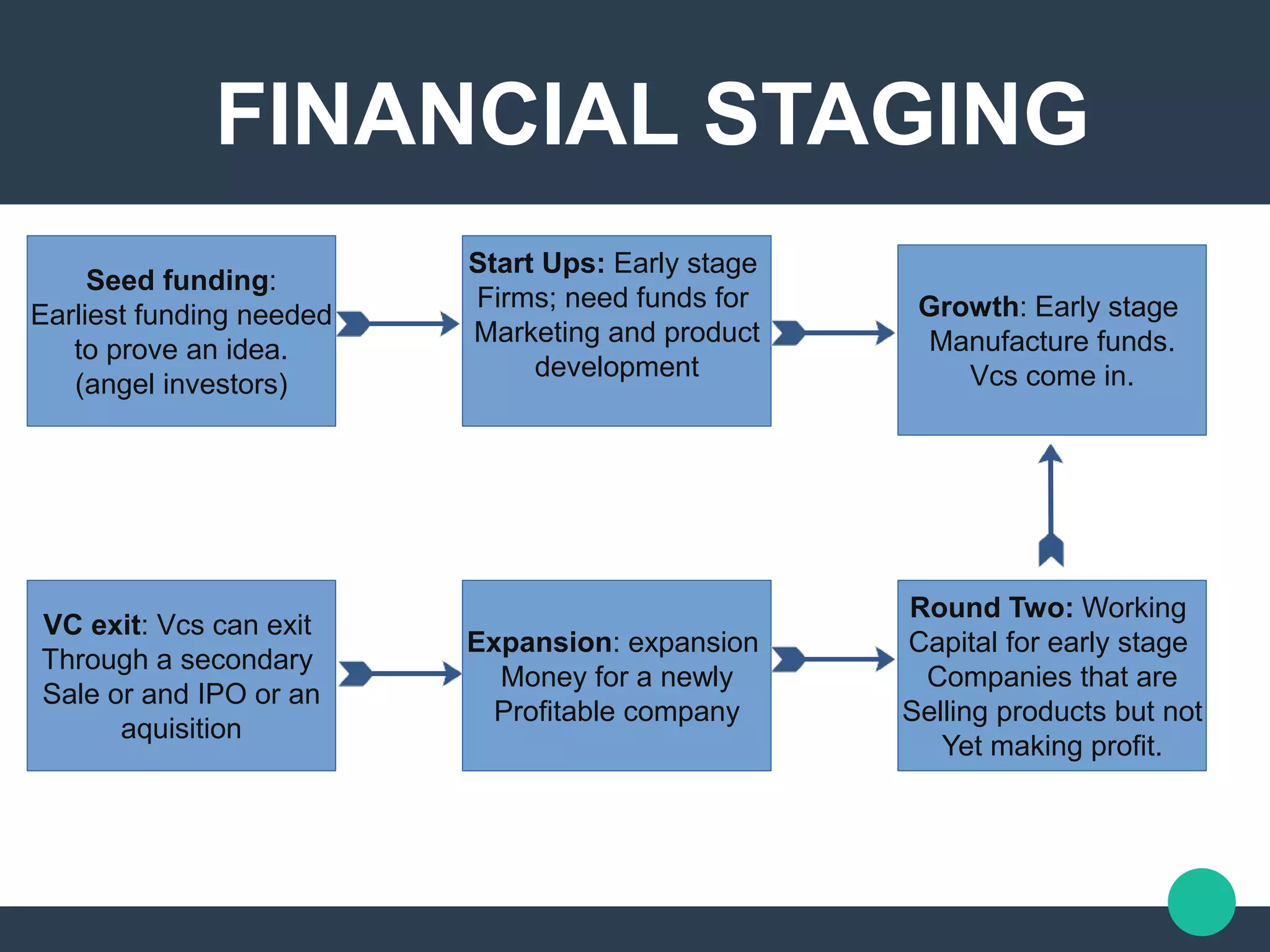
Venture capitalism involves VC firms providing financing to small emerging companies in exchange for equity. VC firms are structured as partnerships with general partners who manage investment funds raised from limited partners like pension funds and insurance companies. Funding is provided in stages from seed funding to help prove ideas to later expansion funding for profitable companies. In return, VC firms receive management fees and a carried interest typically around 20% of profits, providing startups with financial as well as business expertise and connections. However, startups lose some control and ownership as VCs seek involvement matched to their ownership stake.