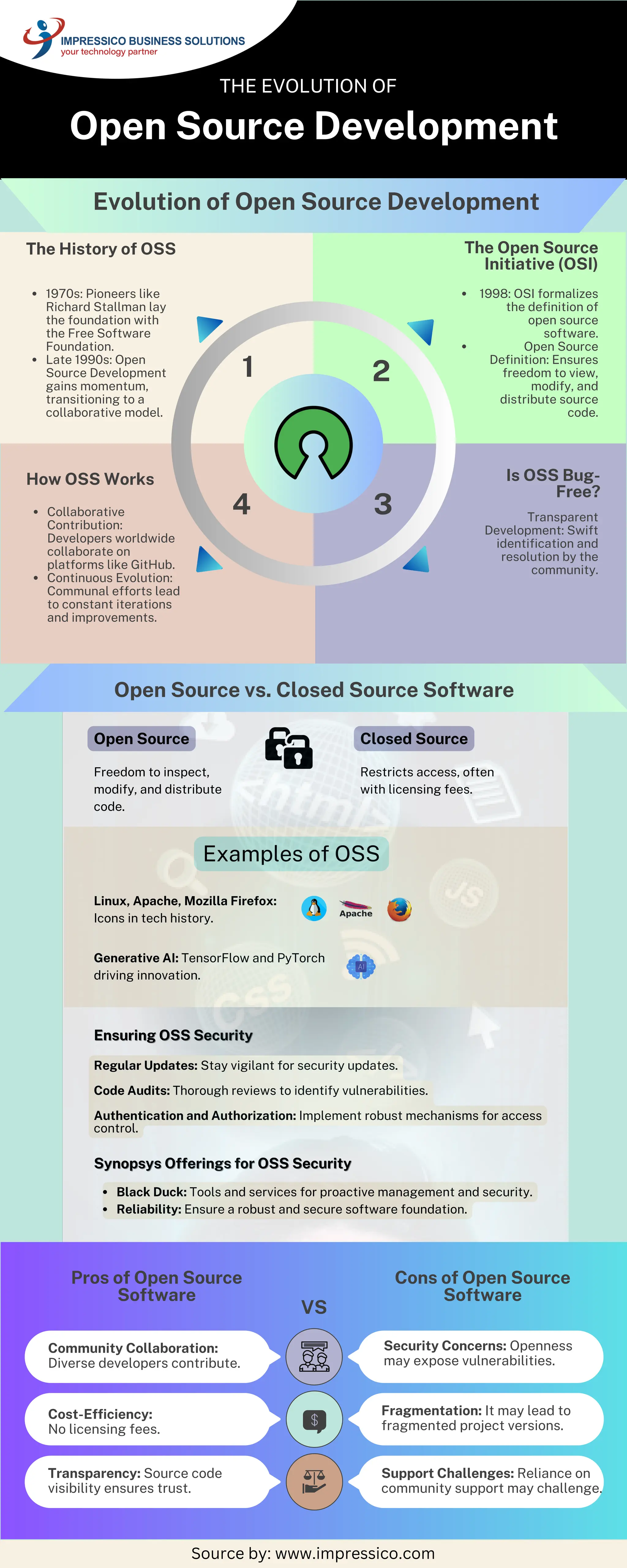
The document compares open source software (OSS) with closed source software, highlighting OSS's freedoms and community-driven development while mentioning security concerns and challenges. It outlines the history of OSS, including key milestones and the role of the Open Source Initiative in formalizing its definition. Key points include the benefits of community collaboration, cost-efficiency, and transparency, along with potential drawbacks like security vulnerabilities and reliance on community support.