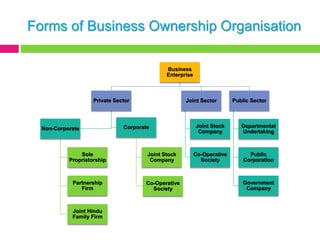
This document outlines the syllabus for a course on the legal environment of Indian business. It covers topics like the Indian Companies Act of 1956, including the meaning and nature of companies, registration and incorporation procedures, memorandums and articles of association, directors' duties and powers, and general meetings. It also provides important links to resources on the Companies Act, the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, and company law basics. The key aspects of a company that are discussed include its separate legal identity, perpetual succession, ownership of property, limited liability of shareholders, transferable shares and board management structure.