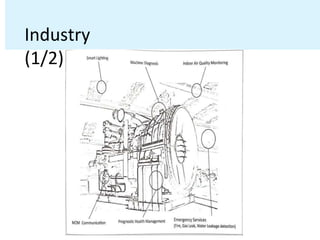
This document outlines various applications of IoT across different domains including home automation, cities, environment, energy, retail, logistics, agriculture, industry, and health & lifestyle. It provides examples of how IoT can be used in each domain such as using sensors and devices to monitor homes, infrastructure, environmental conditions, energy systems, inventory levels, fleet tracking, agricultural processes, machine operations, and individual health and fitness. The goal is to collect data from distributed sensors and devices to provide insights, automation, and alerts to improve processes and operations in each sector.