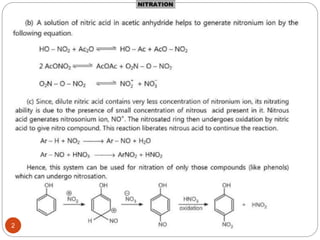
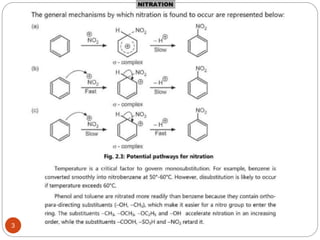
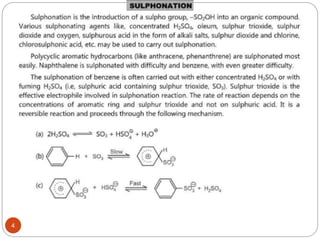
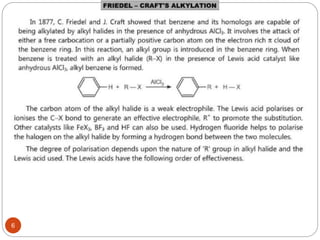
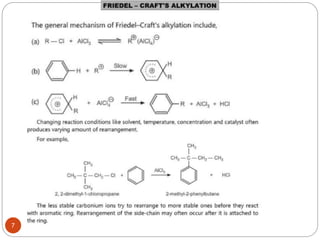
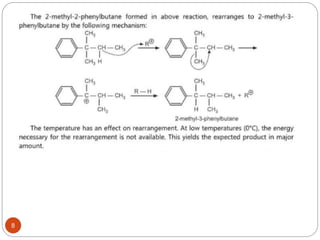
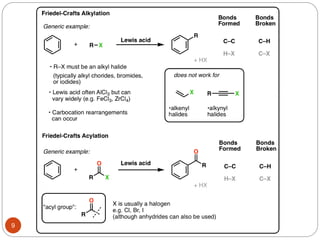
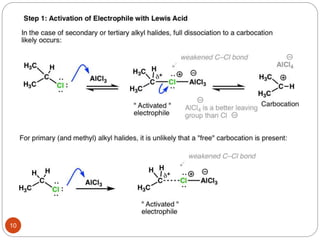
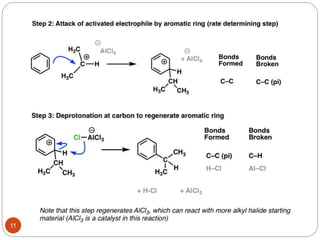
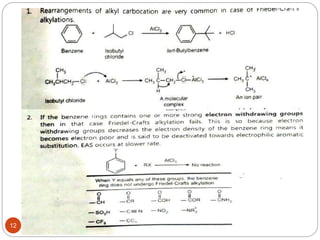
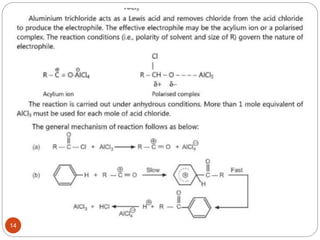
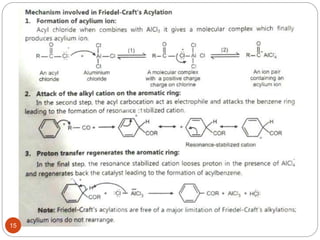
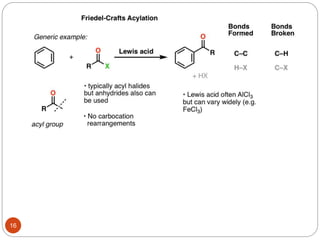
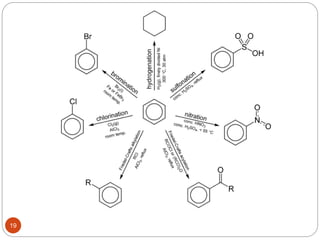
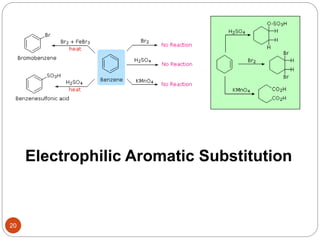
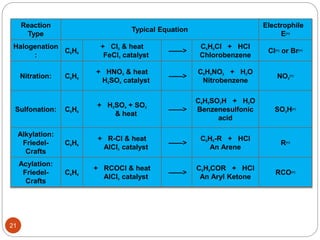
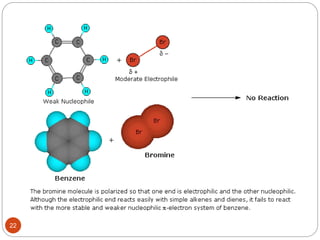
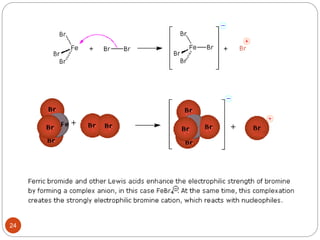
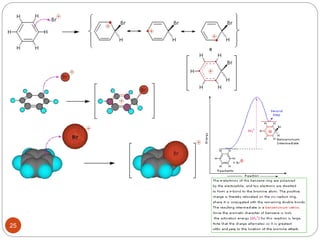
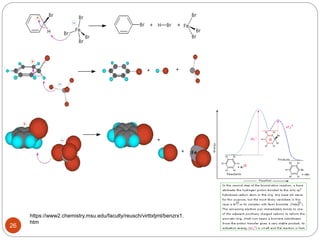
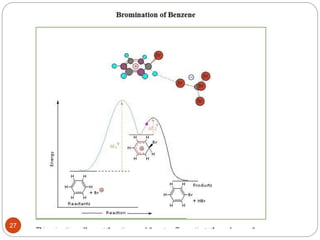
The document discusses electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions of benzene, including nitration, sulfonation, halogenation, Friedel-Crafts alkylation, and Friedel-Crafts acylation. These reactions involve an electrophilic species attacking the benzene ring. A two-step mechanism is proposed where the electrophile first forms a sigma complex with the benzene ring, generating a positively charged intermediate. This is then followed by a rapid loss of a proton to form the substituted benzene product.