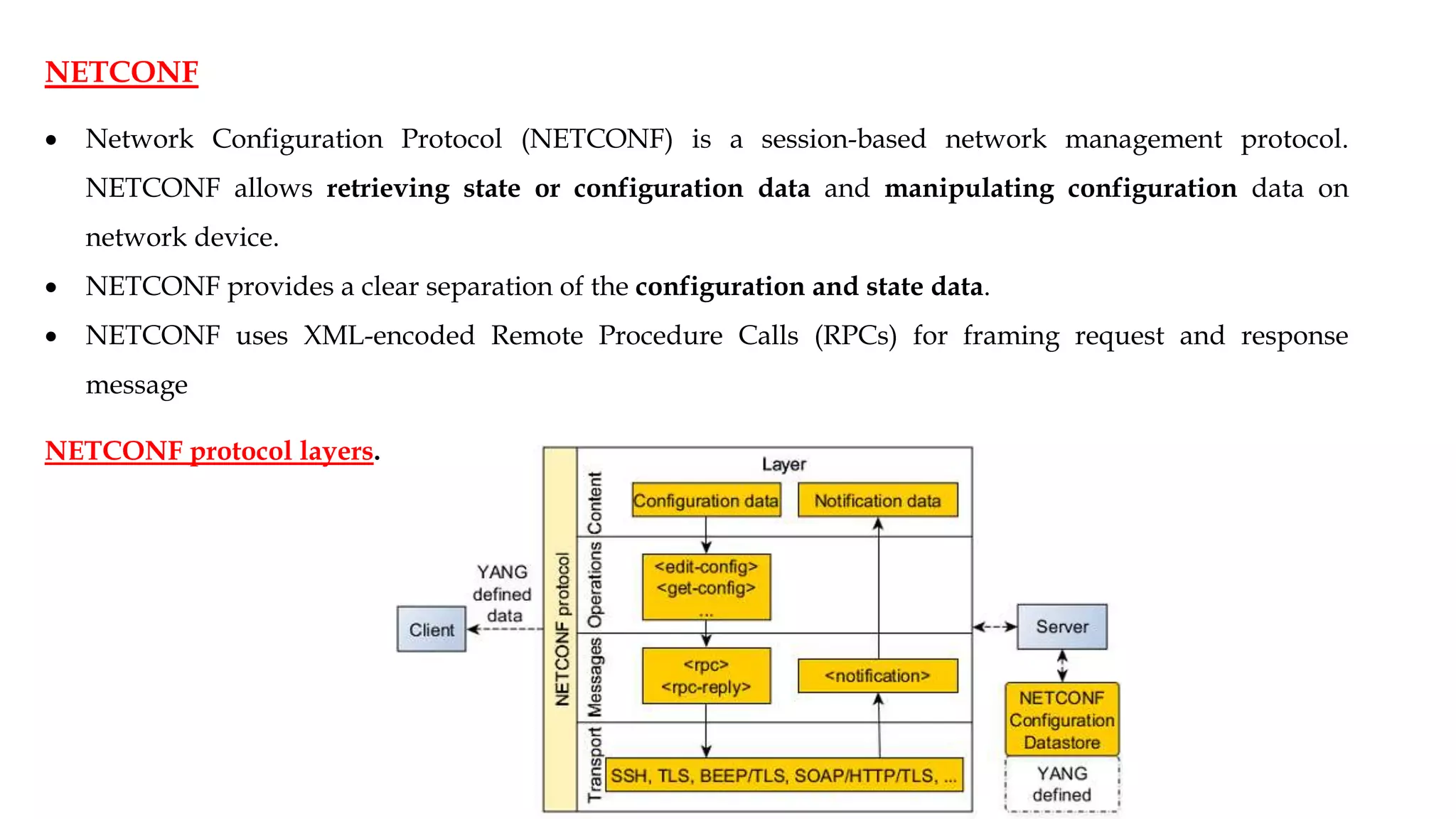
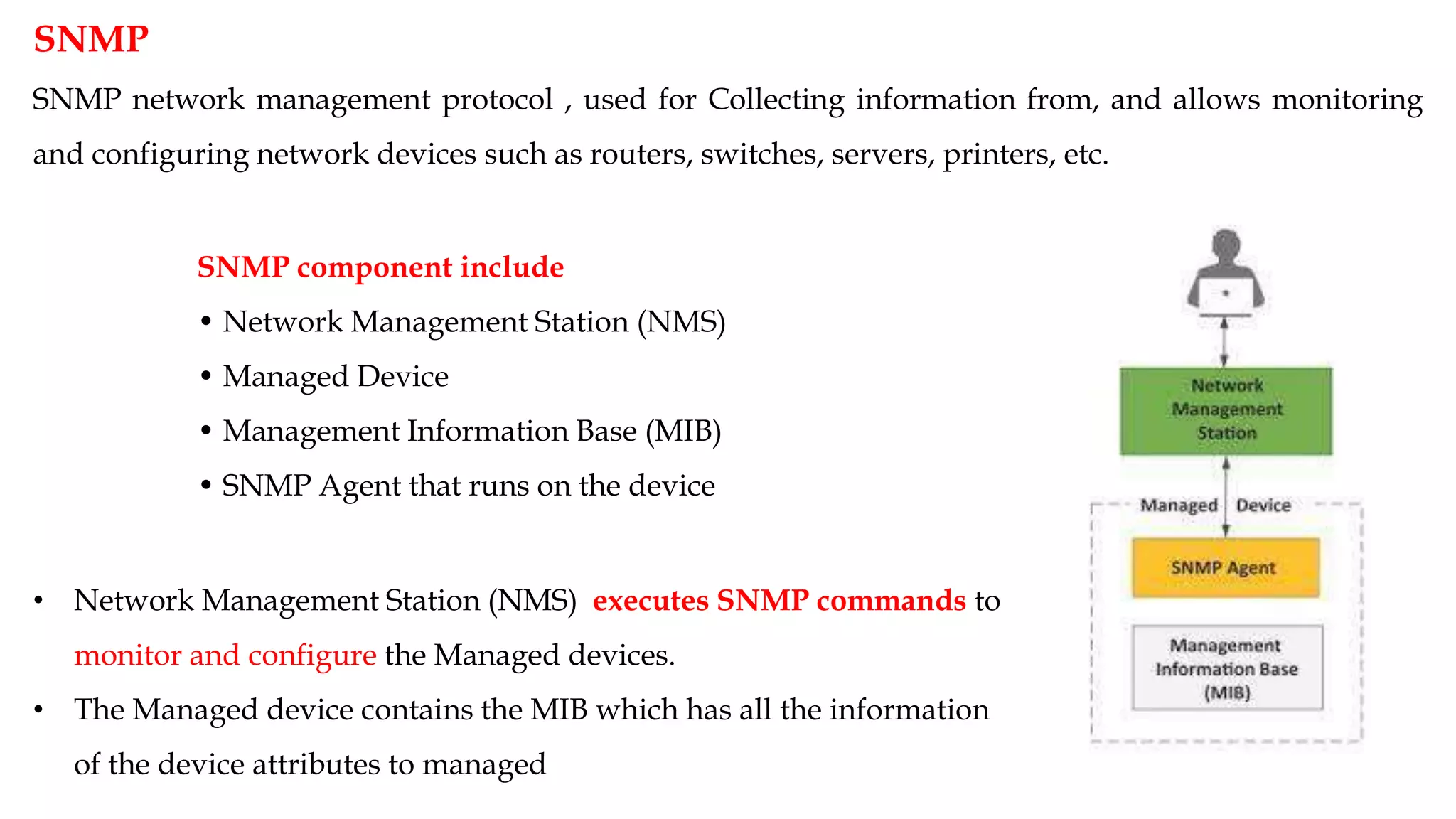
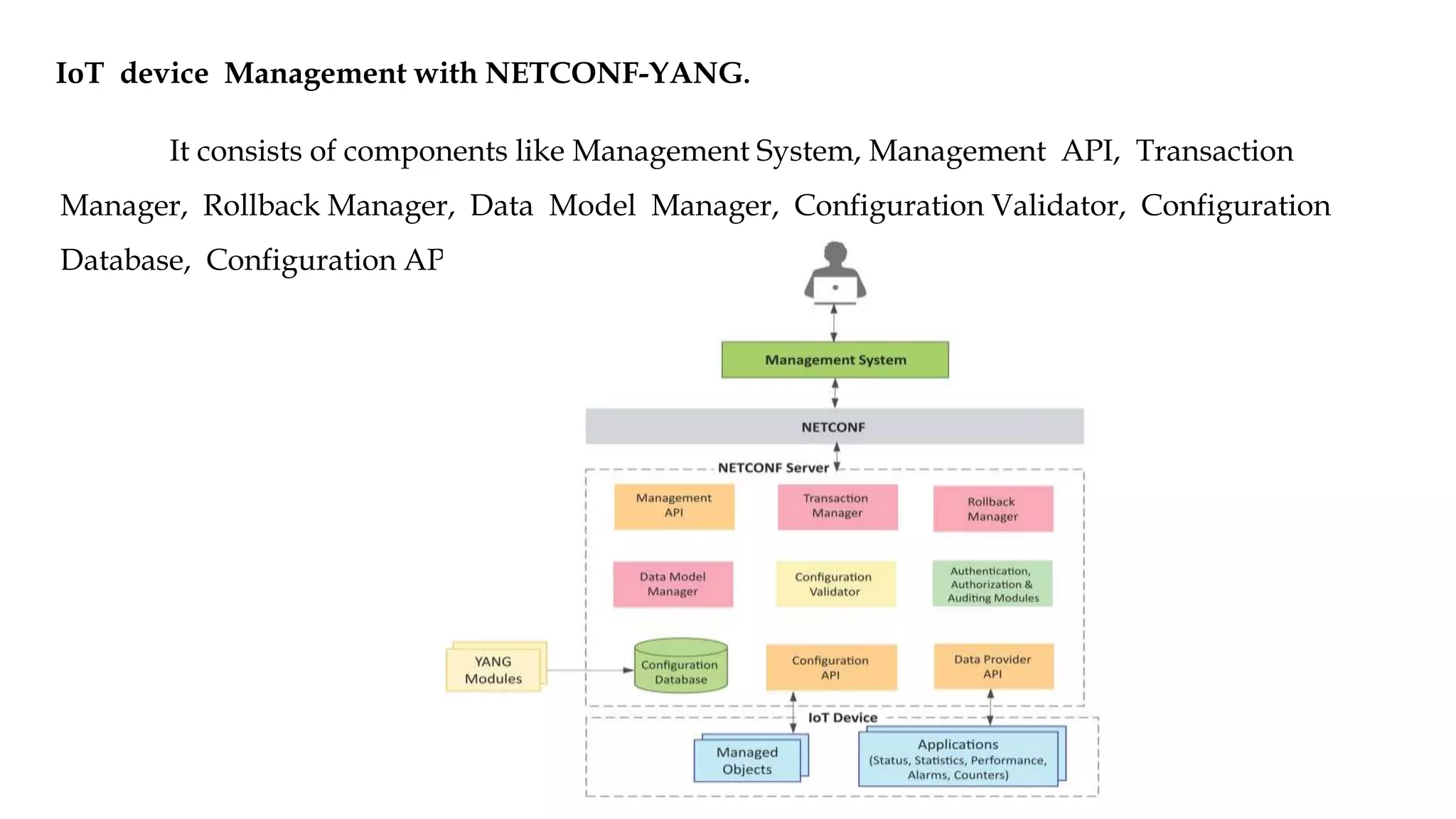
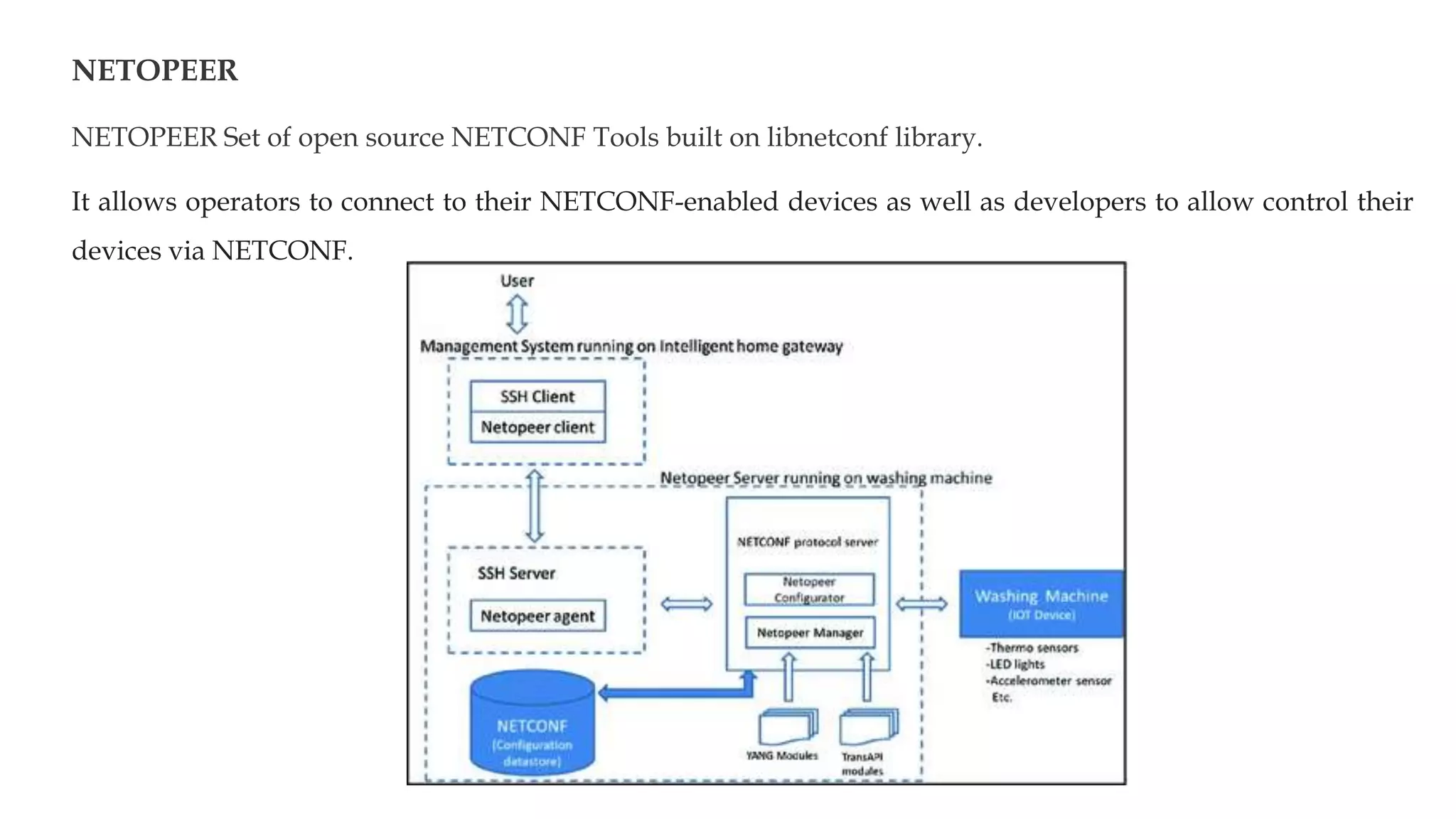
NETCONF is a network configuration protocol that uses XML-encoded RPCs to install, manipulate, and retrieve configuration data from network devices. It provides a clear separation of configuration and state data and uses a layered model including a secure transport layer, message layer, operations layer, and content layer based on YANG modeling. NETCONF allows network administrators to manage device configurations and models network data.