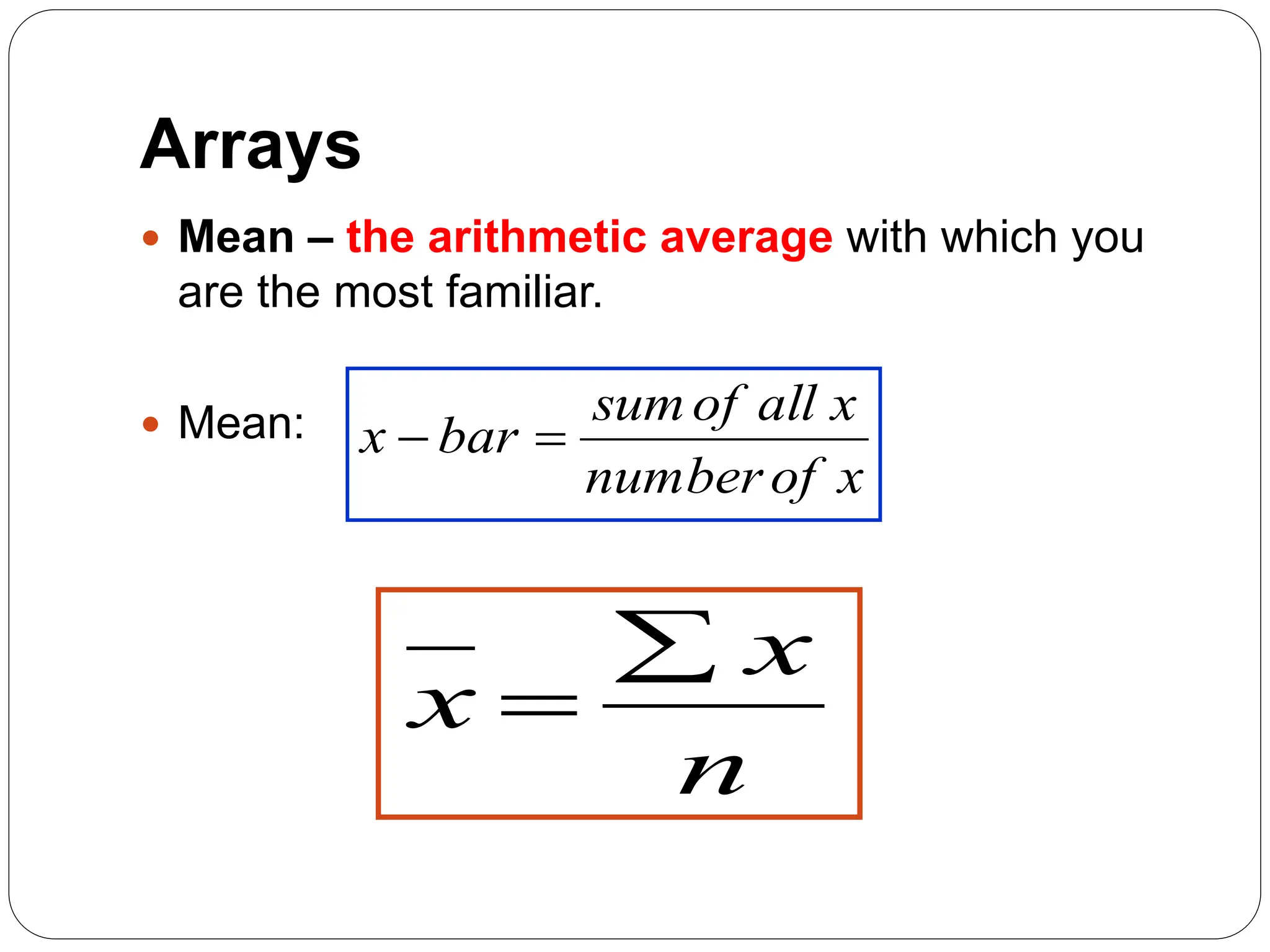
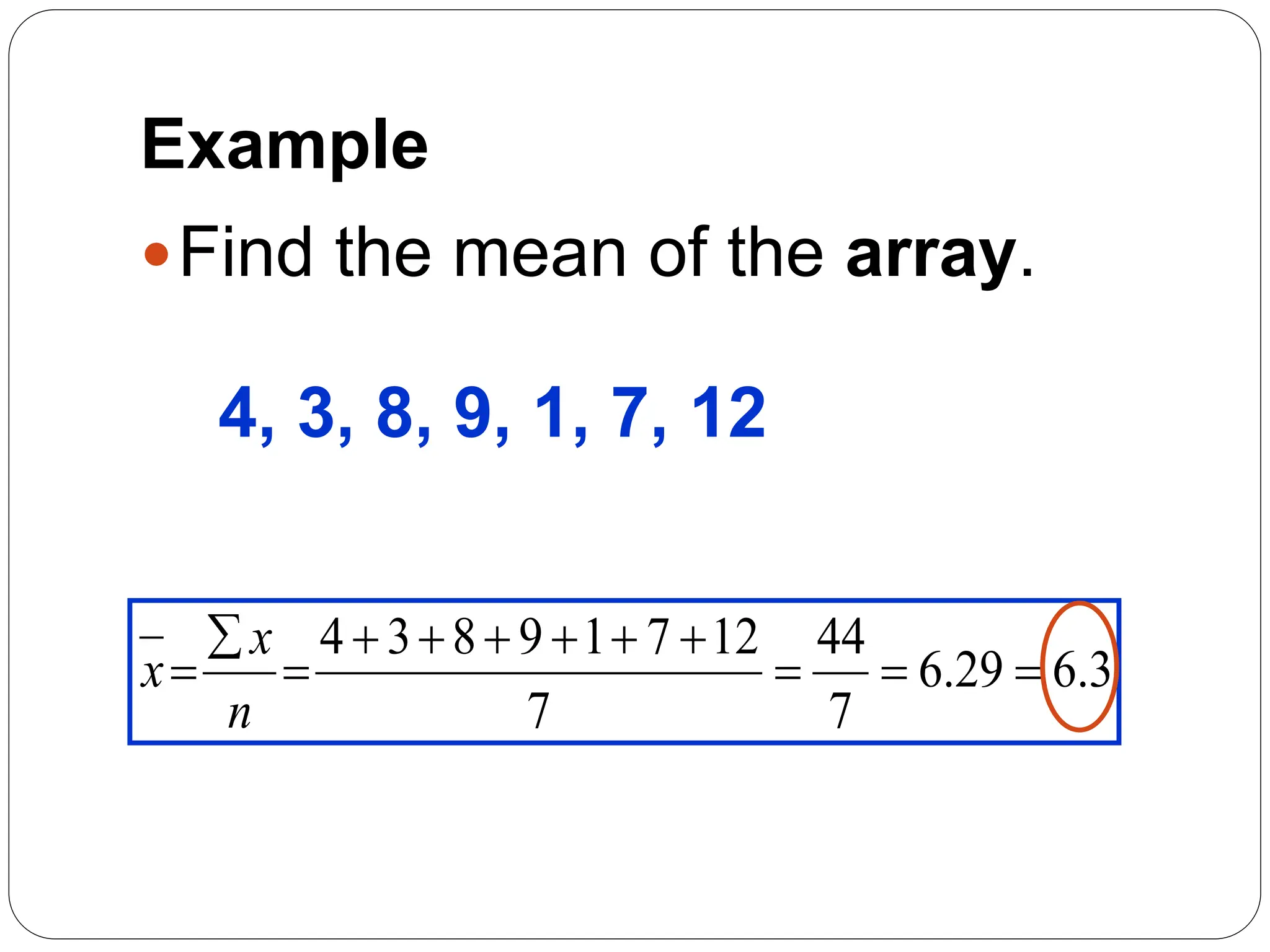
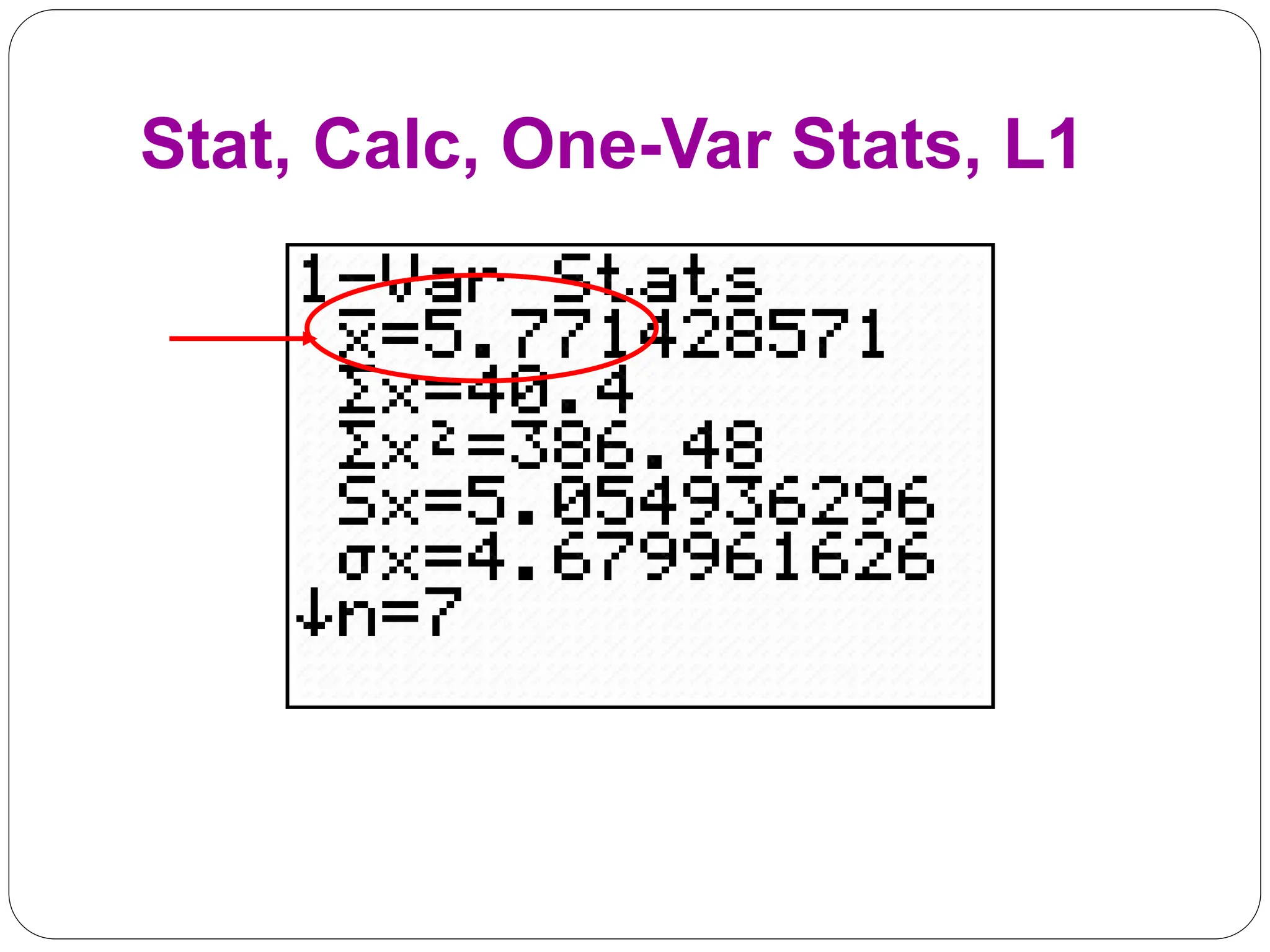
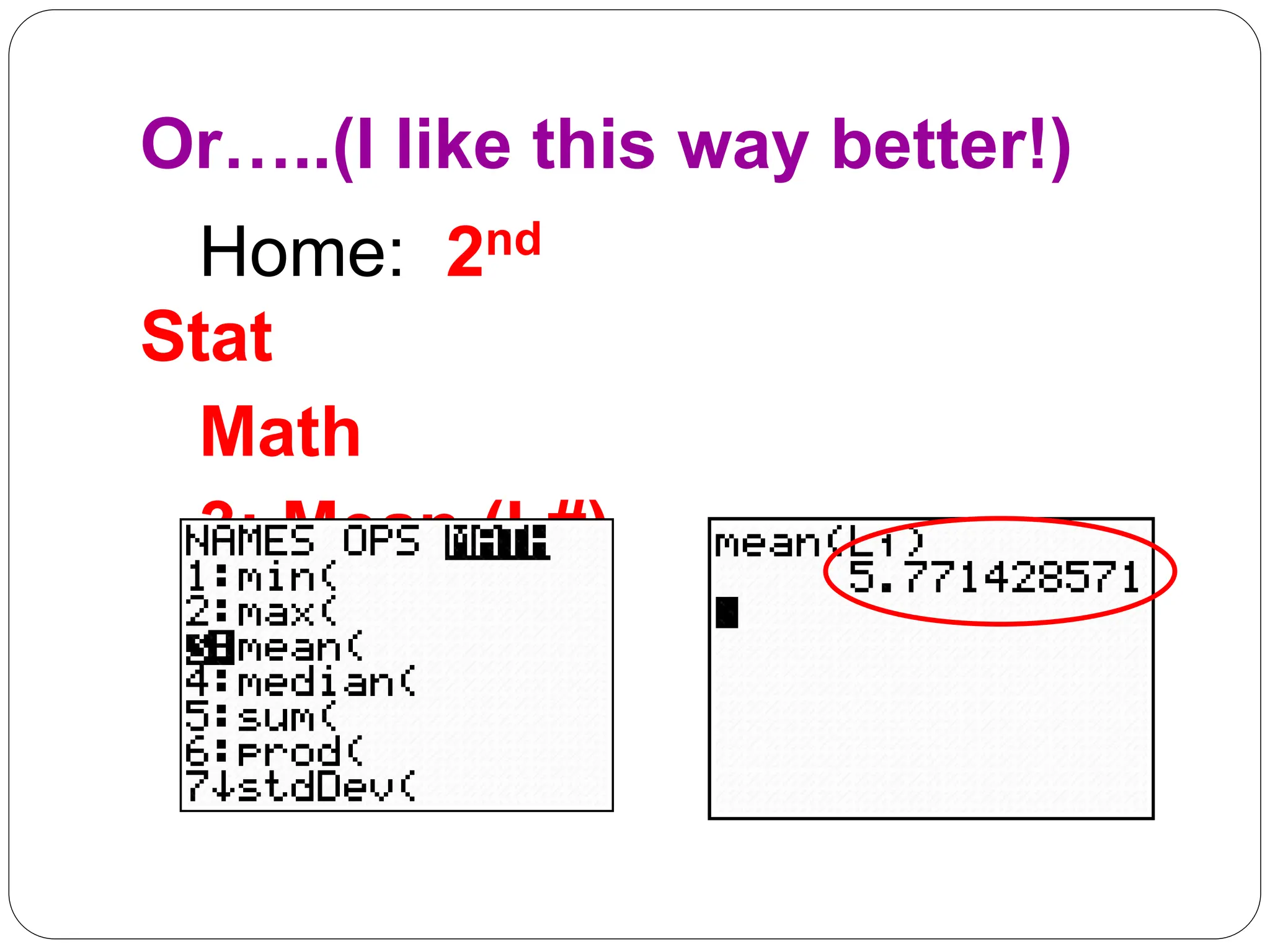
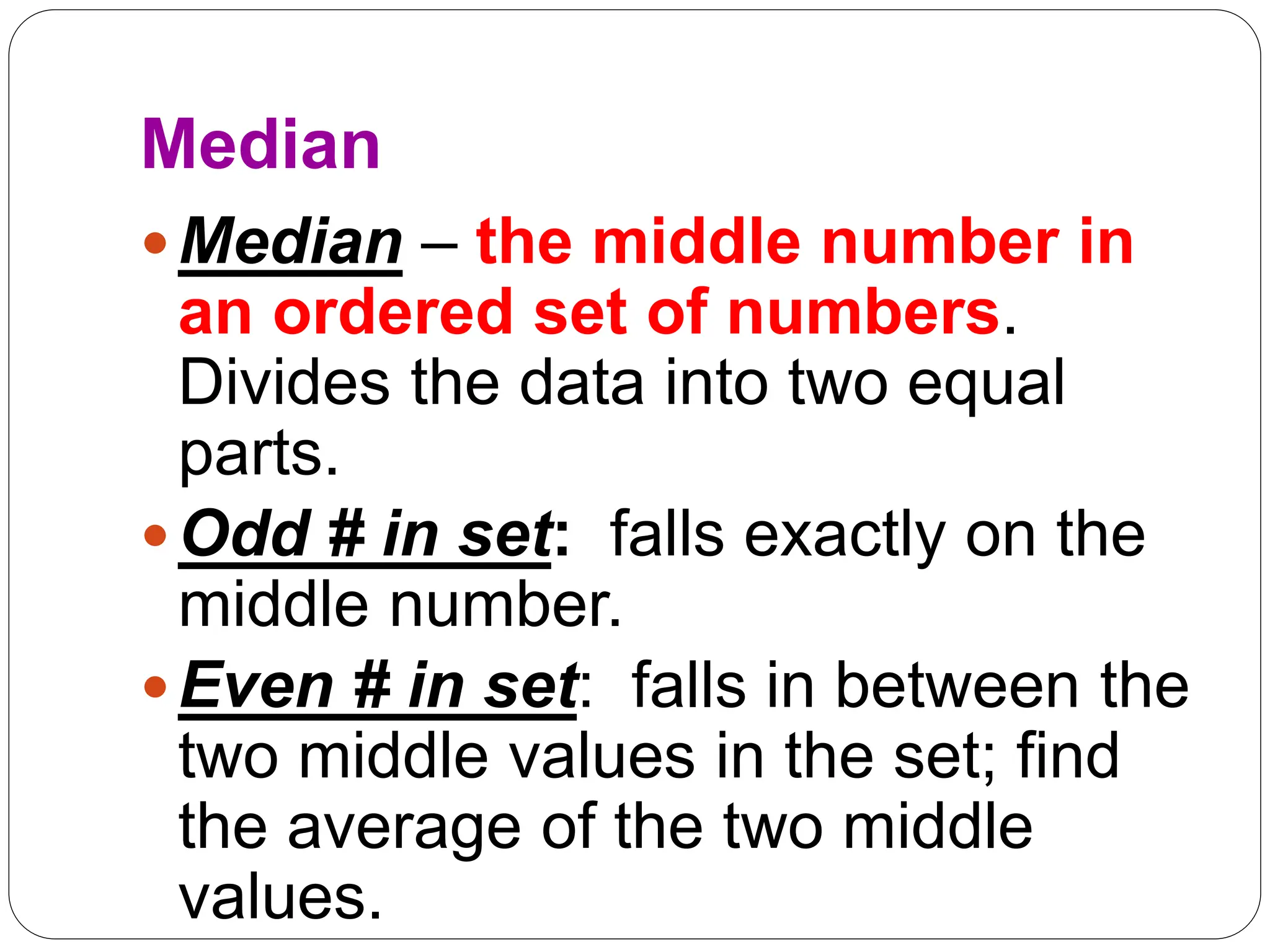
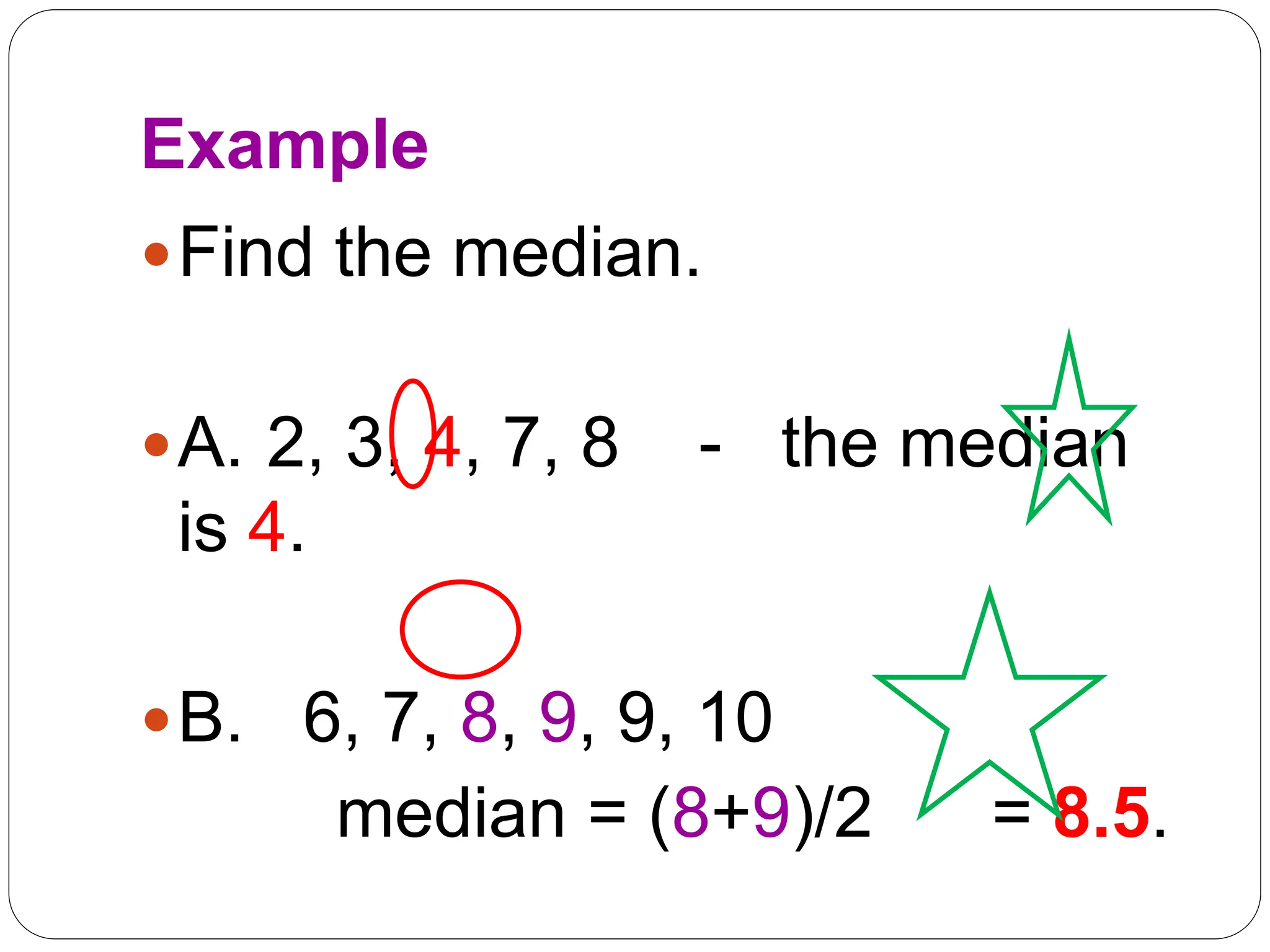
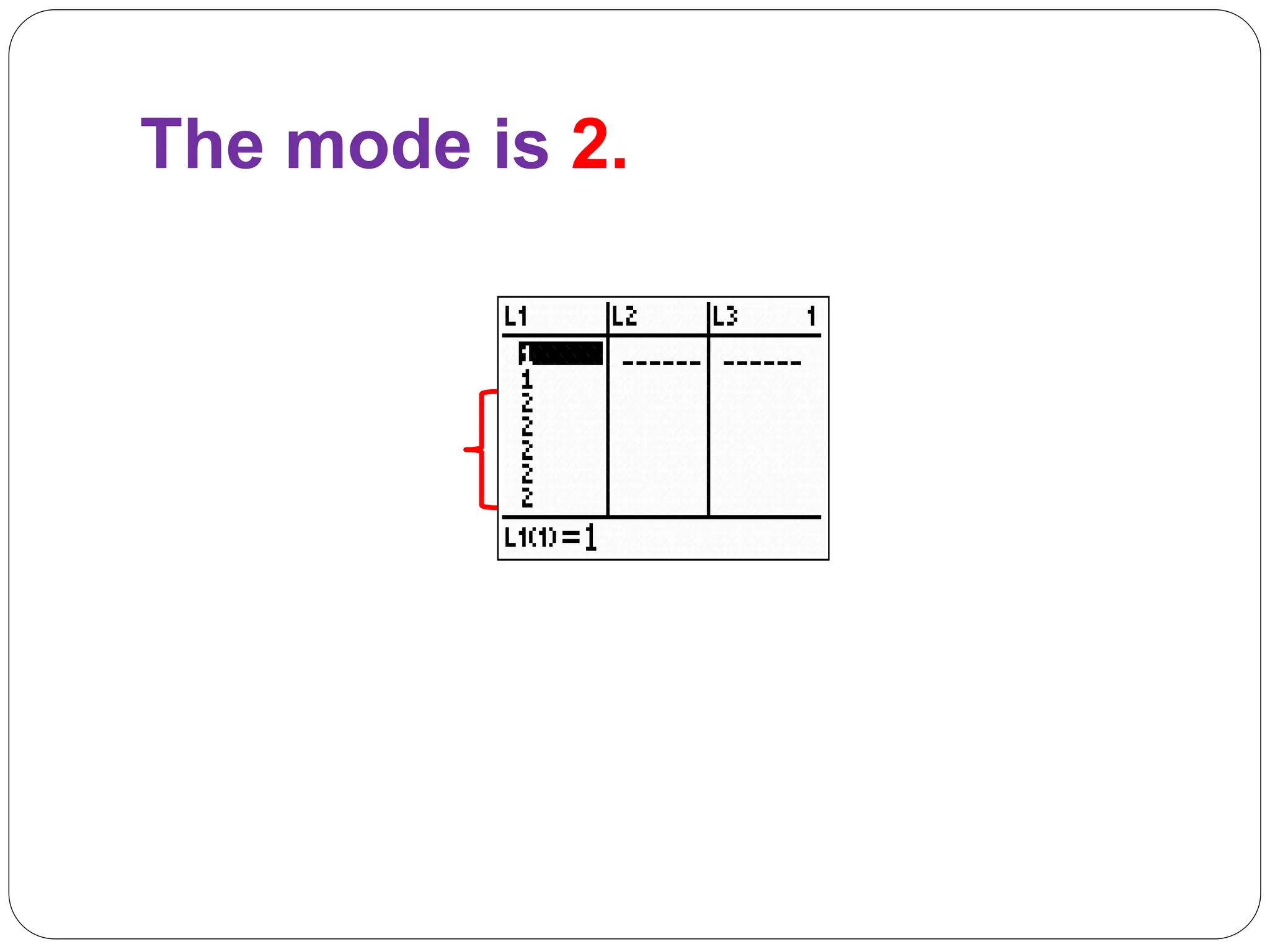
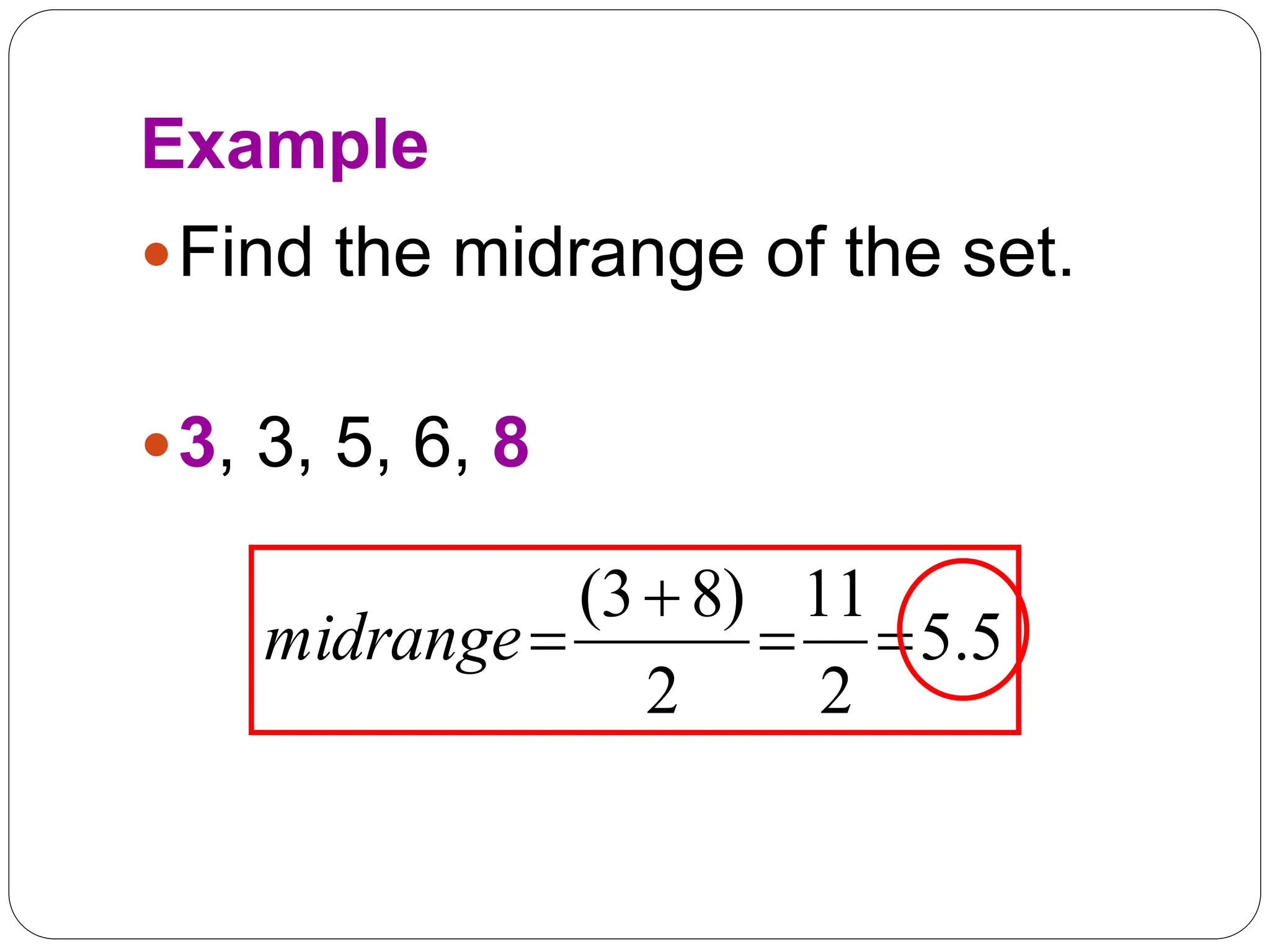
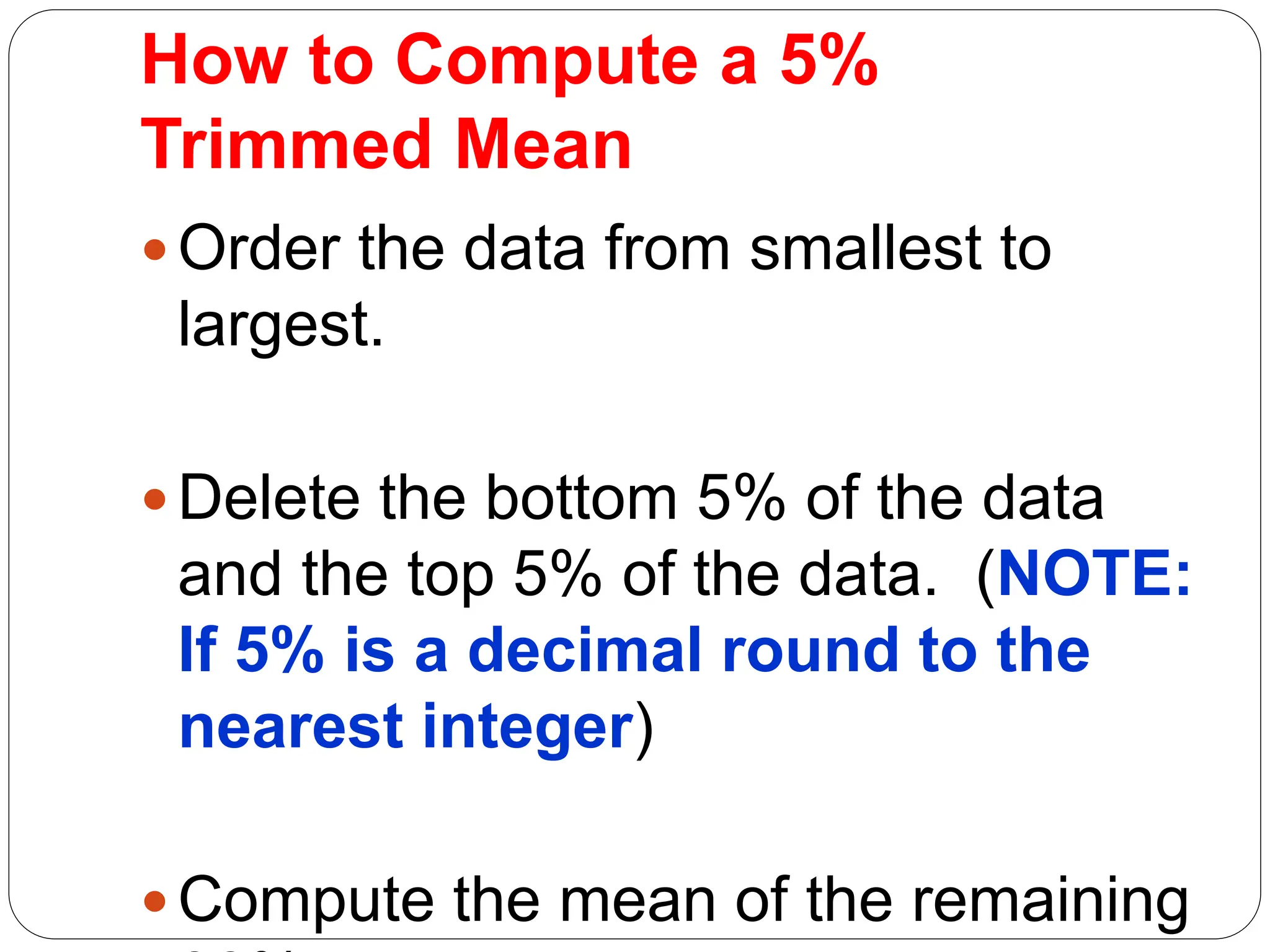
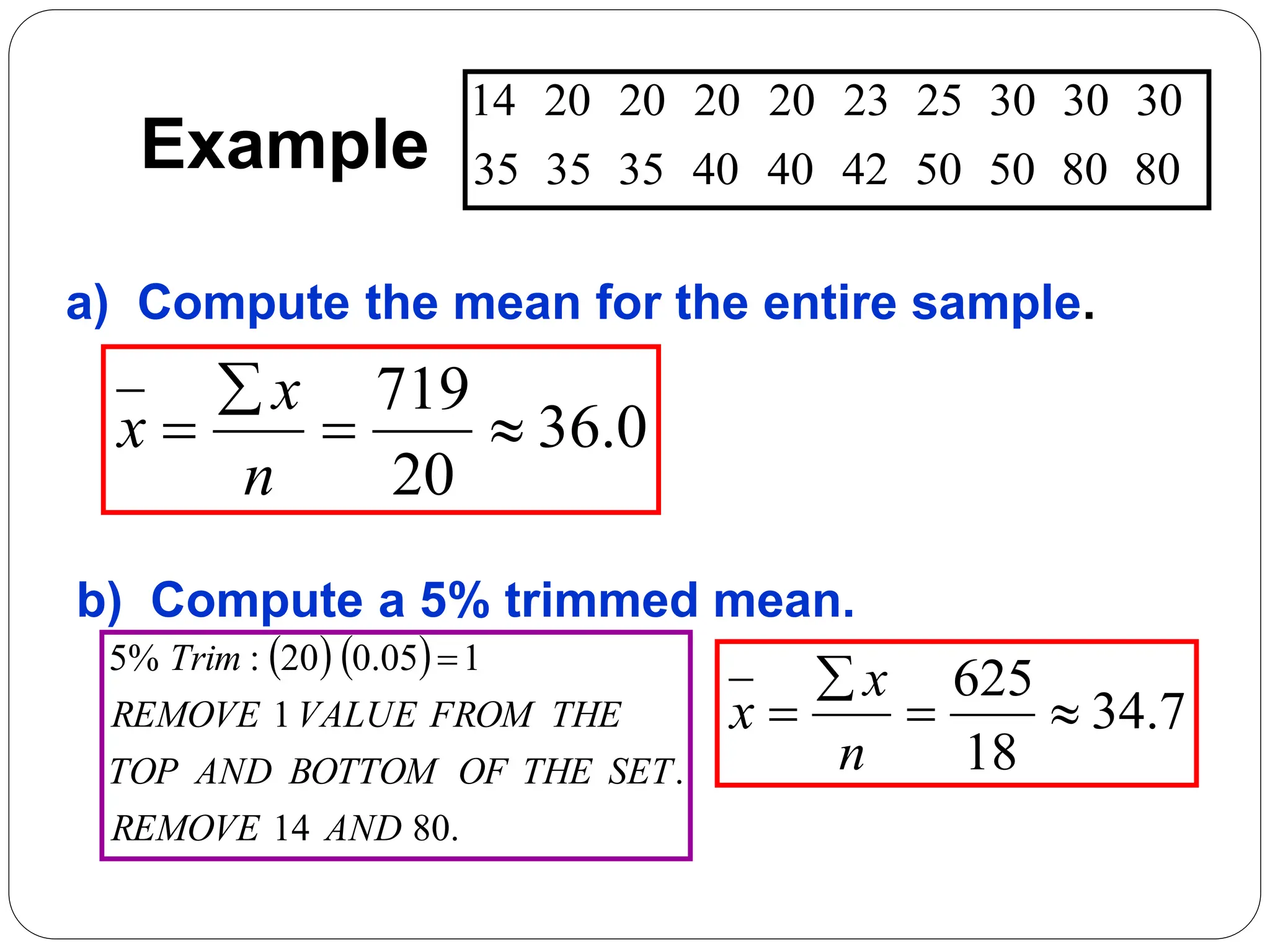
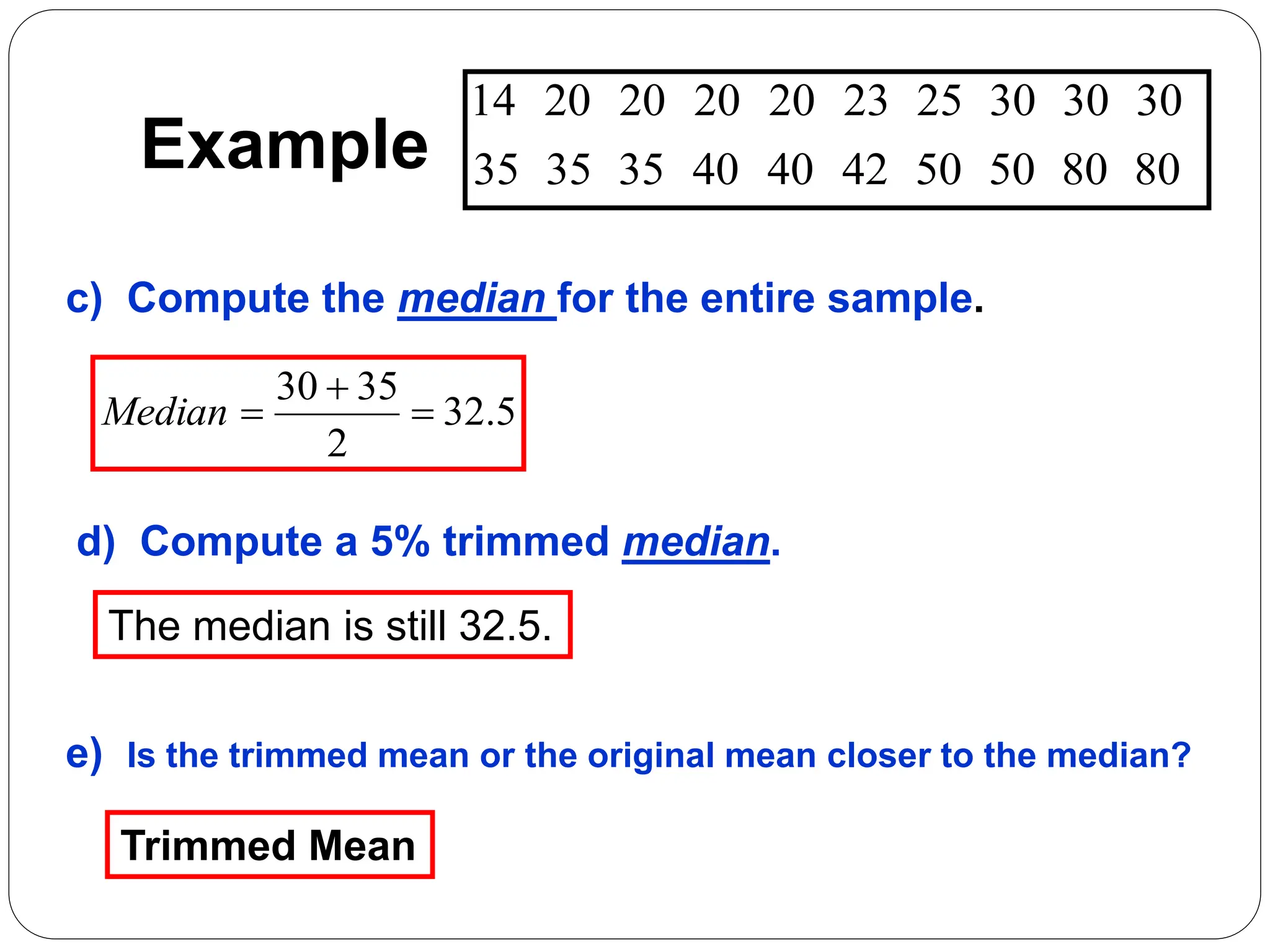
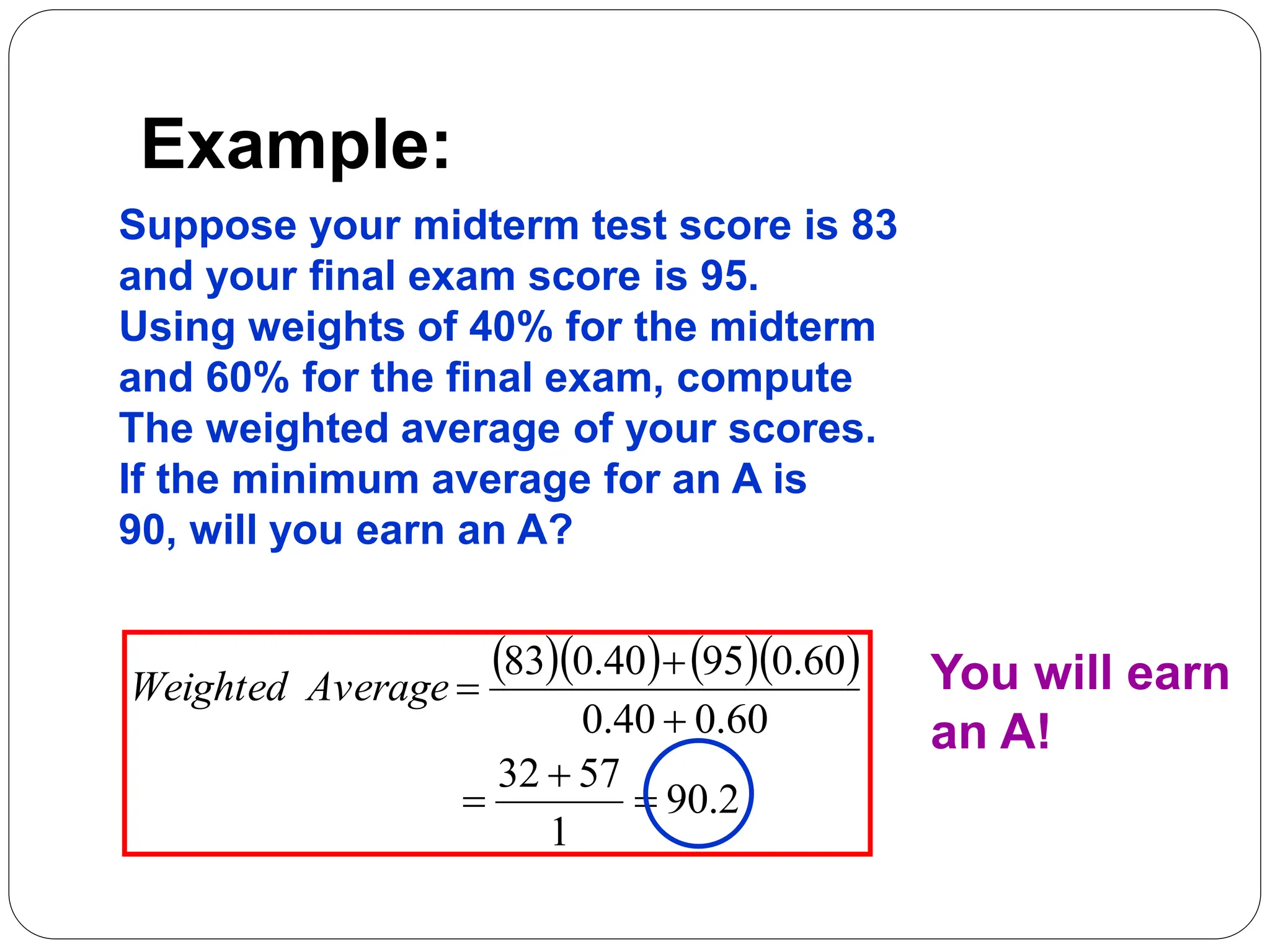
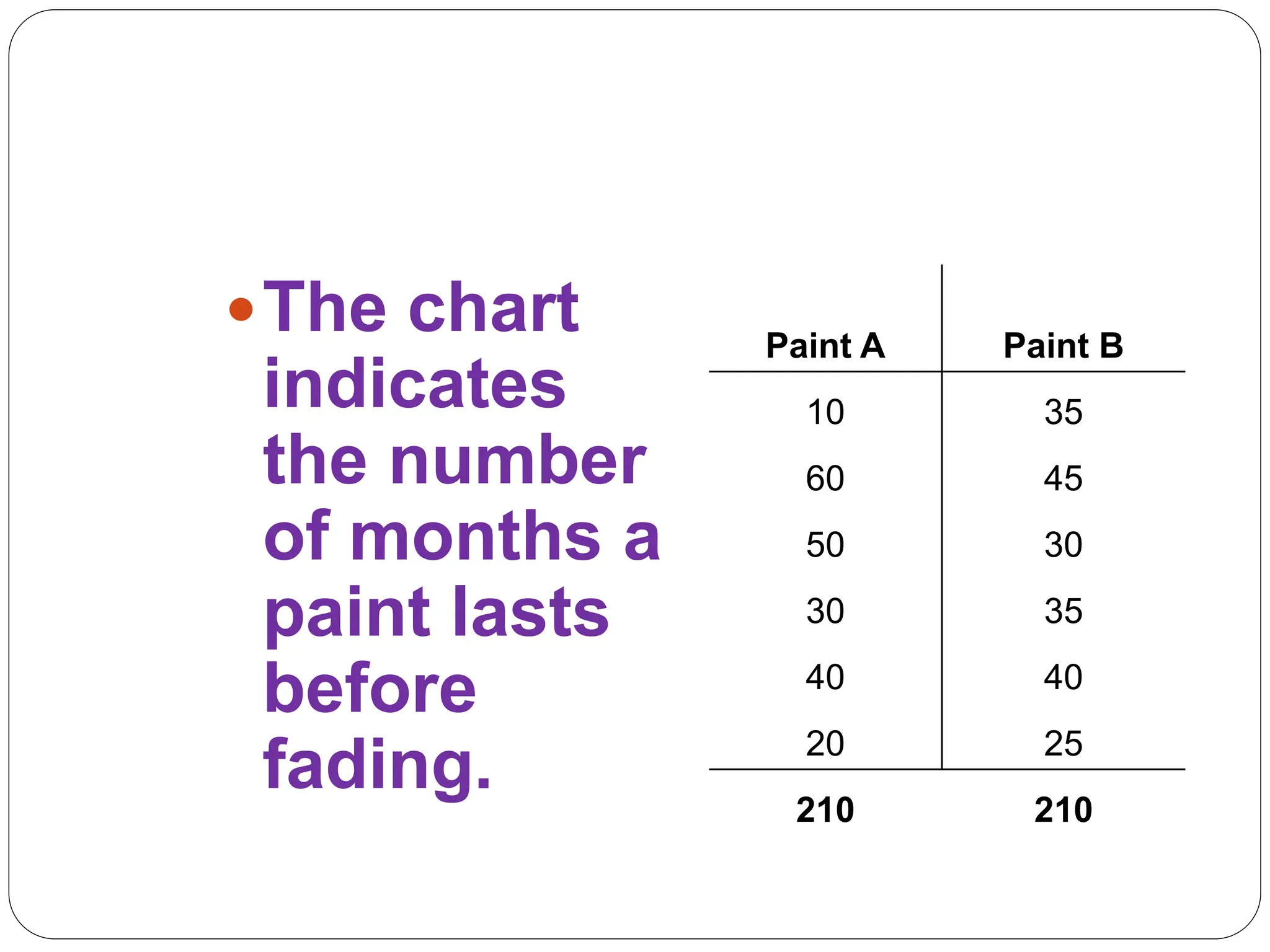
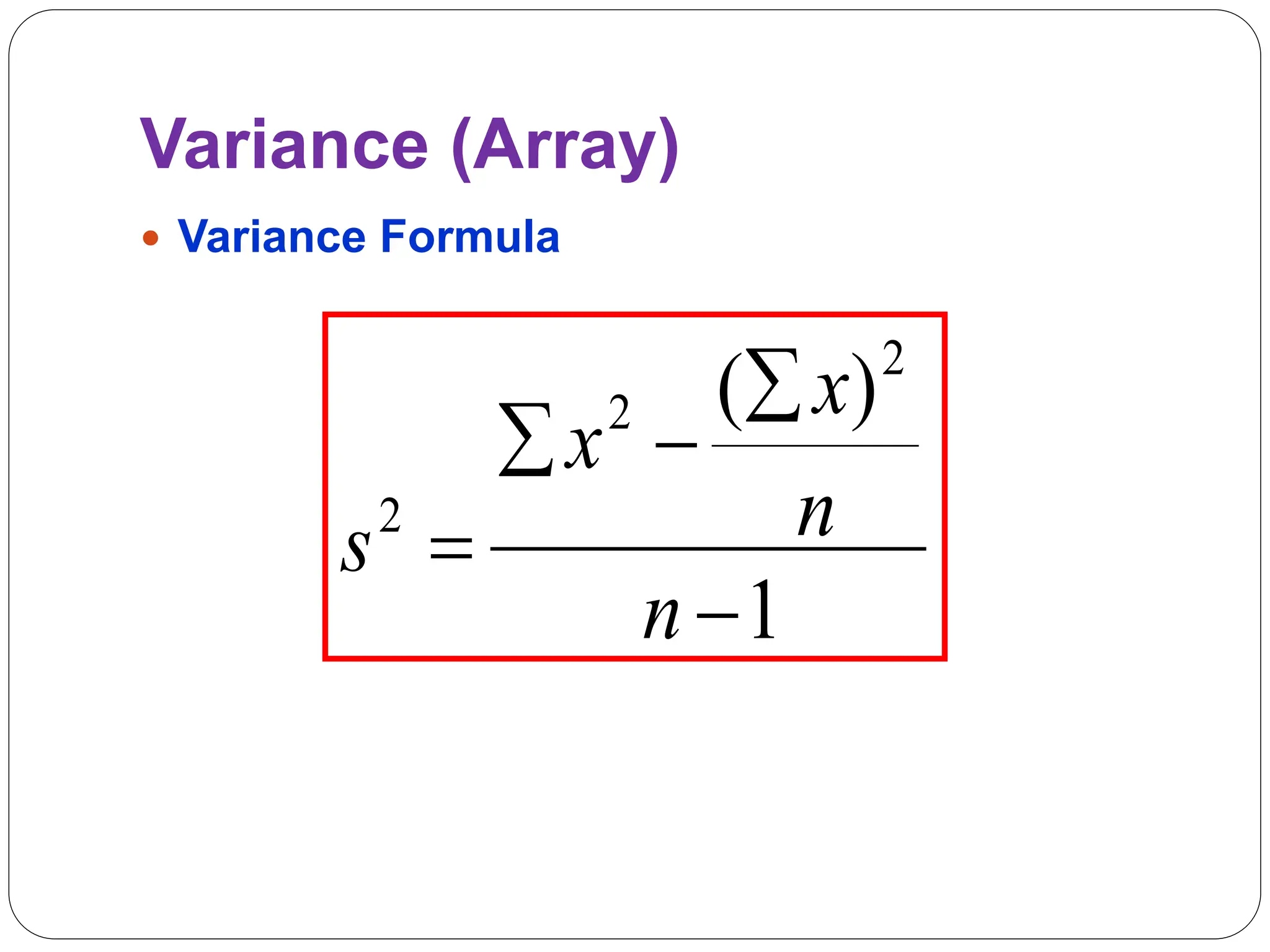
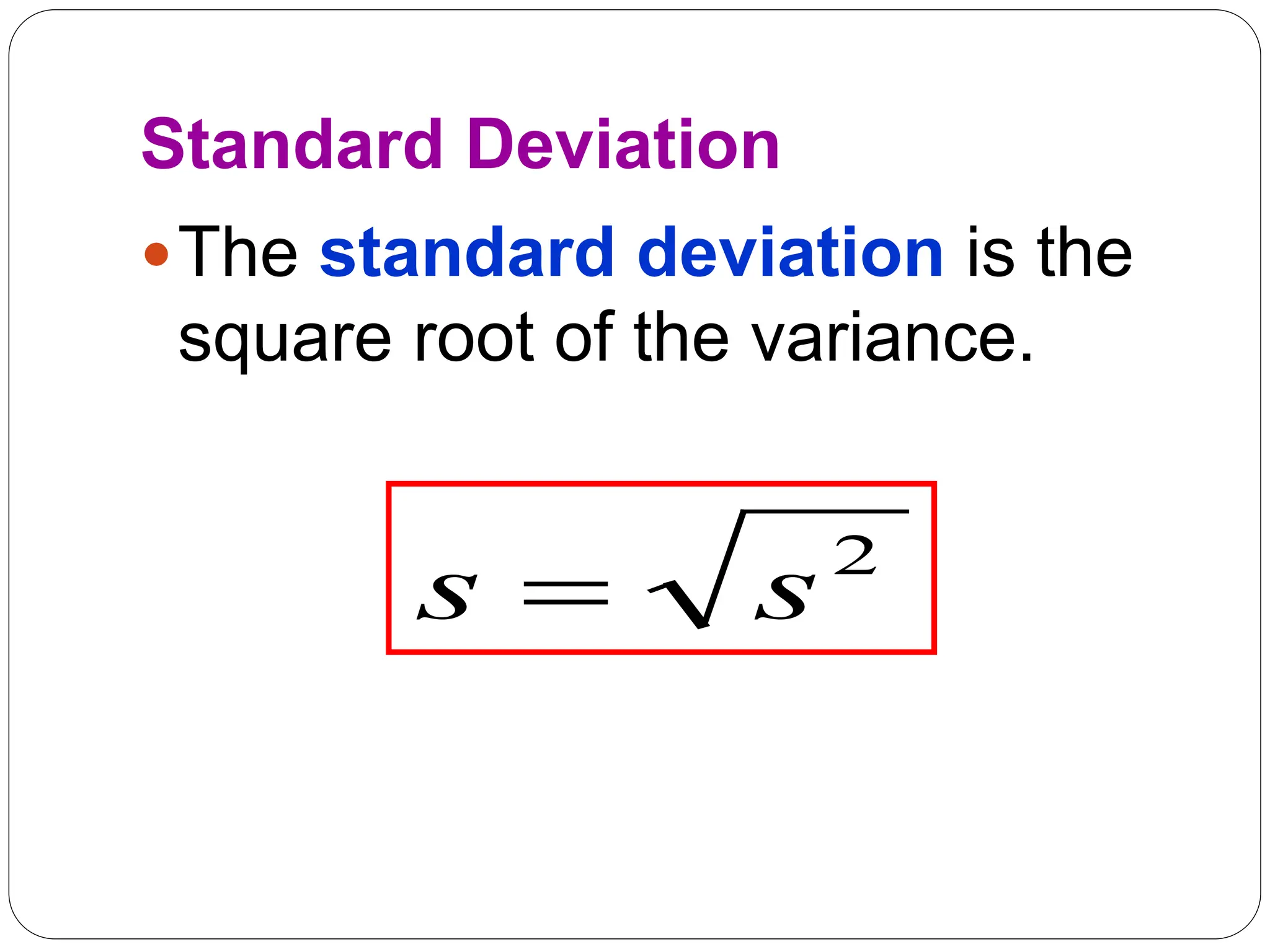
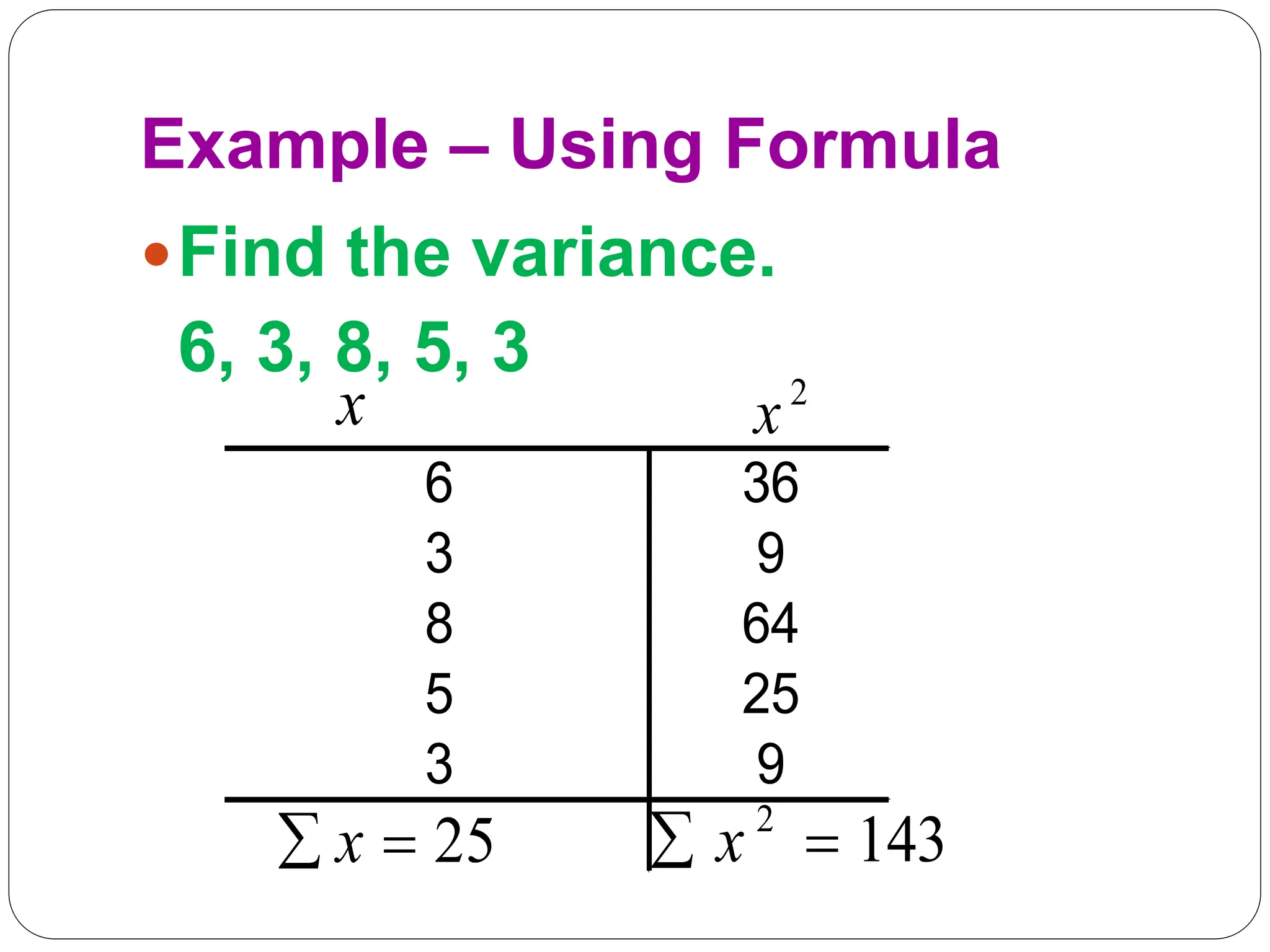
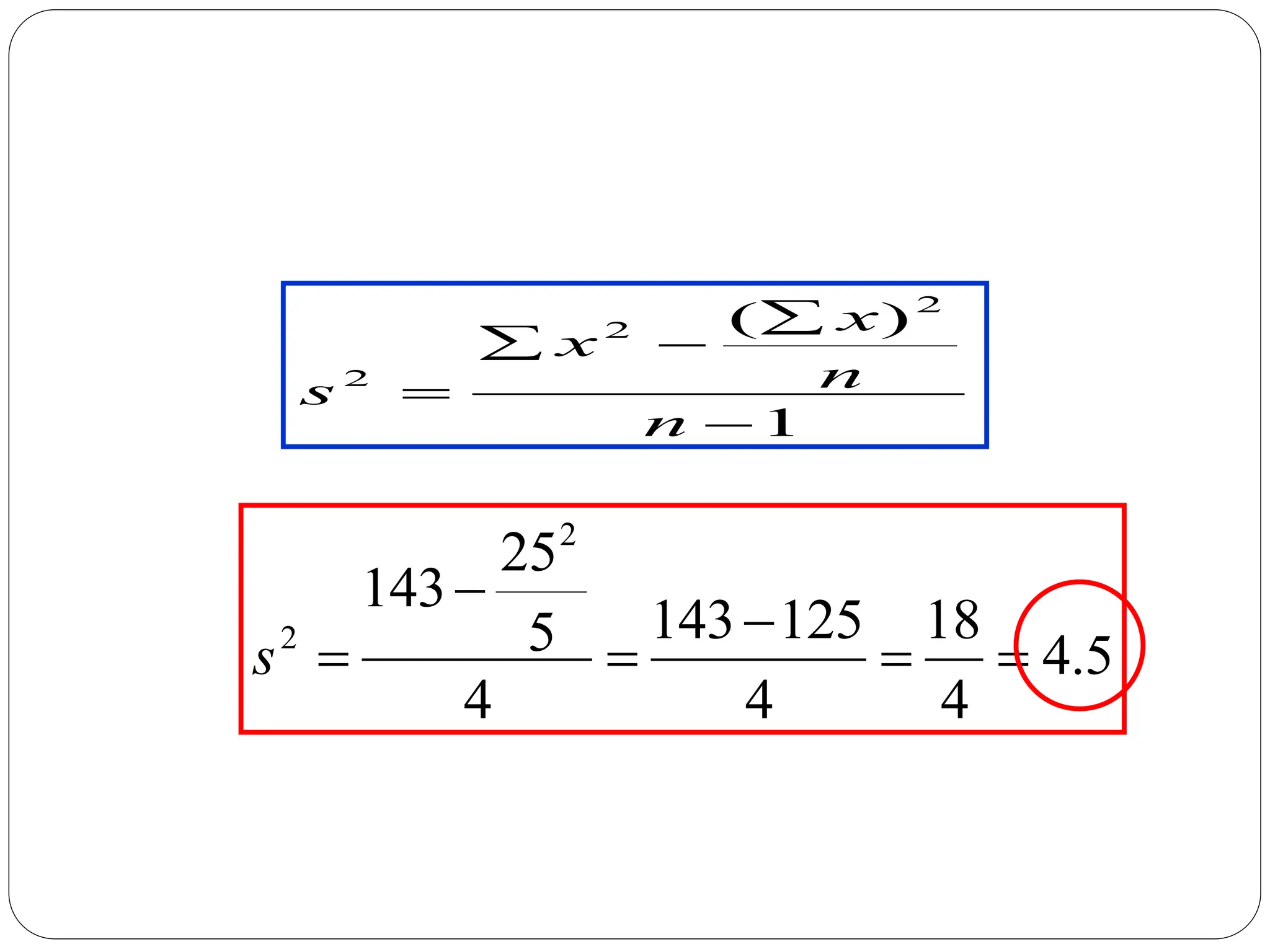
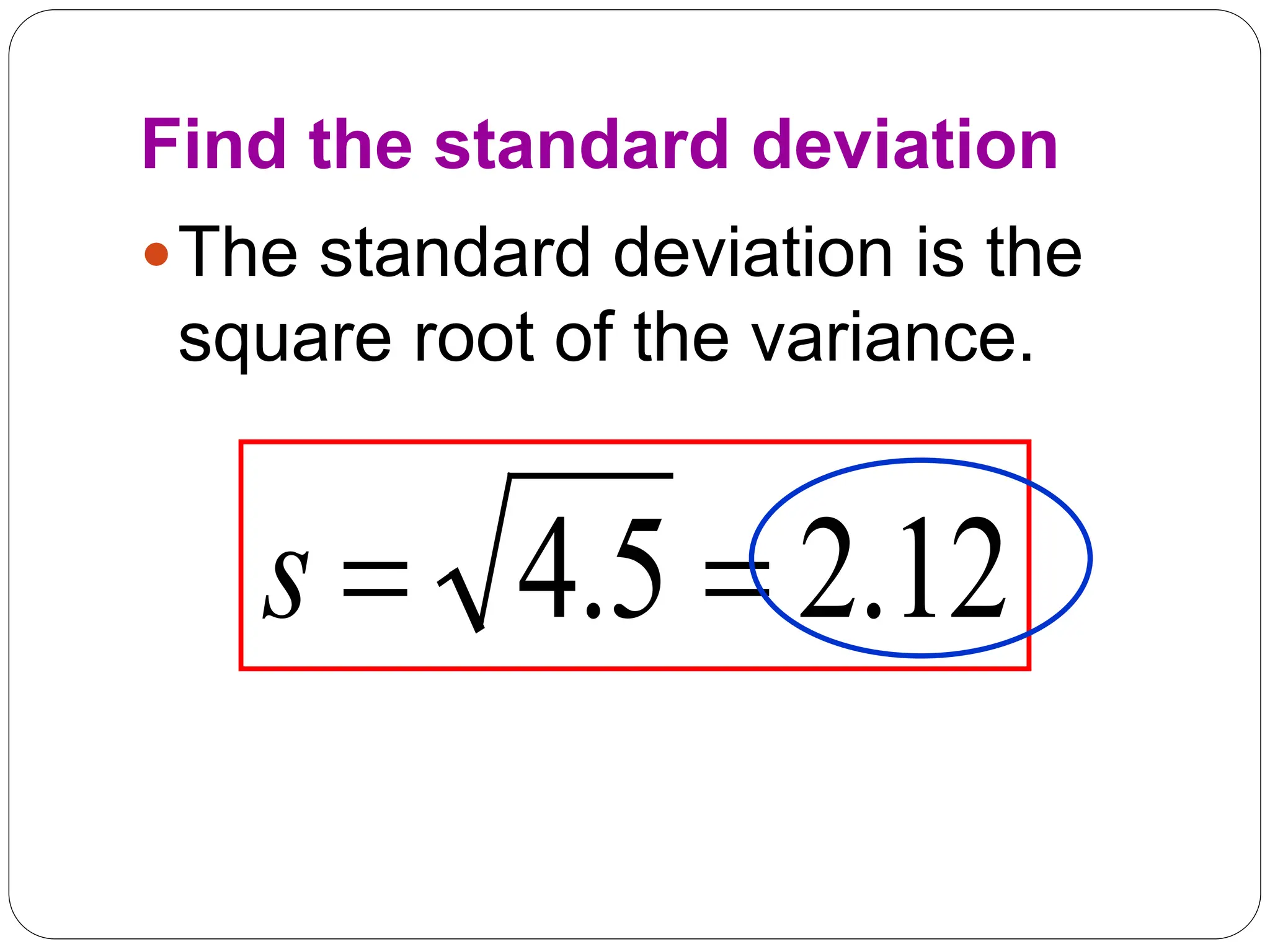
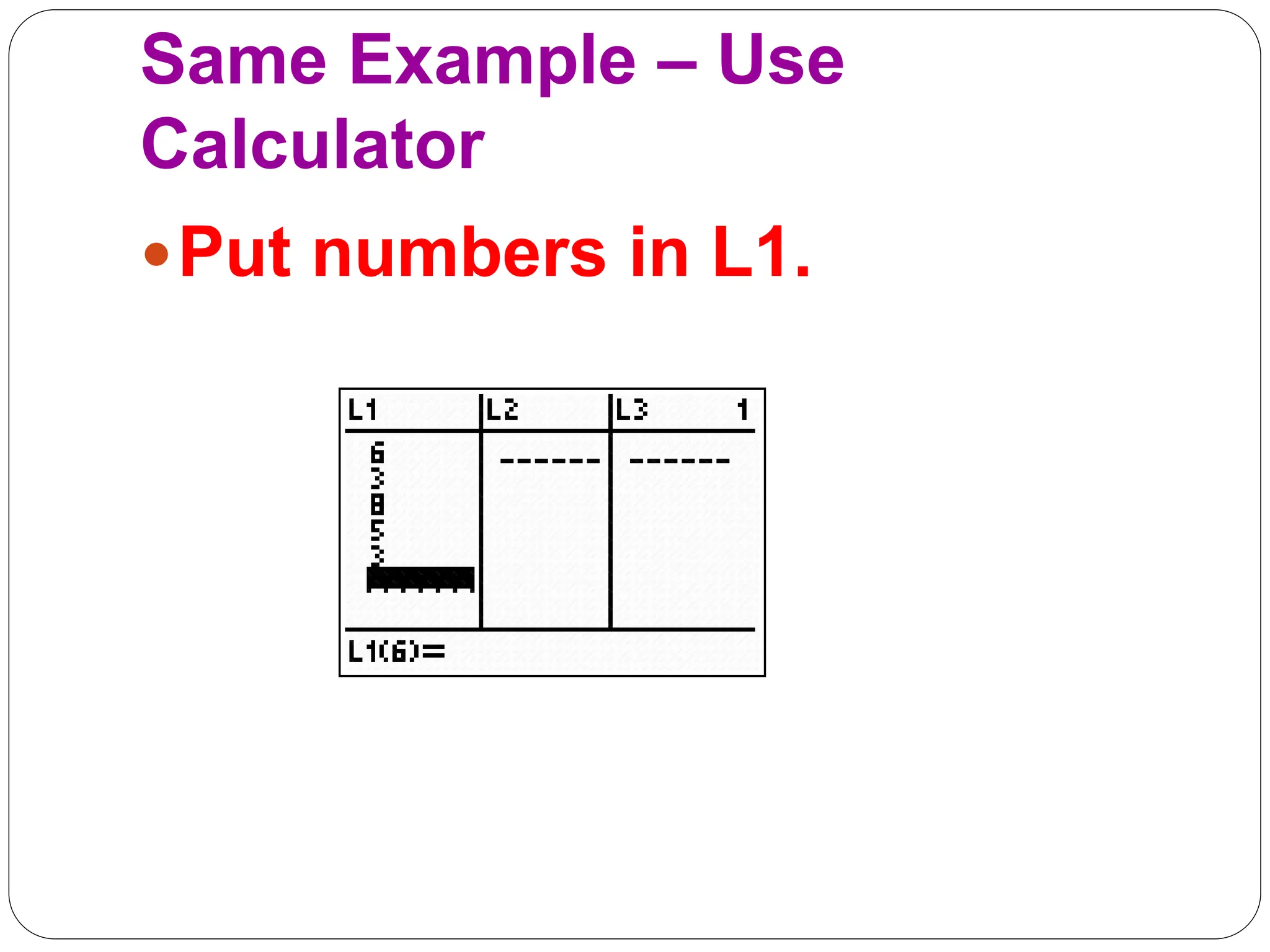
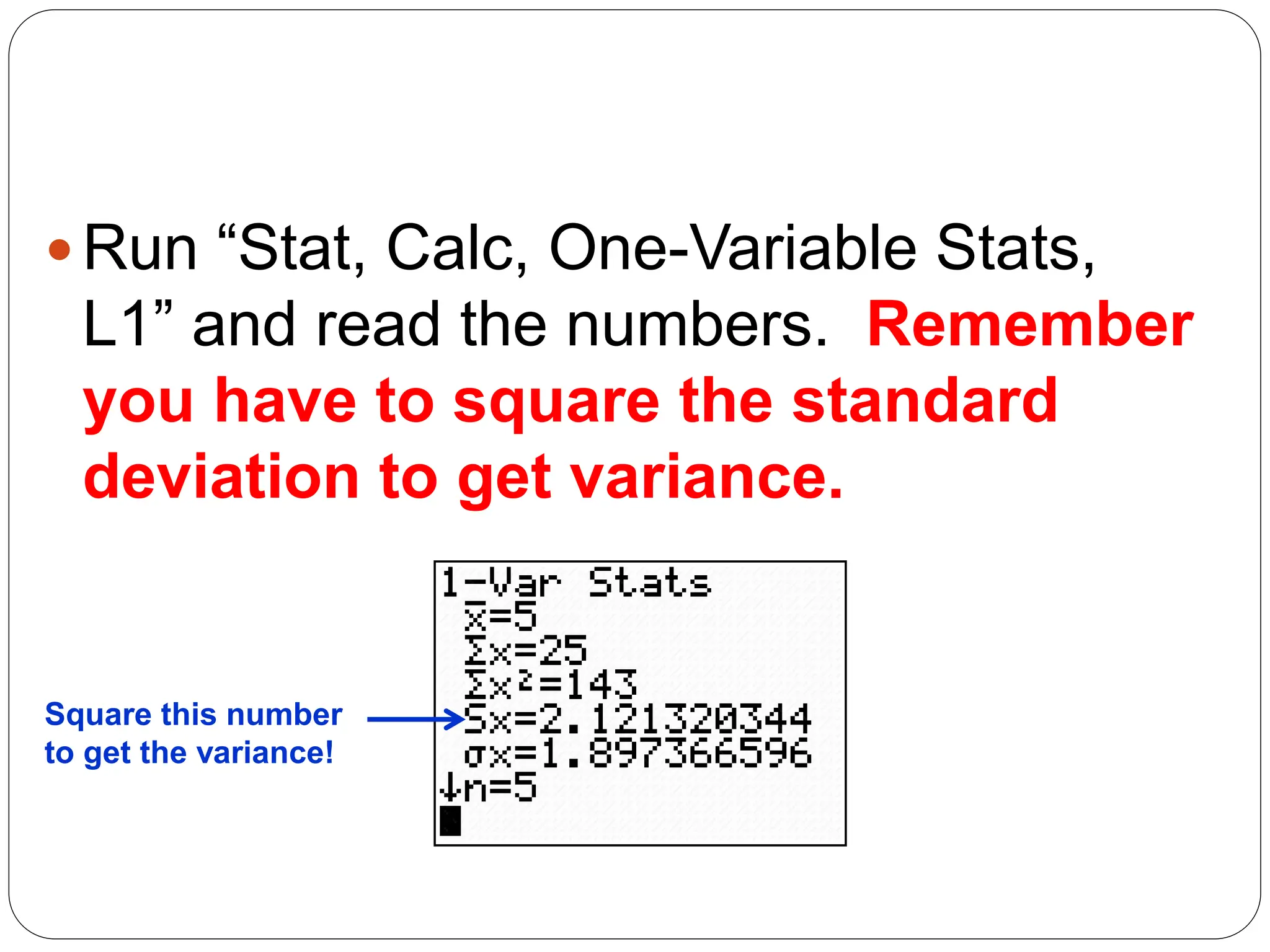
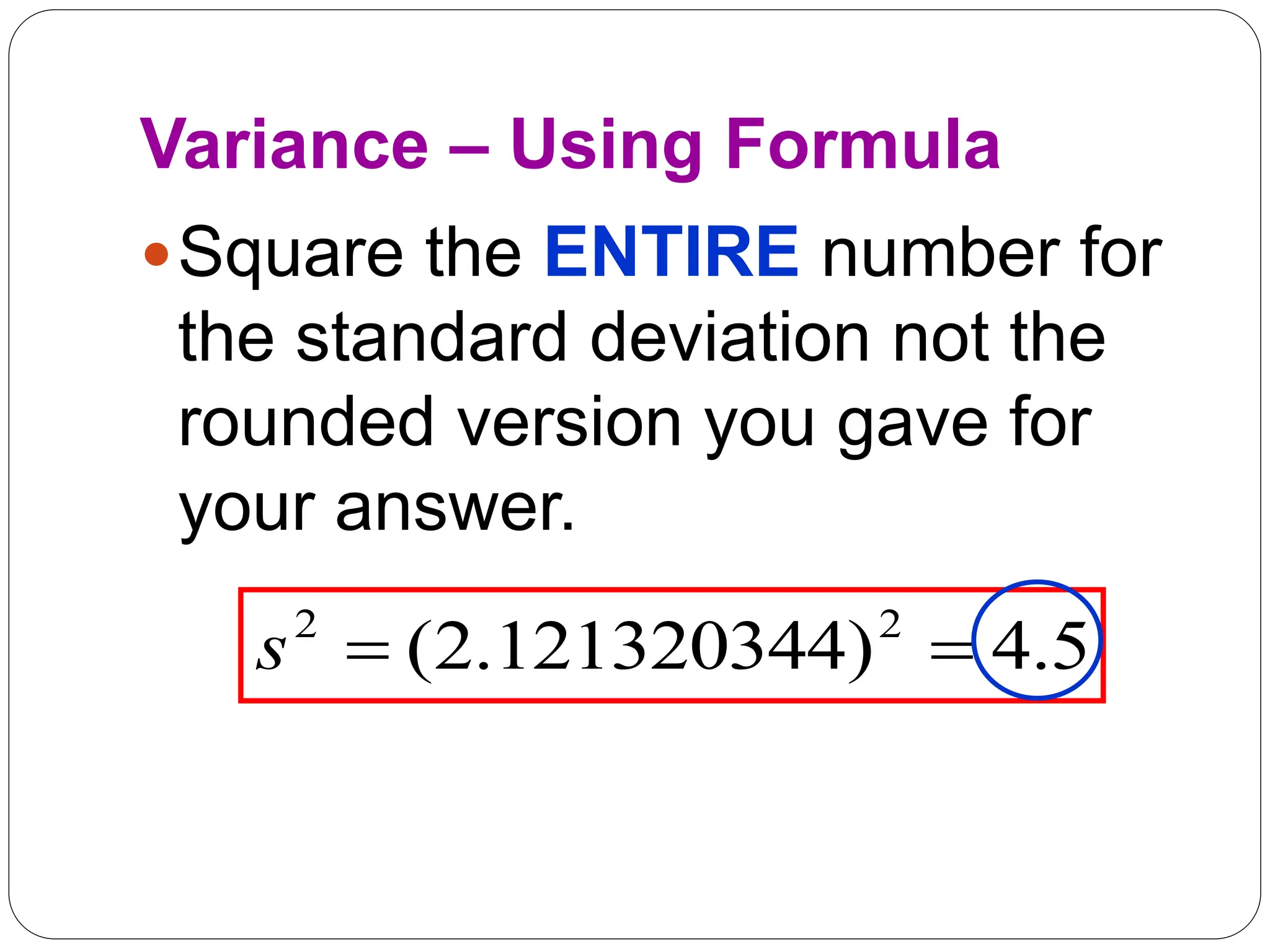
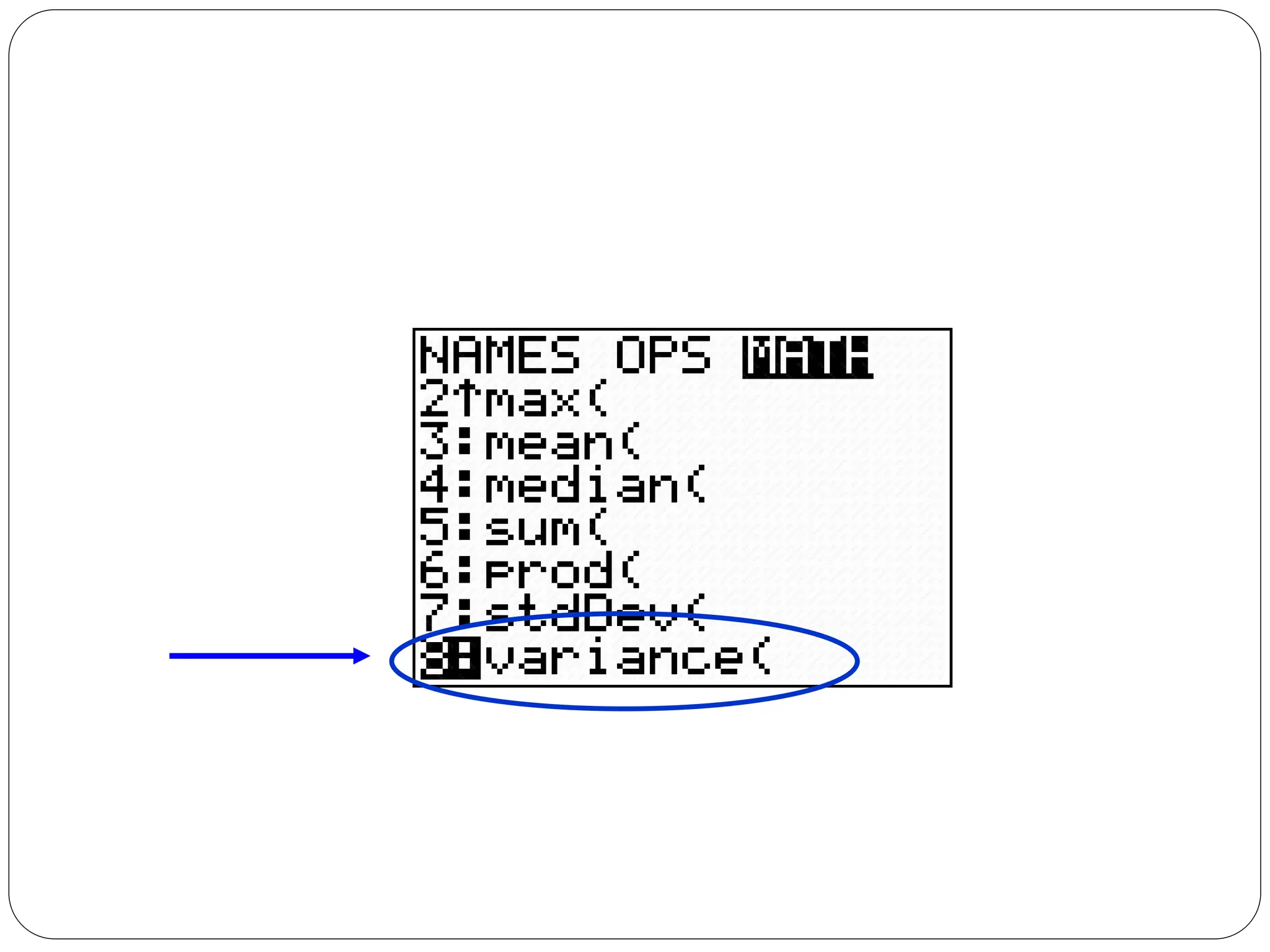
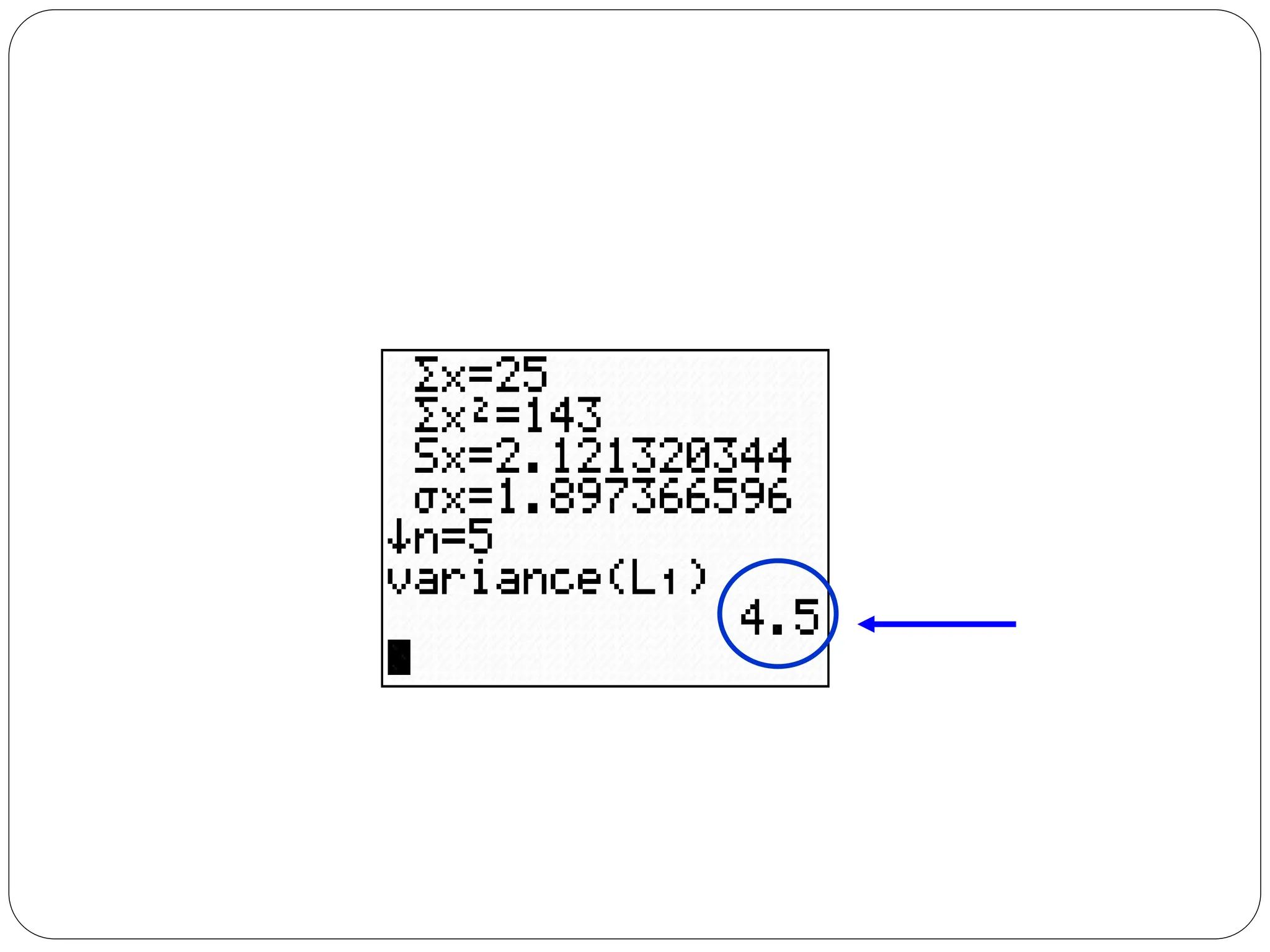
This document provides information on measures of central tendency and dispersion in data sets. It defines and provides examples of calculating the mean, median, mode, and midrange as common measures of central tendency. It also discusses weighted averages and trimmed means. The document then covers measures of dispersion such as range, variance and standard deviation. It provides formulas and examples of calculating these measures to quantify the spread of data around the central tendency.