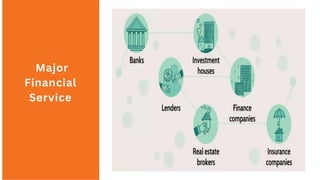
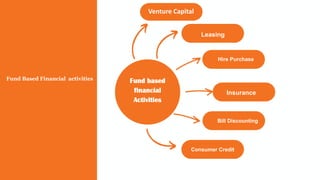
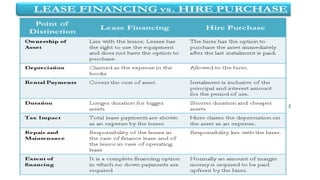
The document discusses various types of financial services. It defines financial services as the economic services provided by the finance industry, which includes banks, credit unions, insurance companies, and other businesses that manage money. It then provides details on important financial services like banking, wealth management, mutual funds, insurance, stock markets, treasury instruments, consulting, and portfolio management. It also distinguishes between fund-based financial activities like leasing, hire purchase, and bill discounting, and non-fund-based activities such as merchant banking, credit rating, and loan syndication.