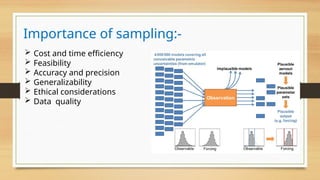
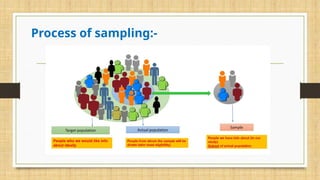
The document discusses the process and importance of sampling in research, highlighting characteristics of good sampling such as goal orientation, measurability, practicality, economy, independence, homogeneity, and adequacy. It explains the significance of sampling for cost and time efficiency, feasibility, accuracy, generalizability, ethical considerations, and data quality. The sampling process involves defining the target population, determining the sampling frame, selecting techniques, deciding sample size, and executing the sampling.