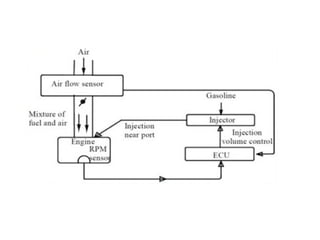
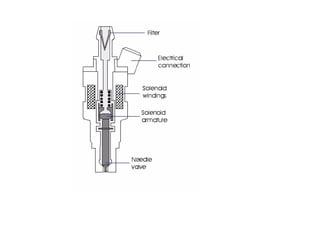
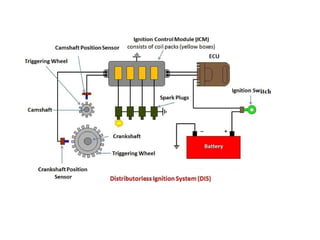
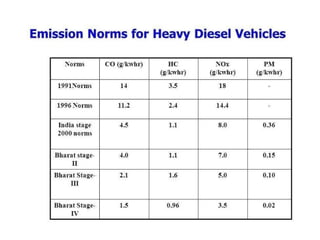
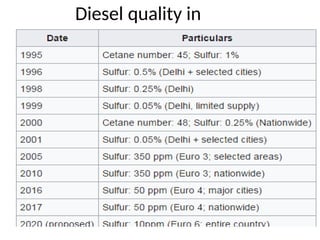
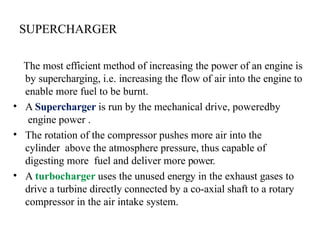
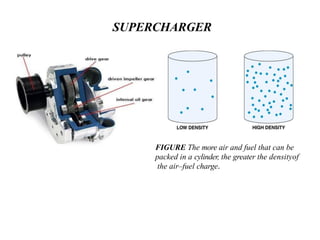
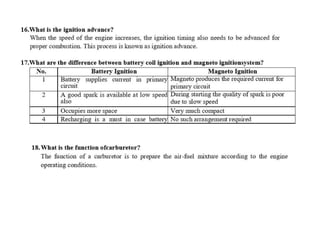
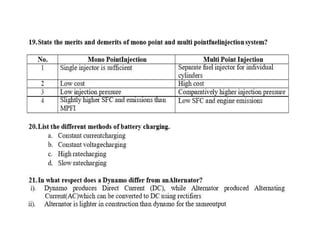
The document covers various aspects of automobile engineering, including engine auxiliary systems such as fuel injection and ignition systems, as well as turbochargers and catalytic converters. It also discusses transmission systems, steering, braking, and suspension systems, detailing the components and mechanisms involved. Additionally, alternative energy sources and electric/hybrid vehicles are mentioned, with practical training recommendations for students on engine parts and systems assembly.