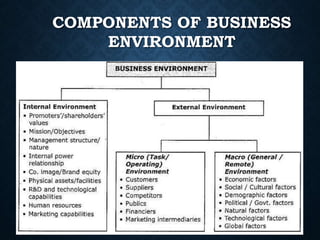
This document discusses the business environment and its key components. It defines business and outlines its key characteristics. It distinguishes between economic and non-economic activities and describes the objectives and importance of business. It then defines the business environment and explains that it consists of internal and external factors. The internal environment includes factors under a business's control, while the external environment includes social, economic, political, technological, and other factors outside a business's control. It provides details on the various elements of the micro and macro external environment that businesses must consider.